Summary
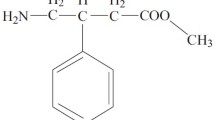
The pharmacokinetics of mofebutazone was investigated in man after oral administration of [4-14C] mofebutazone in suspension form (7 mg/kg body weight). The blood concentration / time course was found to fit a two compartment open model with first order absorption (ka=10.1 h−1) where elimination (kel=0.304 h−1) occurs only from compartment 1. The maximum concentration was reached after 0.3 h in compartment 1 and after 2 h in compartment 2. Mofebutazone was found to be excreted almost exclusively via the kidney; 97% of the administered dose was found in urine already at 72 h. Excretion takes place very rapidly; 24% of the dose was excreted in 1.5 h and 45% in 3 h. 92% of the mofebutazone excreted was the conjugated form. Two glucuronides were detected in the 24 h urine; one of these seemed to be identical to a glucuronide fractionated from the urine of rat. The renal clearance of mofebutazone in man was found to be 3.38 1/h. The almost complete recovery of mofebutazone in the urine indicates that after oral administration, this drug has a very high bioavailability via the oral route.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krohs W. (1965): Pyrazole Derivatives in ‘Analgetics’, edited by G. deStevens, Academic Press, New York, pp. 331–403.
Larsen V., Dredahl E. (1966): The embryotoxic effect on rabbits of monophenyl butazone (Monazan) compared with phenylbutazone and thalidomide. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol.,24, 443–455.
Thune S. (1967): Comparison of phenyl- and monophenylbutazone (Mobutazon), especially in respect to the incidence of side effects. A double blind study. Acta Rheumatolog. Scand.,13, 63–80.
Woodbury J.F.L., Turner W.A., Tiongson R. (1969): Rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of treatment with monophenylbutazone and phenylbutazone. Can. Med. Assoc. J.101, 801–803.
Scarselli V. (1959): Tossicita e cinetica dell eliminazione del 2-fenil, 3,5-diossi, 4-n-butil, pirazolidina comparativamente a quelle del 1,2-difenil-derivato. II Farmaco, Ed. Sci.,14, 347–351.
Holmen-Christensen H. (1967): Identification and UV spectrophotometric determination of phenylbutazone analogues from thinlayer chromatograms, in ‘Scientiae Pharmaceuticae’ Vol. II (Proceedings of the 25th Congress of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Prague, 1965), edited by O. Hanc and J. Hubik. Butterworths, London, pp. 152–160.
Bass V.-M., Mrongovius R.I. and Schulte K.E. (1980): Disposition of 4-14C mofebutazone in the rat. Eur. J. Drug Metabol. Pharmacok.5, 201–206.
Mrongovius, R., Bass V.-M., and Schulte K.E. (1982): Anti-inflamtory activity and disposition in the rat of mofebutazone and two degradation products. Eur. J. Med. Chem.17, 275–279.
Miller J.P. (1971): Health Hazards of Radioactive Pharmaceuticals, in International Encyclopedia of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Ed.: Peters G., Section 78, Radionucleotides in Pharmacology, Section Ed.: Y. Cohen, Vol. II, pp. 883–901.
Wagner J.G. (1975): Fundamentals of Clinical Pharmacokinetics, pp. 102–106, the Hamilton Press, Inc., Hamilton, Illinois.
Dieterle W., Faigle J.W., Früh F., Mory H., Theobald W., Alt K.O., and W. Richter (1976): Metabolism of phenylbutazone in man. Arzneim.-Forsch.26, 572–577.
Leber H.W., Härders A., and Schütterle G. (1972): Untersuchungen zum Einfluss der Urämie auf die Metabolisierung von Phenylbutazon und Aminophenazon beim Menschen. Klin. Wschr.50, 1092–1096.
Rowland M., and Riegelman S. (1968): Pharmacokinetics of acetylsalicylic acid after intraveneous administration to rats. J. Pharm. Sci.57, 1313–1319.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kassem, M.A., Schulte, K.E. Pharmacokinetics of [4-14C] Mofebutazone after oral administration in man. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 9, 223–227 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189645
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189645