Abstract
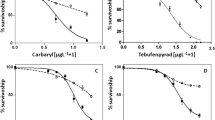
Bombina orientalis is one of the most common amphibians in the world and comprise a large proportion of their total number in Korea. B. orientalis, spawns in the farming regions at Spring when the massive application of agricultural chemicals occurs. Carbaryl, carbamate chemical is a slightly to highly toxic insecticide inhibiting acetylcholinesterase. The embryotoxicity and teratogenic effects of carbaryl on B. orientalis embryos were investigated at 5, 10, 50 and 100 μM. The survival rates of embryos at 312 h post fertilization were decreased with concentration dependent manner. Exposure to carbaryl produced 4 types of severe external abnormalities such as bent trunk, thick-set body, bent tail and ventral blister. At 5 μM carbaryl, a dose of no observed effect on embryonic survival, developmental abnormalities were significantly increased. The developmental abnormalities showed in order of frequency with bent trunk, thick-set body, bent tail and ventral blister. This result suggests that carbaryl is detrimental for embryonic survival and teratogenic by causing the axial skeletal defects in B. orientalis embryos.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alford RA, Richards SJ (1999) Global amphibian declines: a problem in applied ecology. Ann Rev Ecolog Syst 30:133–165
Bacchetta R, Mantecca P, Andrioletti M, Vismara C, Vailati G (2008) Axial-skeletal defects caused by carbaryl in Xenopus laevis embryos. Sci Total Environ 392:110–118
Boone MD, Bridges CM (1999) The effect of temperature on the potency of carbaryl for survival of tadpoles of the green frog (Rana clamitans). Environ Toxicol Chem 18:1482–1484
Boone MD, Semlitsch RD (2001) Interactions of an insecticide with larval density and predation in experimental amphibian communities. Conserv Biol 15:228–238
Boone MD, Semlitsch RD (2002) Interactions of an insecticide with competition and pond drying in amphibian communities. Ecol Appl 12:307–316
Bridges CM (1997) Tadpole activity and swimming performance affected by sublethal levels of carbaryl. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:1935–1939
Bridges CM (2000) Long-term effects of pesticide exposure at various life stages of the southern leopard frog (Rana sphenocephala). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:91–96
Bridges CM, Dwyer FJ, Hardesty DK, Whites DW (2002) Comparative contaminant toxicity: are amphibian larvae more sensitive than fish? Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 69:562–569
Calumpang SM, Medina MJ, Tejada AW, Medina JR (1997) Toxicity of chlopyrifos, fenubucarb, monocrotophos, and methyl parathion to fish and frogs after a simulated overflow of paddy water. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 58:909–914
Davidson C (2004) Declining downwind: amphibian population declines in California and historical pesticides use. Ecol Appl 14:1892–1902
Davidson C, Benard MF, Shaffer HB, Parker JM, O’leary C, Conlon JM, Rollins-Smith LA (2007) Effects of chytrid and carbaryl exposure on survival, growth and skin peptide defenses in foothill yellow-legged frogs. Environ Sci Technol 41:1771–1776
Ecobichon DJ (2001) Carbamate insecticides. In: Krieger R (ed) Hand-book of pesticide toxicology, vol 2. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 1087–1106
Fulton MH, Key PB (2001) Acetylcholinesterase inhibition in estuarine fish and invertebrates as indicator of organophosphorus insecticide exposure and effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:37–45
Houlahan JE, Findlay CS, Schmidt BR, Meyer AH, Kuzmin SL (2000) Quantitative evidence for global amphibian population declines. Nature 404:752–755
John M, Oommen A, Zachariah A (2003) Muscle injury in organophosphorus poisoning and its role in the development of intermediate syndrome. Neurotoxicology 24:43–53
Kang HS, Gye MC, Kim MK (2005) Effects of alachlor on survival and development of Bombina orientalis (Boulenger) embryos. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 74:1199–1206
Kang HS, Gye MC, Kim MK (2008) Effects of endosulfan on survival and development of Bombina orientalis (Boulenger) embryos. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81:262–265
Kang HS, Park CJ, Gye MC (2009) Effects of molinate on survival and development of Bombina orientalis (Boulenger) embryos. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82:305–309
Karalliedde L, Henry JA (1993) Effects of organophosphates on skeletal muscle. Hum Exp Toxicol 12:289–296
Mathew L, Reddy MLP, Rao TP, Iyer GSP, Damodaran AC (1995) Simple spectrophotometric method for the determination of carbaryl in soil and insecticide formulations. Analyst 120:1799–1801
O’Malley M (1997) Clinical evaluation of pesticide exposure and poisonings. Lancet 349:1161–1166
Relyea RA (2003) Predator cues and pesticides: a double dose of danger for amphibians. Ecol Appl 13:1515–1521
Relyea RA (2004) The growth and survival of five amphibian species exposed to combinations of pesticides. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1737–1742
Relyea RA, Mills N (2001) Predator-induced stress makes the pesticide carbaryl more deadly to gray treefrog tadpoles (Hyla versicolor). PNAS 98:2491–2496
Rugh R (1962) Experimental embryology, 3rd edn. Burgess Publishing Co., Minneapolis
US Environmental Protection Agency (1999) Assesing contaminant sensitivity of endangered and threatened species: toxicant classes. EPA/600/R-99/098 USEPA. Office of Research and Development, Washington
Venturino A, Rosenbaum E, Caballero de Castro A, Anguiano OL, Gauna L, Fonovich de Schroeder T, Pechen de D’Angelo AM (2003) Biomarkers of effect in toads and frogs. Biomarkers 8:167–186
Zaga A, Little EE, Rabeni CF, Ellersieck MR (1998) Photoenhanced toxicity of a carbamate insecticide to early life stage anuran amphibians. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:2543–2553
Acknowledgments
This subject is supported by Korea Ministry of Environment as “The Eco-technopia 21 project” (#091-091-025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, H.S., Park, C.J. & Gye, M.C. Effect of Carbaryl on Survival and Development in Bombina orientalis (Boulenger) Embryos. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84, 550–553 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-010-9979-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-010-9979-y