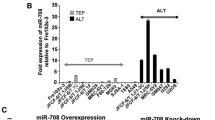
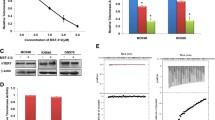
Abstract
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most aggressive cancer of central nervous system with worst patient outcome. Telomere maintenance is a crucial mechanism governing GBM initiation and progression making it an attractive target. microRNAs (miRNAs) have shown therapeutic potential in GBM. Earlier, we showed miR-490 is downregulated in GBM patients and plays a tumor suppressive role. Here, we show that miR-490 regulates telomere maintenance program in GBM by directly targeting Telomeric Repeat-binding Factor 2 (TERF2) of the shelterin complex, Tankyrase 2 (TNKS2) and Serine/Threonine-protein kinase, SMG1. Overexpression of miR-490 resulted in effects characteristic to hampered telomere maintenance via TERF2 inhibition. These include induction of telomere dysfunction-induced foci and global DNA damage (53BP1 foci), along with an increase in p-γH2AX levels. Further, it led to inhibition of telomere maintenance hallmarks via reduced stemness (SOX2 and SOX4 downregulation) and induction of senescence (H3K9me3 marks gain and SIRT1 downregulation). It also initiated downstream DNA damage response (DDR) leading to p53 pathway activation. Moreover, microarray data analysis highlighted an overlap between miR-490 expression and REST-inhibition responses in GBM. Thus, miR-490-mediated targeting of telomere maintenance could be therapeutically important in GBM.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Upon reasonable request.
References
Delgado-López PD, Corrales-García EM (2016) Survival in glioblastoma: a review on the impact of treatment modalities. Clin Transl Oncol 18:1062–1071
Gaspar TB, Sá A, Lopes JM et al (2018) Telomere maintenance mechanisms in cancer. Genes (Basel) 9(5):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9050241
Whittemore K, Vera E, Martínez-Nevado E et al (2019) Telomere shortening rate predicts species life span. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:15122–15127. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1902452116
De Lange T (1994) Activation of telomerase in a human tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:2882–2885
Chiba K, Lorbeer FK, Shain AH et al (2017) Mutations in the promoter of the telomerase gene TERT contribute to tumorigenesis by a two-step mechanism. Science 80(357):1416–1420. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao0535
Bai Y, Lathia JD, Zhang P et al (2014) Molecular targeting of TRF2 suppresses the growth and tumorigenesis of glioblastoma stem cells. Glia 62:1687–1698. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22708
Miyazaki T, Pan Y, Joshi K et al (2012) Telomestatin impairs glioma stem cell survival and growth through the disruption of telomeric G-quadruplex and inhibition of the proto-oncogene, c-Myb. Clin Cancer Res 18:1268–1280. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1795
Bejarano L, Schuhmacher AJ, Méndez M et al (2017) Inhibition of TRF1 telomere protein impairs tumor initiation and progression in glioblastoma mouse models and patient-derived xenografts. Cancer Cell 32:590–607.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2017.10.006
Polito F, Cucinotta M, Abbritti RV et al (2018) Silencing of telomere-binding protein adrenocortical dysplasia (ACD) homolog enhances radiosensitivity in glioblastoma cells. Transl Res 202:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2018.07.005
Gao K, Li G, Qu Y et al (2016) TERT promoter mutations and long telomere length predict poor survival and radiotherapy resistance in gliomas. Oncotarget 7(8):8712–8725. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6007
Kondo Y, Kondo S, Tanaka Y et al (1998) Inhibition of telomerase increases the susceptibility of human malignant glioblastoma cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 16:2243–2248. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201754
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
ZHANG Y, CRUICKSHANKS N, PAHUSKI M, et al (2017) Noncoding RNAs in Glioblastoma. In: Glioblastoma. Codon Publications, pp 95–130
Novakova J, Slaby O, Vyzula R, Michalek J (2009) MicroRNA involvement in glioblastoma pathogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 386:1–5
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs–MicroRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:259–269
Vinchure OS, Sharma V, Tabasum S et al (2019) Polycomb complex mediated epigenetic reprogramming alters TGF-β signaling via a novel EZH2/miR-490/TGIF2 axis thereby inducing migration and EMT potential in glioblastomas. Int J Cancer 145(5):1254–1269. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.32360
