Abstract
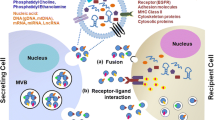
In multicellular organisms, effective communication between cells is a crucial part of cellular and tissue homeostasis. This communication mainly involves direct cell–cell contact as well as the secretion of molecules that bind to receptors at the recipient cells. However, a more recently characterized mode of intercellular communication—the release of membrane vesicles known as exosomes—has been the subject of increasing interest and intensive research over the past decade. Following the discovery of the exosome-mediated immune activation, the pathophysiological roles of exosomes have been recognized in different diseases, including cancer. In this review, we describe the biogenesis and main physical characteristics that define exosomes as a specific population of secreted vesicles, with a special focus on their role in oncogenic transformation and cancer progression.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trams EG, Lauter CJ, Salem N, Heine U (1981) Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 645:63–70
Harding C, Heuser J, Stahl P (1983) Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J Cell Biol 97:329–339
Pan BT, Teng K, Wu C, Adam M, Johnstone RM (1985) Electron microscopic evidence for externalization of the transferrin receptor in vesicular form in sheep reticulocytes. J Cell Biol 101:942–948
Johnstone RM, Adam M, Hammond JR, Orr L, Turbide C (1987) Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem 262:9412–9420
Vlassov AV, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R, Conrad R (2012) Exosomes: current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820:940–948. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.03.017
Rak J, Guha A (2012) Extracellular vesicles–vehicles that spread cancer genes. BioEssays 34:489–497. doi:10.1002/bies.201100169
Théry C, Zitvogel L, Amigorena S (2002) Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol 2:569–579. doi:10.1038/nri855
Robbins PD, Morelli AE (2014) Regulation of immune responses by extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Immunol 14:195–208. doi:10.1038/nri3622
Colombo M, Moita C, van Niel G, Kowal J, Vigneron J, Benaroch P, Manel N, Moita LF, Thery C, Raposo G (2013) Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J Cell Sci 126:5553–5565. doi:10.1242/jcs.128868
Trajkovic K, Hsu C, Chiantia S, Rajendran L, Wenzel D, Wieland F, Schwille P, Brugger B, Simons M (2008) Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 319:1244–1247. doi:10.1126/science.1153124
Théry C, Ostrowski M, Segura E (2009) Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol 9:581–593. doi:10.1038/nri2567
Ela S, Mager I, Breakefield XO, Wood MJ (2013) Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:347–357. doi:10.1038/nrd3978
Heijnen HF, Schiel AE, Fijnheer R, Geuze HJ, Sixma JJ (1999) Activated platelets release two types of membrane vesicles: microvesicles by surface shedding and exosomes derived from exocytosis of multivesicular bodies and alpha-granules. Blood 94:3791–3799
Stein JM, Luzio JP (1991) Ectocytosis caused by sublytic autologous complement attack on human neutrophils. The sorting of endogenous plasma-membrane proteins and lipids into shed vesicles. Biochem J 274:381–386 (Pt 2)
Cocucci E, Racchetti G, Meldolesi J (2009) Shedding microvesicles: artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol 19:43–51. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2008.11.003
Thery C, Boussac M, Veron P, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Raposo G, Garin J, Amigorena S (2001) Proteomic analysis of dendritic cell-derived exosomes: a secreted subcellular compartment distinct from apoptotic vesicles. J Immunol 166:7309–7318
Azmi AS, Bao B, Sarkar FH (2013) Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and drug resistance: a comprehensive review. Cancer Metastasis Rev 32:623–642. doi:10.1007/s10555-013-9441-9
