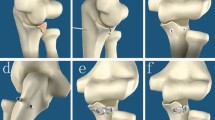
Abstract
Operative treatment of coronoid fracture often requires a large dissection of soft tissue, resulting in elbow stiffness and functional limitation. The authors present a minimal invasive, safe technique, useful in the case of isolated coronoid fracture associated with elbow dislocation. This technique does not require soft tissue dissection and allows an early unlimited resumption of sports activities.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breitfuss H, Muhr G, Neumann K, Neumann C, Rehn J (1991) Arthrolysis of post-traumatic stiff elbow. Which factors influence the end result. Unfallchirurg 94(1):33–39
Broberg MA, Morrey BF (1987) Results of treatment of fracture-dislocations of the elbow. Clin Orthop 216:109–119
Closkey RF, Goode JR, Kirschenbaum D, Cody RP (2000) The role of the coronoid process in elbow stability. A biomechanical analysis of axial loading. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82(A):1749–1753
Cobb TK, Morrey BF (1995) Use of distraction arthroplasty in unstable fracture dislocations of the elbow. Clin Orthop 312:201–210
Deutch SR, Jensen SL, Tyrdal S, Olsen BS, Sneppen O (2003) Elbow joint stability following experimental osteoligamentous injury and reconstruction. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 12(5):466–471
Mezera K, Hotchkiss R (1996) Fractures and dislocations of the elbow. In: Rockwood CAGD, Buchholz RW, Heckman JD (eds) Rockwood and Green’s fractures in adults, 5th edn. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, pp 921–951
Josefsson PO, Gentz CF, Johnell O, Wendeberg B (1989) Dislocations of the elbow and intraarticular fractures. Clin Orthop 246:126–130
Kalicke T, Westhoff J, Wingenfeld C, Muhr G, Arens S (2003) Fracture dislocation of the elbow involving the coronoid process. Unfallchirurg 106(4):300–305
Linscheid RL, Wheeler DK (1965) Elbow dislocations. JAMA 194(11):1171–1176
Morrey B, O’Driscoll SW (2002) Fractures of the coronoid and complex in stability of the elbow. In: Morrey B (ed) Master techniques in orthopaedic surgery—the elbow, 2nd edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 127–138
Regan W, Morrey B (1989) Fractures of the coronoid process of the ulna. J Bone Joint Surg Am 71(9):1348–1354
Ring D, Jupiter JB (2002) Surgical Exposure of Coronoid Fractures. Tech Shoulder Elbow Surg 3(1):48–56
Spencer EE, JC K (2003) A simple technique for coronoid fixation. Tech Shoulder Elbow Surg 4(1):1–3
Terada N, Yamada H, Seki T, Urabe T, Takayama S (2000) The importance of reducing small fractures of the coronoid process in the treatment of unstable elbow dislocation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 9(4):344–346
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garofalo, R., Bollmann, C., Kombot, C. et al. Minimal invasive surgery for coronoid fracture: technical note. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13, 608–611 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-004-0594-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-004-0594-5