Abstract
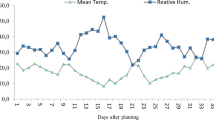
Three different treatments by calcium (102M), namely seed treatment, foliar spraying and their combination were applied on field-grown rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. Ratna) under both water stressed and non-stressed conditions in the course of plant development. The relative water content and leaf water potential decreased with increase in age of stressed and non-stressed plants. Pretreatment of seeds with Ca improved the water status of the plants most prominently at the vegetative stage but the effect gradually faded away with plant development. The foliar spraying by Ca was more effective in improving the water status of the plants at the reproductive stage. The combined Ca treatment significantly improved water status of the plants both at the vegetative and reproductive stages. The contents of chlorophyll and protein decreased and the activities of protease and RNase increased in the course of plant development in both non-stressed and even more in stressed plants. Ca treatments of seeds or plants or their combination inhibited the decline in chlorophyll and protein contents and the rising trends of protease and RNase activities, the combined treatment being most effective. During plant development free proline content increased significantly more in water stressed plants. In non-stressed plants there was a marked increase in the free proline content at the mature fruit stage. Ca treatment inhibited the rise of free proline in stressed plants. A significant reduction in yield components and yield of the crop in water stressed plants was increased by Ca treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnon, D. I.: Copper enzyme in isolated chloroplast. Polyphenoloxidase inBeta vulgaris. - Plant Physiol.24: 1–15, 1949.
Bates, L. S., Waldenz, R. P., Teaee, I. D.: Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. - Plant Soil39: 205–207, 1973.
Biswas, A. K., Choudhuri, M. A.: Mechanism of monocarpic senescence in rice. - Plant Physiol.65 : 340–345, 1980.
Chokwang, Y. I., Todd, W.: Changes in ribonuclease activity of wheat plants during water stress. - Physiol. Plant.46: 13–18, 1979.
Dwivedi, S., Kar, M., Mishra, D.: Biochemical changes in excised leaves ofOryza sativa subjected to water stress. - Physiol. Plant.45: 35–40, 1979.
Fick, N. G., Qualset, C. O.: Genetic control of endosperm amylase activity and gibberellin responses in standard height and short statured wheat. - Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA72: 892–895, 1975.
Fisher, R. A., Yates, F.: Statistical Tables for Biological, Agricultural and Medical Research. 6th Ed. -Longman Gr., London 1974.
Gates, C. T.: Water deficits and growth of herbaceous plants. - In:Kozlowski, T. T. (ed.): Water Deficits and Plant Growth. Vol. 2. Pp. 135–190. Academic Press, New York-London 1968.
Hanson, A. D., Nelsen, C. E., Everson, E. H.: Evaluation of proline accumulation as an index of drought resistance using two contrasting barley cultivars. - Crop Sci.17: 720–726, 1977.
Hsiao, T. C.: Plant response to water stress. - Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.24: 519–570, 1973.
Hsiao, T. C., Acevedo, E., Fereres, E.: Stress metabolism-water stress, growth and osmotic adjustment. - Phil. Trans. roy. Soc. Lond. B273: 479–500, 1976.
Knipling, E. B.: Measurement of leaf water potential by the dye method. - Ecology48: 1038 to 1041, 1967.
Levitt, J.: Responses of Plants to Environmental Stresses. - Academic Press, New York-London 1972.
Livne, A., Vaadia, Y.: Water deficits and hormone relations. - In:Kozlowski, T. T. (ed.): Water Deficits and Plant Growth. Vol. 3. Pp. 255–276. Academic Press, New York-London 1972.
Lowry, O., Rosebrough, N. J., Fare, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with Folin-phenol reagent. - J. biol. Chem.193: 265–275, 1951.
Mali, P. C., Mehta, S. L.: Effect of drought on enzymes and free proline in rice varieties. - Phytochemistry16: 1355–1358, 1977.
Mukherjee, S. P., Choudhuri, M. A.: Effect of water stress on some oxidative enzymes and senescence inVigna seedlings. - Physiol. Plant.51: 37–42, 1981.
Parija, P., Pillay, K. P.: Effect of presowing treatment on the drought resistance in rice. - Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. India15B: 6–14, 1945.
Poovaiah, B. W., Leopold, A. C.: Deferral of leaf senescence with calcium. - Plant Physiol.52: 235–239, 1973.
Ray, S., Choudhuri, M. A.: Mobilization of metabolites from leaves to grains as the cause of monocarpie senescence in rice plant. - Plant Physiol.68: 1345–1348, 1981.
Salim, M. H., Todd, G. W.: Seed soaking as a presowing, drought hardening treatment in wheat and barley seeds. -Agron. J.60: 179–182, 1968.
Snell, F. D., Snell, C. T.: Colorimetric Methods of Analysis. Vol. IV. - Van Nostrand Reinhold Co., New York 1971.
Stewart, C. R., Morris, C. J., Thompson, J. F.: Changes in amino acid content of excised leaves during incubation II. Roles of sugar in the accumulations of proline in wilted leaves. - Plant Physiol.41: 1585–1590, 1966.
Tully, R. E., Hanson, A. D., Nelsen, C. E.: Proline accumulation in water stress barley leaves in relation to translocation and nitrogen budget. - Plant Physiol.63: 518–523, 1979.
Weatherley, P. E.: Studies in the water relations of the cotton plant I. The field measurement of water deficit in leaves. -New Phytol.49: 81–97, 1950.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nayek, B., Biswas, A.K. & Choudhuri, M.A. Effect of calcium on water-stress-induced biochemical changes and yield of field-grown rice. Biol Plant 25, 117–123 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02902121
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02902121