Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to detect the pre- and intra-operative influential factors for lower limb alignment correction error in open-wedge high tibial osteotomy (OWHTO).
Methods
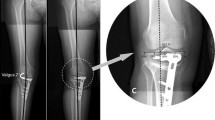
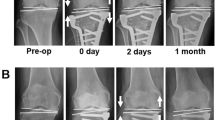
This study involved 69 patients (71 knees) undergoing OWHTO for primary medial osteoarthritis. The weight-bearing line (WBL) ratio, medial proximal tibial angle (MPTA), and joint line convergence angle (JLCA) were measured on radiographs preoperatively and at 1 month after surgery, and the differences between the pre- and postoperative values were calculated. The correction angle during surgery was also investigated. The radiological correction angle was defined as the difference between the pre- and postoperative MPTA. The correction error was defined as the difference between the correction angle during surgery and the radiological correction angle. The ideal correction angle was defined as when the postoperative WBL passed through Fujisawa’s point (WBL = 62.5%), and the alignment error was defined as the difference between the postoperative WBL ratio and 62.5. The correlations among the alignment error, the correction error, correction angle during surgery, pre- and postoperative WBL ratio, MPTA, and JLCA and the differences between the pre and postoperative WBL ratio, MPTA, and JLCA were investigated. In addition, the factor most influential on the alignment error was determined.
Results
The preoperative MPTA was the only predictor of the alignment error after OWHTO. The alignment error was positively correlated with the correction error and correction angle during surgery, and negatively correlated with pre- and postoperative WBL ratio, MPTA, and differences between the pre- and postoperative WBL ratio and JLCA.
Conclusion
The preoperative MPTA was the only pre- and intra-operative predictor of the alignment error after OWHTO. The larger the correction angle, the greater the alignment error. The MPTA was recommended as an indicator for improving the correction accuracy. Accurate correction based on the MPTA provides good lower limb alignment and better clinical results.
Level of evidence
III Case–control study/Retrospective comparative study.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bito H, Takeuchi R, Kumagai K, Aratake M, Saito I, Hayashi R, Sasaki Y, Aota Y, Saito T (2009) A predictive factor for acquiring an ideal lower limb realignment after opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 17:382–389
Briem K, Ramsey DK, Newcomb W, Rudolph KS, Snyder-Mackler L (2007) Effects of the amount of valgus correction for medial compartment knee osteoarthritis on clinical outcome, knee kinetics and muscle co-contraction after opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. J Orthop Res 25:311–318
Dahl MT (2000) Preoperative planning in deformity correction and limb lengthening surgery. Instr Course Lect 49:503–509
Dugdale TW, Noyes FR, Styer D (1992) Preoperative planning for high tibial osteotomy. The effect of lateral tibiofemoral separation and tibiofemoral length. Clin Orthop Relat Res 274:248–264
El-Azab HM, Morgenstern M, Ahrens P, Schuster T, Imhoff AB, Lorenz SG (2011) Limb alignment after open-wedge high tibial osteotomy and its effect on the clinical outcome. Orthopedics 34:e622–e628
Gaasbeek RD, Nicolaas L, Rijnberg WJ, van Loon CJ, van Kampen A (2010) Correction accuracy and collateral laxity in open versus closed wedge high tibial osteotomy. A one-year randomized controlled study. Int Orthop 34:201–207
Fujisawa Y, Masuhara K, Shiomi S (1979) The effect of high tibial osteotomy on osteoarthritis of the knee. An arthroscopic study of 54 knee joints. Orthop Clin N Am 10:585–608
Gaasbeek RDA, Nicolaas L, Rijnberg WJ, van Loon CJM, van Kampen A (2009) Correction accuracy and collateral laxity in open versus closed wedge high tibial osteotomy. A one-year randomised controlled study. Int Orthop 34:201–207
Hankemeier S, Hufner T, Wang G, Kendoff D, Zeichen J, Zheng G, Krettek C (2006) Navigated open-wedge high tibial osteotomy: advantages and disadvantages compared to the conventional technique in a cadaver study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 14:917–921
Hankemeier S, Mommsen P, Krettek C, Jagodzinski M, Brand J, Meyer C, Meller R (2010) Accuracy of high tibial osteotomy: comparison between open- and closed-wedge technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18:1328–1333
Hoell S, Suttmoeller J, Stoll V, Fuchs S, Gosheger G (2005) The high tibial osteotomy, open versus closed wedge, a comparison of methods in 108 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 125:638–643
Jung WH, Takeuchi R, Chun CW, Lee JS, Jeong JH (2015) Comparison of results of medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy with and without subchondral drilling. Arthroscopy 31:673–679
Kim SH, Ro DH, Lee YM, Cho Y, Lee S, Lee MC (2017) Factors associated with discrepancies between preoperatively planned and postoperative alignments in patients undergoing closed-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee 24:1129–1137
Lee DH, Park SC, Park HJ, Han SB (2016) Effect of soft tissue laxity of the knee joint on limb alignment correction in open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24:3704–3712
Ogawa H, Matsumoto K, Ogawa T, Takeuchi K, Akiyama H (2016) Preoperative varus laxity correlates with overcorrection in medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 136:1337–1342
Pearle AD, Goleski P, Musahl V, Kendoff D (2009) Reliability of image-free navigation to monitor lower-limb alignment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91:90–94
Pornrattanamaneewong C, Narkbunnam R, Chareancholvanich K (2012) Medial proximal tibial angle after medial opening wedge HTO: a retrospective diagnostic test study. Indian J Orthop 46(5):525–530
Rudan J, Harrison M, Simurda MA (1999) Optimizing femorotibial alignment in high tibial osteotomy. Can J Surg 42:366–370
Sabharwal S, Zhao C (2008) Assessment of lower limb alignment: supine fluoroscopy compared with a standing full-length radiograph. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90:43–51
Shaw JA, Dungy DS, Arsht SS (2004) Recurrent varus angulation after high tibial osteotomy: an anatomic analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 420:205–212
Specogna AV, Birmingham TB, Hunt MA, Jones IC, Jenkyn TR, Fowler PJ (2007) Radiographic measures of knee alignment in patients with varus gonarthrosis: effect of weightbearing status and associations with dynamic joint load. Am J Sports Med 35:65–70
Takeuchi R, Ishikawa H, Aratake M, Bito H, Saito I, Kumagai K, Akamatsu Y, Saito T (2009) Medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy with early full weight bearing. Arthroscopy 25:46–53
Terauchi M, Shirakura K, Katayama M, Higuchi H, Takagishi K, Kimura M (2002) Varus inclination of the distal femur and high tibial osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Br 84:223–226
Tsukeoka T, Lee TH (2012) Sagittal flexion of the femoral component affects flexion gap and sizing in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 27:1094–1099
Funding
No external funding was used.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declartion and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubota, M., Ohno, R., Sato, T. et al. The medial proximal tibial angle accurately corrects the limb alignment in open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27, 2410–2416 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-018-5216-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-018-5216-8