Segura E, Amigorena S, Thery C (2005) Mature dendritic cells secrete exosomes with strong ability to induce antigen-specific effector immune responses. Blood Cells Mol Dis 35:89–93. doi:10.1016/j.bcmd.2005.05.003
Yuyama K, Sun H, Mitsutake S, Igarashi Y (2012) Sphingolipid-modulated exosome secretion promotes clearance of amyloid-beta by microglia. J Biol Chem 287:10977–10989. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.324616
Subra C, Laulagnier K, Perret B, Record M (2007) Exosome lipidomics unravels lipid sorting at the level of multivesicular bodies. Biochimie 89:205–212. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2006.10.014
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO (2007) Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol 9:654–659. doi:10.1038/ncb1596
Abd Elmageed ZY, Yang Y, Thomas R, Ranjan M, Mondal D, Moroz K, Fang Z, Rezk BM, Moparty K, Sikka SC, Sartor O, Abdel-Mageed AB (2014) Neoplastic reprogramming of patient-derived adipose stem cells by prostate cancer cell-associated exosomes. Stem Cells 32:983–997. doi:10.1002/stem.1619
Morelli AE, Larregina AT, Shufesky WJ, Sullivan ML, Stolz DB, Papworth GD, Zahorchak AF, Logar AJ, Wang Z, Watkins SC, Falo LD Jr, Thomson AW (2004) Endocytosis, intracellular sorting, and processing of exosomes by dendritic cells. Blood 104:3257–3266. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-03-0824
Johnstone RM, Mathew A, Mason AB, Teng K (1991) Exosome formation during maturation of mammalian and avian reticulocytes: evidence that exosome release is a major route for externalization of obsolete membrane proteins. J Cell Physiol 147:27–36. doi:10.1002/jcp.1041470105
Al-Nedawi K, Szemraj J, Cierniewski CS (2005) Mast cell-derived exosomes activate endothelial cells to secrete plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:1744–1749. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000172007.86541.76
Janowska-Wieczorek A, Wysoczynski M, Kijowski J, Marquez-Curtis L, Machalinski B, Ratajczak J, Ratajczak MZ (2005) Microvesicles derived from activated platelets induce metastasis and angiogenesis in lung cancer. Int J Cancer 113:752–760. doi:10.1002/ijc.20657
Kriebel PW, Barr VA, Rericha EC, Zhang G, Parent CA (2008) Collective cell migration requires vesicular trafficking for chemoattractant delivery at the trailing edge. J Cell Biol 183:949–961. doi:10.1083/jcb.200808105
Camussi G, Deregibus MC, Bruno S, Grange C, Fonsato V, Tetta C (2011) Exosome/microvesicle-mediated epigenetic reprogramming of cells. Am J Cancer Res 1:98–110
Jang YY, Collector MI, Baylin SB, Diehl AM, Sharkis SJ (2004) Hematopoietic stem cells convert into liver cells within days without fusion. Nat Cell Biol 6:532–539. doi:10.1038/ncb1132
Ratajczak J, Miekus K, Kucia M, Zhang J, Reca R, Dvorak P, Ratajczak MZ (2006) Embryonic stem cell-derived microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors: evidence for horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery. Leukemia 20:847–856. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2404132
Bhatnagar S, Schorey JS (2007) Exosomes released from infected macrophages contain Mycobacterium avium glycopeptidolipids and are proinflammatory. J Biol Chem 282:25779–25789. doi:10.1074/jbc.M702277200
Bhatnagar S, Shinagawa K, Castellino FJ, Schorey JS (2007) Exosomes released from macrophages infected with intracellular pathogens stimulate a proinflammatory response in vitro and in vivo. Blood 110:3234–3244. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-03-079152
McDonald MK, Tian Y, Qureshi RA, Gormley M, Ertel A, Gao R, Aradillas Lopez E, Alexander GM, Sacan A, Fortina P, Ajit SK (2014) Functional significance of macrophage-derived exosomes in inflammation and pain. Pain. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2014.04.029
van Balkom BW, de Jong OG, Smits M, Brummelman J, den Ouden K, de Bree PM, van Eijndhoven MA, Pegtel DM, Stoorvogel W, Wurdinger T, Verhaar MC (2013) Endothelial cells require miR-214 to secrete exosomes that suppress senescence and induce angiogenesis in human and mouse endothelial cells. Blood 121:3997–4006. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-02-478925
