Abstract
Objective
Since recent study demonstrated beneficial effects of β-adrenergic blocker in sepsis, we tested the hypothesis that infusion of selective β1-blocker, esmolol, improves outcome in sepsis by modulating inflammatory responses and gut barrier function.
Design
Prospective randomized animal study.
Setting
University research laboratory.
Subjects
Male Wistar rats.
Interventions
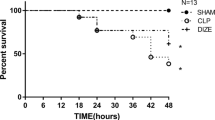
To assess the effects of esmolol infusion on survival time, 19 animals that underwent cecal ligation and perforation were randomized into control (n = 9) or esmolol (n = 10) groups, the latter of which received esmolol infusion (15 mg/kg/h) throughout the study period. In an additional 20 animals, levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in both plasma and intraperitoneal fluid were measured, and mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs) and ileum were excised for evaluation of bacterial translocation and mucosal injury at the 18-h study period.
Measurements and results
Mean survival time in the esmolol group was significantly longer compared with the control group (69.5 ± 26.8 versus 28.6 ± 11.0 h). Plasma TNF-α was not detectable in either group, while intraperitoneal fluid TNF-α level was elevated in the control group but significantly depressed in the esmolol group (16.8 ± 10.7 versus 5.4 ± 7.1 pg/ml, P < 0.05). Simultaneously, the Escherichia coli positive rate of MLNs was higher (100% versus 44%, P < 0.05) and the gut mucosal injury score was elevated (4.1 ± 0.6 versus 2.8 ± 0.6, P < 0.01) in the control compared with the esmolol group.
Conclusions
Beta-1 blocker therapy improves outcome in sepsis possibly through modulation of gut mucosal integrity and local inflammatory response.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Norbury WB, Jeschke MG, Herndon DN (2007) Metabolism modulators in sepsis: propranolol. Crit Care Med 35:S616–S620
Herndon DN, Hart DW, Wolf SE, Chinkes DL, Wolfe RR (2001) Reversal of catabolism by beta-blocker after severe burns. N Engl J Med 345:1223–1229
Ackland GL, Yao ST, Rudiger A, Dyson A, Stidwill R, Poputnikov D, Singer M, Gourine AV (2010) Cardioprotection, attenuated systemic inflammation, and survival benefit of beta1-adrenoceptor blockade in severe sepsis in rats. Crit Care Med 38:388–394
Suzuki T, Morisaki H, Serita R, Yamamoto M, Kotake Y, Ishizaka A, Takeda J (2005) Infusion of the β-adrenergic blocker esmolol attenuates myocardial dysfunction in septic rats. Crit Care Med 33:2294–2301
Hagiwara S, Iwasaka H, Maeda H, Noguchi T (2009) Landiolol, an ultrashort-acting β1-adrenoceptor antagonist, has protective effects in an LPS-induced systemic inflammation model. Shock 31:515–520
Novotny NM, Lahm T, Markel TA, Crisostomo PR, Wang M, Wang Y, Ray R, Tan J, Al-Azzawi D, Meldrum DR (2009) Beta-blockers in sepsis: reexamining the evidence. Shock 31:113–119
Schmitz D, Wilsenack K, Lendemanns S, Schedlowski M, Oberbeck R (2007) Beta-adrenergic blockade during systemic inflammation: Impact on cellular immune function and survival in murine model of sepsis. Resuscitation 72:286–294
Berg RD (1995) Bacterial translocation from the gastrointestinal tract. Trends Microbiol 3:149–154
Mclntyre AS, Thompson DG, Burnham WR, Walker ER (1992) Modulation of human upper intestinal nutrient transit by a beta adrenoreceptor mediated pathway. Gut 33:1062–1070
Husebye E (2005) The pathogenesis of gastrointestinal bacterial overgrowth. Chemotherapy 51(Suppl 1):1–22
Ahluwalia NK, Thompson DG, Barlow J, Heggie (1994) Beta adrenergic modulation of human upper intestinal propulsive forces. Gut 35:1356–1359
Pérez-Paramo M, Muñoz J, Albillos A, Freile I, Portero F, Santos M, Ortiz-Berrocal J (2000) Effect of propranolol on the factors promoting bacterial translocation in cirrhotic rats with ascites. Hepatology 31:43–48
Liu C, Wu Q, Li Q, Liu D, Su H, Shen N, Tai M, Lv Y (2009) Mesenteric lymphatic ducts ligation decreases the degree of gut-induced lung injury in a portal vein occlusion and reperfusion canine model. J Surg Res 154:45–50
Senthil M, Brown M, Xu DZ, Lu Q, Feketeova E, Deitch EA (2006) Gut-lymph hypothesis of systemic inflammatory response syndrome/multiple-organ dysfunction syndrome: validating studies in a porcine model. J Trauma 60:958–965
Rittirsch D, Huber-Lang MS, Flierl MA, Ward PA (2009) Immunodesign of experimental sepsis by cecal ligation and puncture. Nat Protoc 4:31–36
Morisaki H, Sibbald W, Martin C, Doig G, Inman K (1996) Hyperdynamic sepsis depresses circulatory compensation to normovolemic anemia in conscious rats. J Appl Physiol 80:656–664
Qiao Z, Li Z, Li J, Lu L, Lv Y, Li J (2009) Bacterial translocation and change in intestinal permeability in patients after abdominal surgery. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci 29:486–491
