Abstract.
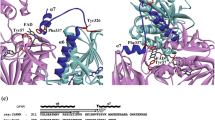
l-Xylulose reductase (XR) is involved in water re-absorption and cellular osmoregulation. The crystal structure of human XR complemented with site-directed mutagenesis (Cys138Ala) indicated that the disulfide bond in the active site between Cys138 and Cys150 is unstable and may affect the reactivity of the enzyme. The effects of reducing agents on the activities of the wild-type and mutant enzymes indicated the reversibility of disulfide-bond formation, which resulted in three-fold decrease in catalytic efficiency. Furthermore, the addition of cysteine (>2 mM) inactivated human XR and was accompanied by a 10-fold decrease in catalytic efficiency. TOF-MS analysis of the inactivated enzyme showed the S-cysteinylation of Cys138 in the wild-type and Cys150 in the mutant enzymes. Thus, the action of human XR may be regulated by cellular redox conditions through reversible disulfide-bond formation and by S-cysteinylation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 25 January 2009; received after revision 12 February 2009; accepted 16 February 2009
H.-T. Zhao, S. Endo: These two authors contribute equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, HT., Endo, S., Ishikura, S. et al. Structure/function analysis of a critical disulfide bond in the active site of l-xylulose reductase. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 1570–1579 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-9065-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-9065-y