Abstract
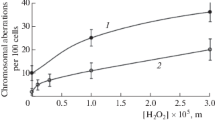
Many surface waters in Europe, Asia and South America have been reported to be contaminated with genotoxic substances. Therefore, it is important to establish strategies for identification of the most critical sources. In this study, we used a battery of four genotoxicity assays namely chromosomal aberration, DNA strand break, DNA laddering and P53 accumulation tests in mononuclear blood cells. Before cleaning of wastewater high levels of genotoxic contamination could be observed. For instance, we observed an increase in chromosomal aberrations from 2.6 ± 1.1 (aberrant cells in %; control), to 33.6 ± 6.6 in a petrochemical plant, 29.4 ± 3.3 in a petroleum refinery and 14.4 ± 1.8 in a coke plant of steel industry. A good correlation between the four assays was found. The most sensitive and reproducible results were obtained with the chromosomal aberration assay. Interestingly, clear differences in the efficiency of wastewater cleaning in three different treatment plants were observed. The first and second treatment plants in petrochemical industry and coke plant of steel industry completely eliminated genotoxicity of the wastewater. However, the third plant in petroleum refinery could achieve a reduction in genotoxicity but significant genotoxic contaminations were still present. In conclusion, our battery of genotoxicity tests allows the identification of critical sources contributing to contamination of surface waters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Api AM, San RH (1999) Genotoxicity tests with 6-acetyl-1, 1, 2, 4, 4, 7-hexamethyltetraline and 1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8-hexahydro-4, 6, 6, 7, 8, 8-hexamethylcyclopenta-gamma-2-benzopyr an. Mutat Res 446:67–81
Birnboim HC, Jevcak JJ (1981) Fluorometric method for rapid detection of DNA strand breaks in human white blood cells produced by low doses of radiation. Cancer Res 41:1889–1892
Bolt HM, Foth H, Hengstler JG et al (2004) Carcinogenicity categorization of chemicals-new aspects to be considered in a European perspective. Toxicol Lett 151:29–41
Brulport M, Schormann W, Bauer A et al (2007) Fate of extrahepatic human stem and precursor cells after transplantation into mouse livers. Hepatology 46:861–870
Bunger J, Krahl J, Munack A et al (2007) Strong mutagenic effects of diesel engine emissions using vegetable oil as fuel. Arch Toxicol 81:599–603
Bureau of Indian Standards IS 2490 (ed) (1982) Tolerance limits for industrial effluents discharged into inland surface waters. Indian Standards Institution, New Delhi
Carmo H, Hengstler JG, de Boer D et al (2005) Metabolic pathways of 4-bromo-2, 5-dimethoxyphenethylamine (2C-B): analysis of phase I metabolism with hepatocytes of six species including human. Toxicology 206:75–89
Carmo H, Brulport M, Hermes M et al (2007) CYP2D6 increases toxicity of the designer drug 4-methylthioamphetamine (4-MTA). Toxicology 229:236–244
Devi SS, Biswas AR, Biswas RA et al (2007) Heavy metal status and oxidative stress in diesel engine tuning workers of central Indian population. J Occup Environ Med 49:1228–1234
Dizer H, Wittekindt E, Fischer B et al (2002) The cytotoxic and genotoxic potential of surface water and wastewater effluents as determined by bioluminescence, umu-assays and selected biomarkers. Chemosphere 46:225–233
EPA US (1986) Quality criteria for water, vol 440/5-86-001. EPA, Wshington, DC
Grover IS, Kaur S (1999) Genotoxicity of wastewater samples from sewage and industrial effluent detected by the Allium root anaphase aberration and micronucleus assays. Mutat Res 426:183–188
Hausherr CK, Schiffer IB, Gebhard S et al (2006) Dephosphorylation of p-ERK1/2 in relation to tumor remission after HER-2 and Raf1 blocking therapy in a conditional mouse tumor model. Mol Carcinog 45:302–308
Hengstler JG, Fuchs J, Oesch F (1992) DNA strand breaks and DNA cross-links in peripheral mononuclear blood cells of ovarian cancer patients during chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide/carboplatin. Cancer Res 52:5622–5626
Hengstler JG, Bogdanffy MS, Bolt HM et al (2003) Challenging dogma: thresholds for genotoxic carcinogens? The case of vinylacetate. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 43:485–520
Hengstler JG, Foth H, Kahl R et al (2006) The REACH concept and its impact on toxicological sciences. Toxicology 220:232–239
