Abstract
Purpose
Historically, extramedullary techniques have focused on finding the femoral head center and referred mainly to the anterosuperior iliac spine (the FHC method) in total knee arthroplasty (TKA). The purpose of this study was to evaluate a new extramedullary alignment system that uses neutral overall limb mechanical alignment as an extramedullary reference (the MA method).
Methods
A retrospective review of 1018 TKAs (508 FHC group, 510 MA group) was performed to compare the radiographic results obtained using these two methods. There were 75 male patients and 577 female patients with varus osteoarthritis of the knee. Limb and prosthesis alignments in the coronal plane were investigated at 2 months after surgery.
Results
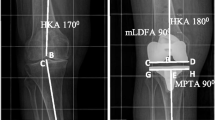
The accuracies of postoperative alignments of implanted prostheses were better in the MA group than in the FHC group, as assessed by (1) overall limb alignment (MA group, varus 1.4° ± 2.7°; FHC group, varus 2.2° ± 2.9°), and (2) femoral component coronal alignment (MA group, 89.4° ± 2.3°; FHC group, 88.0° ± 2.7°). Overall limb alignment was within 0° ± 5° of the mechanical axis in 96.1% of the MA group and in 86.6% of the FHC group. Mean femoral component medial angle was within 0° ± 5° in 98.4% of the MA group and in 92.5% of the FHC group.
Conclusion
The accuracies of the postoperative radiographic alignments of implanted prostheses were found to be improved when the mechanical axis of the overall lower limb was used as an extramedullary reference. This new reference system would help to achieve correct limb and prostheses alignments during TKA.
Level of evidence
III.





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Aglietti P, Baldini A, Sensi L (2006) Quadriceps-sparing versus mini-subvastus approach in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 452:106–111
Baldini A, Adravanti P (2008) Less invasive TKA: extramedullary femoral reference without navigation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466:2694–2700
Bathis H, Perlick L, Tingart M, Luring C, Zurakowski D, Grifka J (2004) Alignment in total knee arthroplasty. A comparison of computer-assisted surgery with the conventional technique. J Bone Jt Surg Br 86:682–687
Bolognesi M, Hofmann A (2005) Computer navigation versus standard instrumentation for TKA: a single-surgeon experience. Clin Orthop Relat Res 440:162–169
Bonutti PM, Zywiel MG, Ulrich SD, Stroh DA, Seyler TM, Mont MA (2010) A comparison of subvastus and midvastus approaches in minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Jt Surg Am 92:575–582
Caillouette JT, Anzel SH (1990) Fat embolism syndrome following the intramedullary alignment guide in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 251:198–199
Cates HE, Ritter MA, Keating EM, Faris PM (1993) Intramedullary versus extramedullary femoral alignment systems in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 286:32–39
Chang RN, Kim JH, Lee H, Baik HJ, Chung RK, Kim CH, Hwang TH (2010) Cerebral fat embolism after bilateral total knee replacement arthroplasty -A case report. Korean J Anesthesiol 59 Suppl:S207–S210
Chauhan SK, Scott RG, Breidahl W, Beaver RJ (2004) Computer-assisted knee arthroplasty versus a conventional jig-based technique. A randomised, prospective trial. J Bone Jt Surg Br 86:372–377
Choong PF, Dowsey MM, Stoney JD (2009) Does accurate anatomical alignment result in better function and quality of life? Comparing conventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 24:560–569
Engh GA, Petersen TL (1990) Comparative experience with intramedullary and extramedullary alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 5:1–8
Heyse TJ, Decking R, Davis J, Boettner F, Laskin RS (2009) Varus gonarthrosis predisposes to varus malalignment in TKA. HSS J 5:143–148
Huang TW, Hsu WH, Peng KT, Hsu RW (2011) Total knee replacement in patients with significant femoral bowing in the coronal plane: a comparison of conventional and computer-assisted surgery in an Asian population. J Bone Jt Surg Br 93:345–350
Jenkins K, Chung F, Wennberg R, Etchells EE, Davey R (2002) Fat embolism syndrome and elective knee arthroplasty. Can J Anaesth 49:19–24
Karachalios T, Giotikas D, Roidis N, Poultsides L, Bargiotas K, Malizos KN (2008) Total knee replacement performed with either a mini-midvastus or a standard approach: a prospective randomised clinical and radiological trial. J Bone Jt Surg Br 90:584–591
Kim YH, Kim JS, Hong KS, Kim YJ, Kim JH (2008) Prevalence of fat embolism after total knee arthroplasty performed with or without computer navigation. J Bone Jt Surg Am 90:123–128
Laskin R (1984) Alignment of total knee components. Orthopedics 7:62–65
Laskin RS (2001) Intramedullary instrumentation: safer and more accurate than extramedullary instrumentation. Orthopedics 24:739
Lee DH, Seo JG, Moon YW (2008) Synchronisation of tibial rotational alignment with femoral component in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 32:223–227
Lin WP, Lin J, Horng LC, Chang SM, Jiang CC (2009) Quadriceps-sparing, minimal-incision total knee arthroplasty: a comparative study. J Arthroplast 24:1024–1032
Mason JB, Fehring TK, Estok R, Banel D, Fahrbach K (2007) Meta-analysis of alignment outcomes in computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty surgery. J Arthroplast 22:1097–1106
