Abstract
Objective
The pathogenesis of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) in septic shock is mainly caused by maldistribution of tissue perfusion and the amplification of inflammatory responses, which may be modulated by β2-adrenoceptor agonists. We evaluated and compared effects of terbutaline on MODS in a cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) model of sepsis.
Design and setting
Prospective controlled animal study in a university laboratory.
Methods
Male adult Wistar rats received CLP or sham operation followed by the administration of saline or terbutaline (0.3 mg/kg i.v. at 3 and 9 h after CLP).
Measurements and results
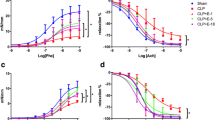
At 0, 9 and 18 h after CLP, the changes of hemodynamics, organ function indexes, as well as the plasma interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and nitrite/nitrate levels were examined. At 18 h after CLP, animals were killed and their lungs, livers and kidneys were immediately excised to analyze superoxide anion (O2 −) levels and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression. These organs were also evaluated by pathological study. Terbutaline significantly (1) prevented delayed hypotension and reduced hepatic and renal dysfunction, (2) diminished plasma IL-1β and nitrite/nitrate, lung iNOS expression, tissue O2 − level and the infiltration of neutrophils in the lung and the liver, and (3) improved the 18-h survival rate.
Conclusions
Terbutaline may be developed as an alternative treatment for severe sepsis-induced MODS. The protective effect of terbutaline seems to be through inhibition of proinflammatory mediators and attenuation of oxidant production.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moreno RP, Metnitz B, Adler L, Hoechtl A, Bauer P, Metnitz PG, SAPS 3 Investigators (2008) Sepsis mortality prediction based on predisposition, infection and response. Intensive Care Med 34:496–504
Matsuda N, Hattori Y (2006) Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS): molecular pathophysiology and gene therapy. J Pharmacol Sci 101:189–198
Victor VM, Rocha M, Esplugues JV, de la Fuente M (2005) Role of free radicals in sepsis: antioxidant therapy. Curr Pharm Des 11:3141–3158
Elenkov IJ, Chrousos GP, Wilder RL (2000) Neuroendocrine regulation of IL-12 and TNF-alpha/IL-10 balance: clinical implications. Ann NY Acad Sci 917:94–105
Muthu K, Deng J, Gamelli R, Shankar R, Jones SB (2005) Adrenergic modulation of cytokine release in bone marrow progenitor-derived macrophage following polymicrobial sepsis. J Neuroimmunol 158:50–57
Straub RH, Linde HJ, Mannel DN, Scholmerich J, Falk W (2000) A bacteria-induced switch of sympathetic effector mechanisms augments local inhibition of TNF-alpha and IL-6 secretion in the spleen. FASEB J 14:1380–1388
Kambalapalli M, Nichani S, Upadhyayula S (2005) Safety of intravenous terbutaline in acute severe asthma: a retrospective study. Acta Paediatr 94:1214–1217
Wu JY, Liaw WJ, Tzao C, Chen SJ, Wang JH, Wu CC (2002) Comparison of terbutaline and dobutamine in rats with endotoxemia. Chin J Physiol 45:155–162
Liaw WJ, Tzao C, Wu JY, Chen SJ, Wang JH, Wu CC (2003) Inhibition by terbutaline of nitric oxide and superoxide anion levels of endotoxin-induced organs injury in the anesthetized rat. Shock 19:281–288
Liaw WJ, Chen TH, Lai ZZ, Chen SJ, Chen A, Tzao C, Wu JY, Wu CC (2005) Effects of a membrane-permeable radical scavenger, Tempol, on intraperitoneal sepsis-induced organ injury in rats. Shock 23:88–96
Tsao CM, Ho ST, Chen A, Wang JJ, Li CY, Tsai SK, Wu CC (2004) Low-dose dexamethasone ameliorates circulatory failure and renal dysfunction in conscious rats with endotoxemia. Shock 21:484–491
Uzuki M, Yamakage M, Fujimura N, Namiki A (2007) Direct inotropic effect of the beta-2 receptor agonist terbutaline on impaired diaphragmatic contractility in septic rats. Heart Lung 36:140–147
Monastra G, Secchi EF (1993) Beta-adrenergic receptors mediate in vivo the adrenaline inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor release. Immunol Lett 38:127–130
van der Poll T, Calvano SE, Kumar A, Coyle SM, Lowry SF (1997) Epinephrine attenuates down-regulation of monocyte tumor necrosis factor receptors during human endotoxemia. J Leukoc Biol 61:156–160