Cheng CF, Fan J, Fedesco M, Guan S, Li Y, Bandyopadhyay B, Bright AM, Yerushalmi D, Liang M, Chen M, Han YP, Woodley DT, Li W (2008) Transforming growth factor alpha (TGFalpha)-stimulated secretion of HSP90alpha: using the receptor LRP-1/CD91 to promote human skin cell migration against a TGFbeta-rich environment during wound healing. Mol Cell Biol 28:3344–3358. doi:10.1128/MCB.01287-07
Blanchard N, Lankar D, Faure F, Regnault A, Dumont C, Raposo G, Hivroz C (2002) TCR activation of human T cells induces the production of exosomes bearing the TCR/CD3/zeta complex. J Immunol 168:3235–3241
Lachenal G, Pernet-Gallay K, Chivet M, Hemming FJ, Belly A, Bodon G, Blot B, Haase G, Goldberg Y, Sadoul R (2011) Release of exosomes from differentiated neurons and its regulation by synaptic glutamatergic activity. Mol Cell Neurosci 46:409–418. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2010.11.004
van Niel G, Raposo G, Candalh C, Boussac M, Hershberg R, Cerf-Bensussan N, Heyman M (2001) Intestinal epithelial cells secrete exosome-like vesicles. Gastroenterology 121:337–349
Quail DF, Joyce JA (2013) Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med 19:1423–1437. doi:10.1038/nm.3394
Kahlert C, Kalluri R (2013) Exosomes in tumor microenvironment influence cancer progression and metastasis. J Mol Med (Berl) 91:431–437. doi:10.1007/s00109-013-1020-6
Yao D, Dai C, Peng S (2011) Mechanism of the mesenchymal-epithelial transition and its relationship with metastatic tumor formation. Mol Cancer Res 9:1608–1620. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0568
Cho JA, Park H, Lim EH, Kim KH, Choi JS, Lee JH, Shin JW, Lee KW (2011) Exosomes from ovarian cancer cells induce adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells to acquire the physical and functional characteristics of tumor-supporting myofibroblasts. Gynecol Oncol 123:379–386. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.08.005
Cho JA, Park H, Lim EH, Lee KW (2012) Exosomes from breast cancer cells can convert adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells into myofibroblast-like cells. Int J Oncol 40:130–138. doi:10.3892/ijo.2011.1193
Garnier D, Magnus N, Lee TH, Bentley V, Meehan B, Milsom C, Montermini L, Kislinger T, Rak J (2012) Cancer cells induced to express mesenchymal phenotype release exosome-like extracellular vesicles carrying tissue factor. J Biol Chem 287:43565–43572. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.401760
Roccaro AM, Sacco A, Maiso P, Azab AK, Tai YT, Reagan M, Azab F, Flores LM, Campigotto F, Weller E, Anderson KC, Scadden DT, Ghobrial IM (2013) BM mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes facilitate multiple myeloma progression. J Clin Invest 123:1542–1555. doi:10.1172/JCI66517
Al-Nedawi K, Meehan B, Micallef J, Lhotak V, May L, Guha A, Rak J (2008) Intercellular transfer of the oncogenic receptor EGFRvIII by microvesicles derived from tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol 10:619–624. doi:10.1038/ncb1725
Demory Beckler M, Higginbotham JN, Franklin JL, Ham AJ, Halvey PJ, Imasuen IE, Whitwell C, Li M, Liebler DC, Coffey RJ (2013) Proteomic analysis of exosomes from mutant KRAS colon cancer cells identifies intercellular transfer of mutant KRAS. Mol Cell Proteomics 12:343–355. doi:10.1074/mcp.M112.022806
Webber J, Steadman R, Mason MD, Tabi Z, Clayton A (2010) Cancer exosomes trigger fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation. Cancer Res 70:9621–9630. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1722
Skog J, Wurdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M, Curry WT Jr, Carter BS, Krichevsky AM, Breakefield XO (2008) Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol 10:1470–1476. doi:10.1038/ncb1800
Fabbri M, Paone A, Calore F, Galli R, Gaudio E, Santhanam R, Lovat F, Fadda P, Mao C, Nuovo GJ, Zanesi N, Crawford M, Ozer GH, Wernicke D, Alder H, Caligiuri MA, Nana-Sinkam P, Perrotti D, Croce CM (2012) MicroRNAs bind to Toll-like receptors to induce prometastatic inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:E2110–E2116. doi:10.1073/pnas.1209414109
