Abstract
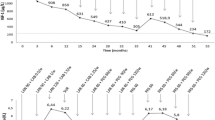
In this case report we demonstrated that treatment with the long-acting D2 receptor agonist cabergoline for 1 year induced normalization of plasma ACTH levels and disappearance of the pituitary tumor in a patient with Nelson’s syndrome. A young man underwent bilateral adrenalectomy and subsequent pituitary irradiation for Cushing’s disease after unsuccessful neurosurgical treatment. Thereafter, he was given cortisone acetate replacement at the dose of 62.5 mg a day. Fifteen months after pituitary irradiation, he developed Nelson’s syndrome, having skin hyperpigmentation, high plasma ACTH levels (376 ng/l) and a pituitary microadenoma (5 mm) documented at magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the pituitary region. After 6 months of cabergoline treatment, given at the dose of 1 mg a week, plasma ACTH levels were significantly decreased (from 376 to 113 ng/l) but they were not normalized. Cabergoline dose was then increased up to 2 mg a week. Six months later plasma ACTH levels were normalized (22 ng/I) and MRI demonstrated the disappearance of the pituitary adenoma. In order to investigate on the direct effect played by cabergoline treatment on the remission of Nelson’s syndrome, the treatment was withdrawn. Plasma ACTH levels significantly increased (119 ng/I) after 3 months of treatment withdrawal. At the last follow- up, during cabergoline treatment at the dose of 2 mg/week plasma ACTH levels were normalized (40.4 ng/I). This case demonstrated that cabergoline treatment is able to induce the remission of Nelson’s syndrome and may be a valid therapeutic alternative in this syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nelson D.H., Meakin J.W., Dealy J.B., Matson D.D., Emerson K., Thorn G.W. ACTH producing tumor of the pituitary gland. N. Engl. J. Med. 1958, 259: 161–164.
Cohen K.L., Noth R.H., Pechinski T. Incidence of pituitary tumors following adrenalectomy: a long-term follow-up study of patients treated for Cushing’s disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1978, 138: 575–579.
Aron D.C., Findling J.W., Fitzgerald P.A., Forsham P.H., Wilson C.B., Tyrrel J.B. Cushing’s syndrome: problems in management. Endocr. Rev. 1982, 3: 229–244.
Kasperlik-Zaluska A.A., Nielubowics J., Wislawski J., Hartwig W., Zaluska J., Jeske W., Migdalska B. Nelson’s syndrome: incidence and prognosis. Clin. Endocrinol. 1983, 19: 693–698.
Miller J.W., Crapo L. The medical treatment of Cushing’s syndrome. Endocr. Rev. 1993, 14: 443–458.
Jones T.J., Gilman B., Beckford U. Effect of treatment with sodium valproate and diazepam on plasma corticotropin in Nelson’s syndrome. Lancet 1981, 1: 1179–1181.
Dornhorst A., Jenkins J.S., Lamberts S.W.J., Abraham R.R., Wynn V., Beckford U., Gillham B., Jones M.T. The evaluation of sodium valproate in the treatment of Nelson’s syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1983, 56: 985–991.
Loli P., Berselli M.E., Vignati F., De Grandi C., Tagliaferri M. Size reduction of an ACTH-secreting pituitary macroadenoma in Nelson’s syndrome by sodium valporate: effect of withdrawal and re-institution of treatment. Acta Endocrinol. 1988, 119: 435–442.
Mercado-Asis L.B., Yanovski J.A., Tracer H.L., Chik C.L., Cutler G.B. Acute effect of bromocriptine, cyproheptadine and valproic acid on plasma adrenocorticotropin secretion in Nelson’s syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82: 514–517.
Krieger D.T. Lack of responsiveness to L-Dopa in Cushing’s disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1973, 36: 277–284.
Whitehead H.M., Beacom R., Sheridan B., Atkinson A.B. The effect of cyproheptadine and/or bromocriptine on plasma ACTH levels in patients cured of Cushing’s disease by bilateral adrenalectomy. Clin. Endocrinol. 1990, 32: 193–201.
Lamberts S.W.J., Birkenhager J.C. Bromocriptine in Nelson’s syndrome and Cushing’s disease. Lancet 1976, 2: 811.
Lamberts S.W.J., Klijn J.G.M., De Quijada M., Timmermans H.A.T., Uitterlinden P., De Jong F.H., Birkenhager J.C. The mechanism of the suppressive action of bromocriptine on adrenocorticotropin secretion in patients with Cushing’s disease and Nelson’s syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1980, 51: 307–311.
Webster J., Piscitelli G., Polli A., Ferrari C., Ismail I., ScanIon M.F., for the Cabergoline Comparative Study Group. A comparison of cabergoline and bromocriptine on plasma ACTH levels in patients cured of Cushing’s disease by bilateral adrenalectomy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 331: 904–909.
Ferrari C., Barbieri C., Caldara R. Long-Iasting prolactin lowering effect of cabergoline, a new dopamine-agonist, in hyperprolactinemic patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1986, 63: 941–945.
Pascal-Vigneron V., Weryha G., Bose M., Leclerc J. Hyperprolactinemic amenorrhea: treatment with cabergoline versus bromocriptine. Presse Med. 1995, 24: 753–759.
Colao A., Di Sarno A., Sarnacchiaro F., Ferone D., Di Renzo G., Merola B., Annunziato L., Lombardi G. Prolactinomas resistant to standard dopamine-agonists respond to chronic cabergoline treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82: 876–883.
Colao A., Di Sarno A., Landi M.L., Cirillo S., Sarnacchiaro F., Facciolli G., Pivonello R., Cataldi M., Merola B., Annunziato L., Lombardi G. Long term and low-dose treatment with cabergoline induces macroprolactinoma shrinkage. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82: 3574–3579.
Oldfield E.H., Doppman J.L., Nieman L.K., Chrousos G.P., Miller D.L., Kats D.A., Cutler G.B., Loriaux D.L. Petrosal sinus sampling with and without corticotropin-releasing hormone for the differential diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325: 897–905.
Jones M.T., Hillhouse E.W., Burden J. Effect of various putative neurotrasmitters on the secretion of corticotrophin-releasing hormone from the rat hypothalamus in vitro: a model of neurotrasmitters involved. J. Endocrinol. 1976, 69: 1–10.
Lamberts S.W.J., De Lange S.A., Stefanko S.Z. Adrenocorticotropin-secreting pituitary adenomas originate from the anterior or intermediate lobe in Cushing’s disease: differences in the regulation of hormone secretion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1982, 54: 286–291.
McNicol M., Teasdale G.M., Beastall G.H. A study of corticotroph adenomas in Cushing’s disease: no evidence of intermediate lobe origin. Clin. Endocrinol. 1986, 24: 715–722.
Strolin-Benedetti M., Dostert P., Barone D., Efthymiopoulos C., Peretti G., Roncucci R. In vivo interactions of cabergoline with rat brain dopamine receptors labelled with (3H)N-n-propyInorapomorphine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1976, 187: 399–408.
Atkinsons A.B., Chestnutt A., Crothers E., Woods R., Weaver J.A., Kennedy L., Sheridan B. Cyclical Cushing’s disease: two distinct rhythms in a patient with a basophil adenoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1985, 60: 328–332.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pivonello, R., Faggiano, A., Di Salle, F. et al. Complete remission of Nelson’s syndrome after 1-year treatment with cabergoline. J Endocrinol Invest 22, 860–865 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03343660
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03343660