Mazzolini R, Gonzàlez N, Garcia-Garijo A et al (2018) Snail1 transcription factor controls telomere transcription and integrity. Nucleic Acids Res 46:146–158. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx958
Dweep H, Gretz N (2015) MiRWalk2.0: a comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat Methods 12(8):697. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3485
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW, Bartel DP (2015) Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 4:e05005. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.05005
Mi H, Thomas P (2009) PANTHER pathway: an ontology-based pathway database coupled with data analysis tools. Methods Mol Biol 563:123–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-175-2_7
Carbon S, Ireland A, Mungall CJ, Shu ShengQiang, Marshall B, Lewis S, the AmiGO Hub, and the WPWG, (2009) AmiGO: online access to ontology and annotation data. Bioinformatics 25:288–289
Karlseder J, Broccoli D, Yumin D et al (1999) p53- and ATM-dependent apoptosis induced by telomeres lacking TRF2. Science 80(283):1321–1325. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.283.5406.1321
Sidler C, Kovalchuk O, Kovalchuk I (2017) Epigenetic regulation of cellular senescence and aging. Front, Genet, p 8
Jeon HY, Kim JK, Ham SW et al (2016) Irradiation induces glioblastoma cell senescence and senescence-associated secretory phenotype. Tumor Biol 37:5857–5867. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4439-2
Zhang W, Feng Y, Guo Q et al (2019) SIRT1 modulates cell cycle progression by regulating CHK2 acetylation−phosphorylation. Cell Death Differ. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-019-0369-7
Schmeer K, Wengerodt, et al (2019) Dissecting aging and senescence—current concepts and open lessons. Cells 8:1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111446
Ikushima H, Todo T, Ino Y et al (2009) Autocrine TGF-β signaling maintains tumorigenicity of glioma-initiating cells through sry-related HMG-box factors. Cell Stem Cell 5:504–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2009.08.018
Li C, Wang Z, Tang X et al (2017) Molecular mechanisms and potential prognostic effects of REST and REST4 in glioma (Review). Mol Med Rep 16:3707–3712
Zhang P, Pazin MJ, Schwartz CM et al (2008) Nontelomeric TRF2-REST interaction modulates neuronal gene silencing and fate of tumor and stem cells. Curr Biol 18:1489–1494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2008.08.048
Wagoner MP, Gunsalus KTW, Schoenike B et al (2010) The transcription factor REST is lost in aggressive breast cancer. PLoS Genet 6:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1000979
Pallini R, Sorrentino A, Pierconti F et al (2006) Telomerase inhibition by stable RNA interference impairs tumor growth and angiogenesis in glioblastoma xenografts. Int J cancer 118:2158–2167. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.21613
Lavanya C, Venkataswamy MM, Sibin MK et al (2018) Down regulation of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) expression by BIBR1532 in human glioblastoma LN18 cells. Cytotechnology 70:1143–1154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-018-0205-9
Santambrogio F, Gandellini P, Cimino-Reale G et al (2014) MicroRNA-dependent regulation of telomere maintenance mechanisms: a field as much unexplored as potentially promising. Curr Pharm Des 20:6404–6421. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612820666140630095918
Dinami R, Ercolani C, Petti E et al (2014) miR-155 drives telomere fragility in human breast cancer by targeting TRF1. Cancer Res 74:4145–4156. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2038
Luo Z, Feng X, Wang H et al (2015) Mir-23a induces telomere dysfunction and cellular senescence by inhibiting TRF2 expression. Aging Cell 14:391–399. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12304
Wang YY, Sun G, Luo H et al (2012) Mir-21 modulates htert through a stat3-dependent manner on glioblastoma cell growth. CNS Neurosci Ther 18:722–728. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00349.x
Naderlinger E, Holzmann K (2017) Epigenetic regulation of telomere maintenance for therapeutic interventions in gliomas. Genes (Basel) 8(5):145. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8050145
El-Badawy A, Ghoneim NI, Nasr MA et al (2018) Telomerase reverse transcriptase coordinates with the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through a feedback loop to define properties of breast cancer stem cells. Biol Open 7(7):bio034181. https://doi.org/10.1242/bio.034181