Casazza A, Di Conza G, Wenes M, Finisguerra V, Deschoemaeker S, Mazzone M (2014) Tumor stroma: a complexity dictated by the hypoxic tumor microenvironment. Oncogene 33:1743–1754. doi:10.1038/onc.2013.121
Bao B, Azmi AS, Ali S, Ahmad A, Li Y, Banerjee S, Kong D, Sarkar FH (2012) The biological kinship of hypoxia with CSC and EMT and their relationship with deregulated expression of miRNAs and tumor aggressiveness. Biochim Biophys Acta 1826:272–296. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.04.008
Park JE, Tan HS, Datta A, Lai RC, Zhang H, Meng W, Lim SK, Sze SK (2010) Hypoxic tumor cell modulates its microenvironment to enhance angiogenic and metastatic potential by secretion of proteins and exosomes. Mol Cell Proteomics 9:1085–1099. doi:10.1074/mcp.M900381-MCP200
King HW, Michael MZ, Gleadle JM (2012) Hypoxic enhancement of exosome release by breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 12:421. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-12-421
Kucharzewska P, Christianson HC, Welch JE, Svensson KJ, Fredlund E, Ringner M, Morgelin M, Bourseau-Guilmain E, Bengzon J, Belting M (2013) Exosomes reflect the hypoxic status of glioma cells and mediate hypoxia-dependent activation of vascular cells during tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:7312–7317. doi:10.1073/pnas.1220998110
Svensson KJ, Kucharzewska P, Christianson HC, Skold S, Lofstedt T, Johansson MC, Morgelin M, Bengzon J, Ruf W, Belting M (2011) Hypoxia triggers a proangiogenic pathway involving cancer cell microvesicles and PAR-2-mediated heparin-binding EGF signaling in endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:13147–13152. doi:10.1073/pnas.1104261108
Ramteke A, Ting H, Agarwal C, Mateen S, Somasagara R, Hussain A, Graner M, Frederick B, Agarwal R, Deep G (2013) Exosomes secreted under hypoxia enhance invasiveness and stemness of prostate cancer cells by targeting adherens junction molecules. Mol Carcinog. doi:10.1002/mc.22124
Nguyen DX, Bos PD, Massague J (2009) Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat Rev Cancer 9:274–284. doi:10.1038/nrc2622
Rana S, Malinowska K, Zoller M (2013) Exosomal tumor microRNA modulates premetastatic organ cells. Neoplasia 15:281–295
Peinado H, Aleckovic M, Lavotshkin S, Matei I, Costa-Silva B, Moreno-Bueno G, Hergueta-Redondo M, Williams C, Garcia-Santos G, Ghajar C, Nitadori-Hoshino A, Hoffman C, Badal K, Garcia BA, Callahan MK, Yuan J, Martins VR, Skog J, Kaplan RN, Brady MS, Wolchok JD, Chapman PB, Kang Y, Bromberg J, Lyden D (2012) Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat Med 18:883–891. doi:10.1038/nm.2753
Hood JL, San RS, Wickline SA (2011) Exosomes released by melanoma cells prepare sentinel lymph nodes for tumor metastasis. Cancer Res 71:3792–3801. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4455
Sidhu SS, Mengistab AT, Tauscher AN, LaVail J, Basbaum C (2004) The microvesicle as a vehicle for EMMPRIN in tumor-stromal interactions. Oncogene 23:956–963. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207070
Yang M, Chen J, Su F, Yu B, Su F, Lin L, Liu Y, Huang JD, Song E (2011) Microvesicles secreted by macrophages shuttle invasion-potentiating microRNAs into breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer 10:117. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-10-117
Luga V, Wrana JL (2013) Tumor-stroma interaction: revealing fibroblast-secreted exosomes as potent regulators of Wnt-planar cell polarity signaling in cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 73:6843–6847. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1791
Luga V, Zhang L, Viloria-Petit AM, Ogunjimi AA, Inanlou MR, Chiu E, Buchanan M, Hosein AN, Basik M, Wrana JL (2012) Exosomes mediate stromal mobilization of autocrine Wnt-PCP signaling in breast cancer cell migration. Cell 151:1542–1556. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.024
