Abstract
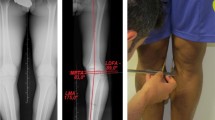
There is only limited information available on the sagittal alignment of the lower extremity of normal subjects under weight-bearing conditions. Our aim was to determine the sagittal alignment of the lower extremity under such conditions. Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs were taken of the 20 lower extremities of 20 healthy female volunteers while standing. The coronal mechanical axis passed through 29% medial to the proximal tibial articulating surface. The sagittal mechanical axis passed through 44% anterior to the distal femoral condyle and 33% anterior to the proximal tibial articulating surface, and also passed 3 mm anterior to the intercondylar notch. Our study showed that the coronal and sagittal mechanical axes of the lower extremity do not always pass through the center of the knee. Our results will provide important information for alignment in surgery of lower extremity such as knee arthroplasty and osteotomy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews M, Noyes FR, Hewett TE, Andriacchi TP (1996) Lower limb alignment and foot angle are related to stance phase knee adduction in normal subjects: a critical analysis of the reliability of gait analysis data. J Orthop Res 14:289–295
Berger RA, Rubash HE, Seel MJ, Thompson WH, Crossett LS (1993) Determining the rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using the epicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 286:40–47
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1(8476):307–310
Cooke TD, Li J, Scudamore RA (1994) Radiographic assessment of bony contributions to knee deformity. Orthop Clin North Am 25:387–393
Ishiguchi T (2005) Radiation dose of CT. J Jpn Med Assoc 134:1732
Jeffery RS, Morris RW, Denham RA (1991) Coronal alignment after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 73:709–714
Hsu RW, Himeno S, Coventry MB, Chao EY (1990) Normal axial alignment of the lower extremity and load-bearing distribution at the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 55:215–227
Koshino T, Tsuchiya K (1979) The effect of high tibial osteotomy on osteoarthritis of the knee. Clinical and histological observations. Int Orthop 3:37–45
Maurer F, Wassmer G (2006) High tibial osteotomy: does navigation improve results? Orthopedics 29(Suppl 10):130–132
Minoda Y, Kobayashi A, Iwaki H, Sugama R, Iwakiri K, Kadoya Y, Ohashi H, Takaoka K (2008) Sagittal alignment of the lower extremity while standing in Japanese male. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 128:435–442
Minoda Y, Kobayashi A, Iwaki H, Ohashi H, Takaoka K (2008) TKA sagittal alignment with navigation systems and conventional techniques vary only a few degrees. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467:1000–1006
Moreland JR, Bassett LW, Hanker GJ (1987) Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69:745–749
Oswald MH, Jakob RP, Schneider E, Hoogewoud HM (1993) Radiological analysis of normal axial alignment of femur and tibia in view of total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 8:419–426
Paley D, Herzenberg JE, Tetsworth K, McKie J, Bhave A (1994) Deformity planning for frontal and sagittal plane corrective osteotomies. Orthop Clin North Am 25:425–465
Sparmann M, Wolke B, Czupalla H, Banzer D, Zink A (2003) Positioning of total knee arthroplasty with and without navigation support. A prospective, randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 85:830–835
Tang WM, Zhu YH, Chiu KY (2000) Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82:1603–1608
Tew M, Waugh W (1985) Tibiofemoral alignment and the results of knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 67:551–556
Wasielewski RC, Galante JO, Leighty RM, Natarajan RN, Rosenberg AG (1994) Wear patterns on retrieved polyethylene tibial inserts and their relationship to technical considerations during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:31–43
White SH, Ludkowski PF, Goodfellow JW (1991) Anteromedial osteoarthritis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br 73:582–586
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugama, R., Minoda, Y., Kobayashi, A. et al. Sagittal alignment of the lower extremity while standing in female. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19, 74–79 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1137-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1137-x