Kamal MM, Sathyan P, Singh SK et al (2012) REST regulates oncogenic properties of glioblastoma stem cells. Stem Cells 30:405–414. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.1020
Liang J, Meng Q, Zhao W et al (2016) An expression based REST signature predicts patient survival and therapeutic response for glioblastoma multiforme. Sci Rep 6:34556. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34556
Xu X, Tao Y, Gao X et al (2016) A CRISPR-based approach for targeted DNA demethylation. Cell Discov 2:16009. https://doi.org/10.1038/celldisc.2016.9
Takai H, Smogorzewska A, De Lange T (2003) DNA damage foci at dysfunctional telomeres. Curr Biol 13:1549–1556. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00542-6
Tutton S, Lieberman PM (2017) A role for p53 in telomere protection. Mol Cell, Oncol, p 4
Suchánková J, Legartová S, Ručková E et al (2017) Mutations in the TP53 gene affected recruitment of 53BP1 protein to DNA lesions, but level of 53BP1 was stable after γ-irradiation that depleted MDC1 protein in specific TP53 mutants. Histochem Cell Biol 148:239–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-017-1567-3
Moureau S, Luessing J, Harte EC et al (2016) A role for the p53 tumour suppressor in regulating the balance between homologous recombination and non-homologous end joining. Open Biol 6(9):160225. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.160225
Hasegawa D, Okabe S, Okamoto K et al (2016) G-quadruplex ligand-induced DNA damage response coupled with telomere dysfunction and replication stress in glioma stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 471:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.01.176
Azzalin CM, Reichenbach P, Khoriauli L et al (2007) Telomeric repeat-containing RNA and RNA surveillance factors at mammalian chromosome ends. Science 80(318):798–801. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1147182
Chawla R, Azzalin CM (2009) The telomeric transcriptome and SMG proteins at the crossroads. Cytogenet Genome Res 122:194–201
Sampl S, Pramhas S, Stern C et al (2012) Expression of telomeres in astrocytoma WHO grade 2 to 4: TERRA level correlates with telomere length, telomerase activity, and advanced clinical grade. Transl Oncol 5:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1593/tlo.11202
Brumbaugh KM, Otterness DM, Geisen C et al (2004) The mRNA surveillance protein hSMG-1 functions in genotoxic stress response pathways in mammalian cells. Mol Cell 14:585–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2004.05.005
Chen J, Crutchley J, Zhang D et al (2017) Identification of a DNA damage–induced alternative splicing pathway that regulates p53 and cellular senescence markers. Cancer Discov 7:766–781. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0908
Bhardwaj A, Yang Y, Ueberheide B, Smith S (2017) Whole proteome analysis of human tankyrase knockout cells reveals targets of tankyrase-mediated degradation. Nat Commun 8(1):2214. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02363-w
Nagy Z, Kalousi A, Furst A et al (2016) Tankyrases promote homologous recombination and check point activation in response to DSBs. PLoS Genet 12(2):e1005791. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005791
Acknowledgements
RK is thankful to the IIT Delhi internal grant for funding this study. OSV thanks the Ministry of Human Resource and Development (MHRD), Govt. of India for Senior Research Fellowship and European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO) for a Short-Term Fellowship. The authors also thank Miguel Jiménez for help with cell culture and the CNIO histopathology and confocal microscopy cores.
Funding
IIT Delhi Internal Research Grant, Senior Research Fellowship, EMBO Short term fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RK and MAB conceived the project. RK supervised the whole study. MAB hosted OSV for an EMBO fellowship and supervised the study pertaining to telomere research at CNIO, Spain. OSV and RK designed the experiments. OSV performed all the experiments. DK assisted in preparation of luciferase assay constructs. KW mentored OSV in performing experiments pertaining to telomere research at CNIO, Spain. RK and OSV wrote the manuscript. KW and MAB reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinchure, O.S., Whittemore, K., Kushwah, D. et al. miR-490 suppresses telomere maintenance program and associated hallmarks in glioblastoma. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 78, 2299–2314 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03644-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03644-2