Morawa LG, Manley MT, Edidin AA, Reilly DT (1996) Transesophageal echocardiographic monitored events during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 331:192–198
Mullaji A, Shetty GM, Kanna R, Sharma A (2010) Variability in the range of inter-anterior superior iliac spine distance and its correlation with femoral head centre. A prospective computed tomography study of 200 adults. Skeletal Radiol 39:363–368
O’Connor MI, Brodersen MP, Feinglass NG, Leone BJ, Crook JE, Switzer BE (2010) Fat emboli in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study of computer-assisted navigation vs standard surgical technique. J Arthroplast 25:1034–1040
Oberst M, Bertsch C, Wurstlin S, Holz U (2003) CT analysis of leg alignment after conventional versus navigated knee prosthesis implantation. Initial results of a controlled, prospective and randomized study. Unfallchirurg 106:941–948
Pagnano MW, Meneghini RM, Trousdale RT (2006) Anatomy of the extensor mechanism in reference to quadriceps-sparing TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res 452:102–105
Papagelopoulos PJ, Apostolou CD, Karachalios TS, Themistocleous GS, Giannakopoulos CK, Ioannidis TT (2003) Pulmonary fat embolism after total hip and total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics 26(523–527):528–529
Rajadhyaksha AD, Mehta H, Zelicof SB (2009) Use of tibialis anterior tendon as distal landmark for extramedullary tibial alignment in total knee arthroplasty: an anatomical study. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 38:E68–E70
RBaJ Rand (1985) Alignment and design in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. In: Dorr LD (ed) The knee papers of t he first scientific meeting of the knee society. University Park Press, Baltimore, pp 121–136
Restrepo C, Hozack WJ, Orozco F, Parvizi J (2008) Accuracy of femoral rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty using computer assisted navigation. Comput Aided Surg 13:167–172
Ritter MA, Campbell ED (1988) A model for easy location of the center of the femoral head during total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 3 Suppl:S59–S61
Ritter MA, Faris GW, Faris PM, Davis KE (2004) Total knee arthroplasty in patients with angular varus or valgus deformities of > or = 20 degrees. J Arthroplasty 19:862–866
Sawant MR, Murty A, Ireland J (2004) A clinical method for locating the femoral head centre during total knee arthroplasty. Knee 11:209–212
Schneider M, Heisel C, Aldinger PR, Breusch SJ (2007) Use of palpable tendons for extramedullary tibial alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 22:219–226
Seo JG, Kim BK, Moon YW, Kim JH, Yoon BH, Ahn TK, Lee DH (2009) Bony landmarks for determining the mechanical axis of the femur in the sagittal plane during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg 1:128–131
Seo JG, Lim JS, Lee HI, Woo KJ (2010) An extramedullary femoral alignment system in total knee arthroplasty using the inter-femoral head center distance. J Korean Orthop Assoc 45:347–355
Seo JG, Moon YW, Lim JS, Park SJ, Kim SM (2011) Mechanical axis-derived femoral component rotation in extramedullary total knee arthroplasty: a comparison between femoral transverse axis and transepicondylar axis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc doi:10.1007/s00167-011-1597-7
Sulek CA, Davies LK, Enneking FK, Gearen PA, Lobato EB (1999) Cerebral microembolism diagnosed by transcranial Doppler during total knee arthroplasty: correlation with transesophageal echocardiography. Anesthesiology 91:672–676
Tillett ED, Engh GA, Petersen T (1988) A comparative study of extramedullary and intramedullary alignment systems in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 230:176–181
Tingart M, Luring C, Bathis H, Beckmann J, Grifka J, Perlick L (2008) Computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty versus the conventional technique: how precise is navigation in clinical routine? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 16:44–50
der Zwaag HM, Valstar ER, van der Molen AJ, Nelissen RG (2008) Transepicondylar axis accuracy in computer assisted knee surgery: a comparison of the CT-based measured axis versus the CAS-determined axis. Comput Aided Surg 13:200–206
Vince KG (1987) Fat embolism and total knee arthroplasty. Can J Surg 30:227
Weiss SJ, Cheung AT, Stecker MM, Garino JP, Hughes JE, Murphy FL (1996) Fatal paradoxical cerebral embolization during bilateral knee arthroplasty. Anesthesiology 84:721–723
Yau WP, Chiu KY, Tang WM, Ng TP (2007) Coronal bowing of the femur and tibia in Chinese: its incidence and effects on total knee arthroplasty planning. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 15:32–36
Yau WP, Chiu KY, Zuo JL, Tang WM, Ng TP (2008) Computer navigation did not improve alignment in a lower-volume total knee practice. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466:935–945
Zimmerman RL, Kroner LF 3rd, Blomberg DJ, Nollet DJ (1983) Fatal fat embolism following total knee arthroplasty. Minn Med 66:213–216
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, JG., Moon, YW., Park, SH. et al. An alternative method to create extramedullary references in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20, 1339–1348 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-011-1668-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-011-1668-9