Wolfers J, Lozier A, Raposo G, Regnault A, Thery C, Masurier C, Flament C, Pouzieux S, Faure F, Tursz T, Angevin E, Amigorena S, Zitvogel L (2001) Tumor-derived exosomes are a source of shared tumor rejection antigens for CTL cross-priming. Nat Med 7:297–303. doi:10.1038/85438
Andre F, Schartz NE, Movassagh M, Flament C, Pautier P, Morice P, Pomel C, Lhomme C, Escudier B, Le Chevalier T, Tursz T, Amigorena S, Raposo G, Angevin E, Zitvogel L (2002) Malignant effusions and immunogenic tumour-derived exosomes. Lancet 360:295–305. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)09552-1
Andreola G, Rivoltini L, Castelli C, Huber V, Perego P, Deho P, Squarcina P, Accornero P, Lozupone F, Lugini L, Stringaro A, Molinari A, Arancia G, Gentile M, Parmiani G, Fais S (2002) Induction of lymphocyte apoptosis by tumor cell secretion of FasL-bearing microvesicles. J Exp Med 195:1303–1316
Huber V, Fais S, Iero M, Lugini L, Canese P, Squarcina P, Zaccheddu A, Colone M, Arancia G, Gentile M, Seregni E, Valenti R, Ballabio G, Belli F, Leo E, Parmiani G, Rivoltini L (2005) Human colorectal cancer cells induce T-cell death through release of proapoptotic microvesicles: role in immune escape. Gastroenterology 128:1796–1804
Klibi J, Niki T, Riedel A, Pioche-Durieu C, Souquere S, Rubinstein E, Le Moulec S, Guigay J, Hirashima M, Guemira F, Adhikary D, Mautner J, Busson P (2009) Blood diffusion and Th1-suppressive effects of galectin-9-containing exosomes released by Epstein-Barr virus-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Blood 113:1957–1966. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-02-142596
Valenti R, Huber V, Iero M, Filipazzi P, Parmiani G, Rivoltini L (2007) Tumor-released microvesicles as vehicles of immunosuppression. Cancer Res 67:2912–2915. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0520
Xiang X, Poliakov A, Liu C, Liu Y, Deng ZB, Wang J, Cheng Z, Shah SV, Wang GJ, Zhang L, Grizzle WE, Mobley J, Zhang HG (2009) Induction of myeloid-derived suppressor cells by tumor exosomes. Int J Cancer 124:2621–2633. doi:10.1002/ijc.24249
Chalmin F, Ladoire S, Mignot G, Vincent J, Bruchard M, Remy-Martin JP, Boireau W, Rouleau A, Simon B, Lanneau D, De Thonel A, Multhoff G, Hamman A, Martin F, Chauffert B, Solary E, Zitvogel L, Garrido C, Ryffel B, Borg C, Apetoh L, Rebe C, Ghiringhelli F (2010) Membrane-associated Hsp72 from tumor-derived exosomes mediates STAT3-dependent immunosuppressive function of mouse and human myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Clin Invest 120:457–471. doi:10.1172/JCI40483
Valenti R, Huber V, Filipazzi P, Pilla L, Sovena G, Villa A, Corbelli A, Fais S, Parmiani G, Rivoltini L (2006) Human tumor-released microvesicles promote the differentiation of myeloid cells with transforming growth factor-beta-mediated suppressive activity on T lymphocytes. Cancer Res 66:9290–9298. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1819
Xiang X, Liu Y, Zhuang X, Zhang S, Michalek S, Taylor DD, Grizzle W, Zhang HG (2010) TLR2-mediated expansion of MDSCs is dependent on the source of tumor exosomes. Am J Pathol 177:1606–1610. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.100245
Wieckowski EU, Visus C, Szajnik M, Szczepanski MJ, Storkus WJ, Whiteside TL (2009) Tumor-derived microvesicles promote regulatory T cell expansion and induce apoptosis in tumor-reactive activated CD8 + T lymphocytes. J Immunol 183:3720–3730. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0900970
Kim JW, Wieckowski E, Taylor DD, Reichert TE, Watkins S, Whiteside TL (2005) Fas ligand-positive membranous vesicles isolated from sera of patients with oral cancer induce apoptosis of activated T lymphocytes. Clin Cancer Res 11:1010–1020
Clayton A, Mitchell JP, Court J, Mason MD, Tabi Z (2007) Human tumor-derived exosomes selectively impair lymphocyte responses to interleukin-2. Cancer Res 67:7458–7466. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3456