Zhang H, Kim YK, Govindarajan A, Baba A, Binnie M, Marco Ranieri V, Liu M, Slutsky AS (1999) Effect of adrenoreceptors on endotoxin-induced cytokines and lipid peroxidation in lung explants. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 160:1703–1710
Knudsen JH, Kjaersgaard E, Christensen NJ (1995) Individual lymphocyte subset composition determines cAMP response to isoproterenol in mononuclear cell preparations from peripheral blood. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 55:9–14
Kuroki K, Takahashi HK, Iwagaki H, Murakami T, Kuinose M, Hamanaka S, Minami K, Nishibori M, Tanaka N, Tanemoto K (2004) Beta2-adrenergic receptor stimulation-induced immunosuppressive effects possibly through down-regulation of co-stimulatory molecules, ICAM-1, CD40 and CD14 on monocytes. J Int Med Res 32:465–483
Mustafa SB, Olson MS (1998) Expression of nitric-oxide synthase in rat Kupffer cells is regulated by cAMP. J Biol Chem 273:5073–5080
Yao J, Mackman N, Edgington TS, Fan ST (1997) Lipopolysaccharide induction of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha promoter in human monocytic cells: regulation by Egr-1, c-Jun, and NF-kappaB transcription factors. J Biol Chem 272:1795–1801
Arai K, Wood JP, Osborne NN (2003) Beta-adrenergic receptor agonists and antagonists counteract LPS-induced neuronal death in retinal cultures by different mechanisms. Brain Res 985:176–186
Mazzio E, Becker A, Soliman KF (2002) Characterization of neurotransmitters and dopamine attenuation of inducible nitric oxide synthase in glioma cells. J Neuroimmunol 131:70–82
Nakamura A, Imaizumi A, Yanagawa Y, Niimi R, Kohsaka T (2003) Suppression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by beta2-adrenoceptor activation: role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in renal mesangial cells. Inflamm Res 52:26–31
Zhang B, Yang L, Konishi Y, Maeda N, Sakanaka M, Tanaka J (2002) Suppressive effects of phosphodiesterase type IV inhibitors on rat cultured microglial cells: comparison with other types of cAMP-elevating agents. Neuropharmacology 42:262–269
Weiss M, Schneider EM, Tarnow J, Mettler S, Krone M, Teschemacher A, Lemoine H (1996) Is inhibition of oxygen radical production of neutrophils by sympathomimetics mediated via beta-2 adrenoceptors? J Pharmacol Exp Ther 278:1105–1113
Youssef HA, Sigurdsson GH, Christenson JT, Owunwanne A (1991) Use of indium-111-labeled transferrin to study plasma extravasation during endotoxin shock and the effects of the beta-2 agonist terbutaline. Am J Physiol Imaging 6:85–89
Schmidt W, Hacker A, Gebhard MM, Martin E, Schmidt H (1998) Dopexamine attenuates endotoxin-induced microcirculatory changes in rat mesentery: role of beta2 adrenoceptors. Crit Care Med 26:1639–1645
Izeboud CA, Hoebe KH, Grootendorst AF, Nijmeijer SM, van Miert AS, Witkamp RR, Rodenburg RJ (2004) Endotoxin-induced liver damage in rats is minimized by beta 2-adrenoceptor stimulation. Inflamm Res 53:93–99
Maris NA, de Vos AF, Dessing MC, Spek CA, Lutter R, Jansen HM, van der Zee JS, Bresser P, van der Poll T (2005) Antiinflammatory effects of salmeterol after inhalation of lipopolysaccharide by healthy volunteers. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172:878–884
Verhoeckx KC, Doornbos RP, van der Greef J, Witkamp RF, Rodenburg RJ (2005) Inhibitory effects of the beta-adrenergic receptor agonist zilpaterol on the LPS-induced production of TNF-alpha in vitro and in vivo. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 28:531–537
Wu JY, Tsou MY, Chen TH, Chen SJ, Tsao CM, Wu CC (2008) Therapeutic effects of melatonin on peritonitis-induced septic shock with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in rats. J Pineal Res 45:106–116
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants NSC 94-2320-B-016-037, 95-2320-B-016-008 and 96-2320-B-016-002 from the National Science Council and DOD 95-07-02, 96-01-08 and 97-08-01 from the National Defense Ministry, Taiwan, ROC
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
C.-M. Tsao and S.-J. Chen have made equal contribution to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsao, CM., Chen, SJ., Shih, MC. et al. Effects of terbutaline on circulatory failure and organ dysfunction induced by peritonitis in rats. Intensive Care Med 36, 1571–1578 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-010-1839-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-010-1839-z