de Souza Gonçalves L, Souto R, Colombo AP (2009) Detection of Helicobacter pylori, Enterococcus faecalis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the subgingival biofilm of HIV-infected subjects undergoing HAART with chronic periodontitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 28:1335–1342
Chiu CJ, McArdle AH, Brown R, Scott HT, Gurd FN (1970) Intestinal mucosal lesion in low flow states. Arch Surg 101:478–483
Cain B, Meldrum DR, Dinarello CA, Meng X, Joo KS, Banerjee A, Harken A (1999) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta synergistically depress human myocardial function. Crit Care Med 27:1309–1318
van Zoelen MA, Yang H, Florquin S, Meijers JC, Akira S, Arnold B, Nawroth PP, Bierhaus A, Tracey KJ, van der Poll T (2009) Role of toll-like receptors 2 and 4, and the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) in HMGB1 induced inflammation in vivo. Shock 31:280–284
Szelenyi J, Selmeczy Z, Brozik A, Medgyesi D, Magocsi M (2006) Dual beta-adrenergic modulation in the immune system: Stimulus-dependent effect of isoproterenol on MAPK activation and inflammatory mediator production in macrophages. Neurochem Int 49:94–103
Casley-Smith R, Gannon BJ (1984) Intestinal microcirculation: spatial organization and fine structure. In: Shepherd AP, Granger DN (eds) Physiology of the intestinal circulation. Raven, New York, pp 9–31
Vincent JL, De Backer D (2005) Microvascular dysfunction as a cause of organ dysfunction in severe sepsis. Crit Care 9(Suppl 4):S9–S12
Brienza N, Ayuse T, Revelly JP, O’Donnell CP, Robotham JL (1995) Effects of endotoxin on isolated porcine liver: pressure-flow analysis. J Appl Physiol 78:784–792
Yao GX, Shen ZY, Xue XB, Yang Z (2006) Intestinal permeability in rats with CCI4-induced portal hypertension. World J Gastroenterol 12:479–481
Garcia-Tsao G, Albillos A, Barden GE, West AB (1993) Bacterial translocation in acute and chronic portal hypertension. Hepatology 17:1081–1085
Zhou M, Das P, Simms HH, Wang P (2005) Gut-derived norepinephrine plays an important role in up-regulating IL-1beta and IL-10. Biochim Biophys Acta 1740:446–452
Kosugi S, Morisaki H, Satoh T, Ai K, Yamamoto M, Serita R, Soejima J, Kotake Y, Ishizaka A, Takeda J (2005) Epidural analgesia prevents endotoxin-induced gut mucosal injury in rabbits. Anesth Analg 101:265–272
Grisanti LA, Evanson J, Marchus E, Jorissen H, Woster AP, DeKrey W, Sauter ER, Combs CK, Porter JE (2010) Pro-inflammatory responses in human monocytes are β1-adrenergic receptor subtype dependent. Mol Immunol 47:1244–1254
POISE Study Group (2008) Effects of extended-release metoprolol succinate in patients undergoing non-cardiac surgery (POISE trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 371:1839–1847
Wallace AW, Au S, Cason BA (2010) Association of the pattern of use of perioperative β-blocker and postoperative mortality. Anesthesiology 113:794–805
Nishina K, Akamatsu H, Mikawa K, Shiga M, Obara H, Niwa Y (2001) A comparison of atenolol, labetalol, esmolol, and landiolol for human neutrophil functions. Anesth Analg 93:641–644
Tennenberg SD, Solomkin JS (1988) Neutrophil activation in sepsis: the relationship between fmet-leu-phe receptor mobilization and oxidative activity. Arch Surg 123:171–175
Remick DG, Newcomb DE, Bolgos GL, Call DR (2000) Comparison of the mortality and inflammatory response of two models of sepsis: lipopolysaccharide VS cecal ligation and puncture. Shock 13:110–116
Ebong S, Call D, Nemzek J, Bolgos G, Newcomb D, Remick D (1999) Immunopathologic alterations in murine models of sepsis of increasing severity. Infect Immun 67:6603–6610
Eskandari MK, Bolgos G, Miller C, Nguyen DT, DeForge LE, Remick DG (1992) Anti-tumor necrosis factor antibody therapy fails to prevent lethality after cecal ligation and puncture or endotoxemia. J Immunol 148:2724–2730
Giebelen IAJ, Le Moine A, van den Pangaart PS, Sedis C, Goldman M, Florquin S, van den Poll T (2008) Deficiency of α7 cholinergic receptors facilitates bacterial clearance in Escherichia coli peritonitis. J Infect Dis 198:750–757
Sewnath ME, Olszyna DP, Birjmohun R, ten Kate FJ, Gouma DJ, van Der Poll T (2001) IL-10 deficient mice demonstrate multiple organ failure and increased mortality during Escherichia coli peritonitis despite an accelerated bacterial clearance. J Immunol 166:6323–6331
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank Dr. Shuji Takabayashi, Hamamatsu University School of Medicine, Hamamatsu, Japan for his excellent instruction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is discussed in the editorial available at: doi:10.1007/s00134-011-2330-1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mori, K., Morisaki, H., Yajima, S. et al. Beta-1 blocker improves survival of septic rats through preservation of gut barrier function. Intensive Care Med 37, 1849–1856 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-011-2326-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-011-2326-x