Cai Z, Yang F, Yu L, Yu Z, Jiang L, Wang Q, Yang Y, Wang L, Cao X, Wang J (2012) Activated T cell exosomes promote tumor invasion via Fas signaling pathway. J Immunol 188:5954–5961. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1103466
Yu S, Liu C, Su K, Wang J, Liu Y, Zhang L, Li C, Cong Y, Kimberly R, Grizzle WE, Falkson C, Zhang HG (2007) Tumor exosomes inhibit differentiation of bone marrow dendritic cells. J Immunol 178:6867–6875
Wendler F, Bota-Rabassedas N, Franch-Marro X (2013) Cancer becomes wasteful: emerging roles of exosomes in cell-fate determination. J Extracell Vesicles 2:24. doi:10.3402/jev.v2i0.22390
Gross JC, Chaudhary V, Bartscherer K, Boutros M (2012) Active Wnt proteins are secreted on exosomes. Nat Cell Biol 14:1036–1045. doi:10.1038/ncb2574
Chairoungdua A, Smith DL, Pochard P, Hull M, Caplan MJ (2010) Exosome release of beta-catenin: a novel mechanism that antagonizes Wnt signaling. J Cell Biol 190:1079–1091. doi:10.1083/jcb.201002049
Yu X, Harris SL, Levine AJ (2006) The regulation of exosome secretion: a novel function of the p53 protein. Cancer Res 66:4795–4801. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4579
Lespagnol A, Duflaut D, Beekman C, Blanc L, Fiucci G, Marine JC, Vidal M, Amson R, Telerman A (2008) Exosome secretion, including the DNA damage-induced p53-dependent secretory pathway, is severely compromised in TSAP6/Steap3-null mice. Cell Death Differ 15:1723–1733. doi:10.1038/cdd.2008.104
Yu X, Riley T, Levine AJ (2009) The regulation of the endosomal compartment by p53 the tumor suppressor gene. FEBS J 276:2201–2212. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.06949.x
Hupalowska A, Miaczynska M (2012) The new faces of endocytosis in signaling. Traffic 13:9–18. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01249.x
Wrighton KH (2011) Tumour suppressors: role of nuclear PTEN revealed. Nat Rev Cancer 11:154. doi:10.1038/nrc3028
Putz U, Howitt J, Doan A, Goh CP, Low LH, Silke J, Tan SS (2012) The tumor suppressor PTEN is exported in exosomes and has phosphatase activity in recipient cells. Sci Signal 5:ra70. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2003084
Beloribi S, Ristorcelli E, Breuzard G, Silvy F, Bertrand-Michel J, Beraud E, Verine A, Lombardo D (2012) Exosomal lipids impact notch signaling and induce death of human pancreatic tumoral SOJ-6 cells. PLoS ONE 7:e47480. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0047480
Sharghi-Namini S, Tan E, Ong LL, Ge R, Asada HH (2014) Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction in a 3D microenvironment. Sci Rep 4:4031. doi:10.1038/srep04031
Ristorcelli E, Beraud E, Mathieu S, Lombardo D, Verine A (2009) Essential role of Notch signaling in apoptosis of human pancreatic tumoral cells mediated by exosomal nanoparticles. Int J Cancer 125:1016–1026. doi:10.1002/ijc.24375
Al-Nedawi K, Meehan B, Kerbel RS, Allison AC, Rak J (2009) Endothelial expression of autocrine VEGF upon the uptake of tumor-derived microvesicles containing oncogenic EGFR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:3794–3799. doi:10.1073/pnas.0804543106
Tesselaar ME, Romijn FP, Van Der Linden IK, Prins FA, Bertina RM, Osanto S (2007) Microparticle-associated tissue factor activity: a link between cancer and thrombosis? J Thromb Haemost 5:520–527. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02369.x
Yang C, Robbins PD (2011) The roles of tumor-derived exosomes in cancer pathogenesis. Clin Dev Immunol 2011:1–11. doi:10.1155/2011/842849
Corcoran C, Rani S, O’Brien K, O’Neill A, Prencipe M, Sheikh R, Webb G, McDermott R, Watson W, Crown J, O’Driscoll L (2012) Docetaxel-resistance in prostate cancer: evaluating associated phenotypic changes and potential for resistance transfer via exosomes. PLoS ONE 7:e50999. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saleem, S.N., Abdel-Mageed, A.B. Tumor-derived exosomes in oncogenic reprogramming and cancer progression. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 72, 1–10 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1710-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1710-4