Hermes M, Schormann W, Brulport M et al (2008) Trastuzumab therapy vs tetracycline controlled ERBB2 downregulation: influence on tumour development in an ERBB2-dependent mouse tumour model. Br J Cancer 98:1525–1532
Hohme S, Hengstler JG, Brulport M et al (2007) Mathematical modelling of liver regeneration after intoxication with CCl(4). Chem Biol Interact 168:74–93
Houk VS (1992) The genotoxicity of industrial wastes and effluents. Mutat Res 277:91–138
Kim Y, Park J, Shin YC (2007) Dye-manufacturing workers and bladder cancer in South Korea. Arch Toxicol 81:381–384
Krishnamurthi K, Devi SS (2007) The genotoxicity of priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) containing sludge samples. Toxicol Mech Methods 17:1–12
Krishnamurthi K, Devi SS, Chakrabarti T (2003) Genotoxic effects of PAH containing sludge extracts in Chinese Hamster ovary cell cultures. Biomed Environ Sci 16:68–82
Lah B, Malovrh S, Narat M et al (2004) Detection and quantification of genotoxicity in wastewater-treated Tetrahymena thermophila using the comet assay. Environ Toxicol 19:545–553
Lilienblum W, Dekant W, Foth H et al (2008) Alternative methods to safety studies in experimental animals: role in the risk assessment of chemicals under the new European Chemicals Legislation (REACH). Arch Toxicol 82:211–236
Lovreglio P, Bukvic N, Fustinoni S et al (2006) Lack of genotoxic effect in workers exposed to very low doses of 1, 3-butadiene. Arch Toxicol 80:378–381
Martikainen P, Kyprianou N, Tucker RW et al (1991) Programmed death of nonproliferating androgen-independent prostatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 51:4693–4700
NEERI Report (1995) Regional environmental impact assessment studies for Jamshedpur region, vol 1. NEERI, Nagpur, p 20
NEERI Report (1998) Rapid environmental impact assessment for expansion plan proposed by IPCL at petrochemicals complex near vadodara. NEERI, Nagpur, p 20
Ohe T, Watanabe T, Wakabayashi K (2004) Mutagens in surface waters: a review. Mutat Res 567:109–149
Periyakaruppan A, Kumar F, Sarkar S et al (2007) Uranium induces oxidative stress in lung epithelial cells. Arch Toxicol 81:389–395
Roos PH, Angerer J, Dieter H et al (2008) Perfluorinated compounds (PFC) hit the headlines: meeting report on a satellite symposium of the annual meeting of the German Society of Toxicology. Arch Toxicol 82:57–59
Schaeffer DJ, Kerster HW (1985) Estimating the mass of mutagens in indeterminate mixtures. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 10:190–196
Schmitt M, Gellert G, Lichtenberg-Frate H (2005) The toxic potential of an industrial effluent determined with the Saccharomyces cerevisiae-based assay. Water Res 39:3211–3218
Schormann W, Hammersen FJ, Brulport M et al (2008) Tracking of human cells in mice. Histochem Cell Biol 130:329–338
Spangenberg C, Lausch EU, Trost TM et al (2006) ERBB2-mediated transcriptional up-regulation of the alpha5beta1 integrin fibronectin receptor promotes tumor cell survival under adverse conditions. Cancer Res 66:3715–3725
Tanner B, Hasenclever D, Stern K et al (2006) ErbB-3 predicts survival in ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:4317–4323
Trost TM, Lausch EU, Fees SA et al (2005) Premature senescence is a primary fail-safe mechanism of ERBB2-driven tumorigenesis in breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 65:840–849
Van Hoof F, Manteleers G (1983) Chlorination of mutagenic fractions of coke-plant effluents. In: Jolley RL, Brungs WA, Cotruvo JA et al (eds) Water chlorination—environmental impact and health effects, vol 4. Butterworth-Heinemann, Ann Arbor, p 1325
Wang YJ, Lin JK (1995) Estimation of selected phenols in drinking water with in situ acetylation and study on the DNA damaging properties of polychlorinated phenols. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 28:537–542
Acknowledgments
Dr. S. Devotta, former Director NEERI, is gratefully acknowledged for providing the necessary facilities, his time-to-time suggestions and encouragement. Dr. S. D. Wachasunder for the help rendered in GC–MS analyses and Dr. S. D. Deshpande for the physicochemical data of wastewater and effluents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnamurthi, K., Saravana Devi, S., Hengstler, J.G. et al. Genotoxicity of sludges, wastewater and effluents from three different industries. Arch Toxicol 82, 965–971 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0380-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0380-0