Abstract
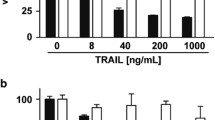
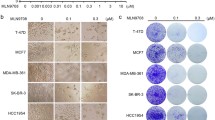
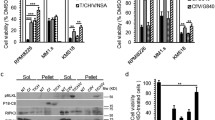
The synergistic interaction between proteasome inhibitors and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a promising approach to induce cell death in tumor cells. However, the molecular and biochemical mechanisms of this synergism have been proven to be cell type specific. We therefore focused our investigation on TRAIL-resistant colon carcinoma cells in this study. DNA fragmentation, mitochondrial membrane depolarization and increased caspase-3-like enzyme activity was exclusively induced only by combined treatment with proteasome inhibitors (epoxomicin, MG132, bortezomib/PS-341) and TRAIL. The expression level of anti-apoptotic proteins (XIAP, survivin, Bcl-2, Bcl-Xl), regulated by NF-κB transcription factor, was not effected by any of these treatments. TRAIL alone induced only partial activation of caspase-3 (p20), while the combination of TRAIL and proteasome inhibition led to the full proteolytic activation of caspase-3 (p17). Only the combination treatment induced marked membrane depolarization and the release of cytochrome c, HtrA2/Omi and Smac/DIABLO. Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) was not released in any of these conditions. These results are consistent with a model where the full activation of caspase-3 by caspase-8 is dependent on the release of Smac/DIABLO in response to the combined treatment. This molecular mechanism, independent of the inhibition NF-kB activity, may provide rationale for the combination treatment of colon carcinomas with proteasome inhibitors and recombinant TRAIL or agonistic antibody of TRAIL receptors. (Pathology Oncology Research Vol 12, No 3, 133–142)
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ac-DEVD-AMC:
-
Ac-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-7-amino-4-methyl-coumarin
- z-VAD-fmk:
-
benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp (OMe)-fluoromethylketone
- z-IETD-fmk:
-
benzyloxycarbonyl-Ile-Glu(OMe)-Thr-Asp (OMe)-fluoromethylketone
- MG132:
-
ben-zyloxycarbonyl-Leu-Leu-Leu-aldehyde
- AIF:
-
apoptosis-inducing factor
- IAP:
-
inhibitor of apoptosis protein
- XIAP:
-
X-linked IAP
- Epo:
-
epoxomicin
References
Chaudan D, Hideshima T, Mitsiades C, et al: Proteasome inhibitor therapy in multiple myeloma. Mol Cancer Ther 4:686–692, 2005
Kloetzel PM: The proteasome and MHC class I antigen processing. Biochim Biophys Acta 1695:225–233, 2004
Roos-Mattjus P, Sistonen L: The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Ann Med 36:285–295, 2004
Sun L, Chen ZJ: The novel functions of ubiquitination in signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16:119–126, 2004
Mani A, Gelmann EP: The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and its role in cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:4776–4789, 2005
Petak I, Vernes R, Szucs KS, et al: A caspase-8-independent component in TRAIL/Apo-2L-induced cell death in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Cell Death Differ 10:729–739, 2003
Petak I, Houghton JA: Shared pathways: death receptors and cytotoxic drugs in cancer therapy. Pathol Oncol Res 7:95–106, 2001
Petak I, Douglas L, Tillman DM, et al: Pediatric rhabdomyo-sarcoma cell lines are resistant to Fas-induced apoptosis and highly sensitive to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res 6:4119–4127, 2000
Zhang L, Fang B: Mechanisms of resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 12:228–237, 2005
Guseva NV, Taghiyev AF, Sturm MT, et al: Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated activation of mitochondria-associated nuclear factor-kappaB in prostatic carcinoma cell lines. Mol Cancer Res 2:574–584, 2004
Aggarwal BB, Bhardwaj U, Takada Y: Regulation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by ectopic expression of antiapoptotic factors. Vitam Horm 67:453–483, 2004
Yang LQ, Fang DC, Wang RQ, Yang SM: Effect of NF-kappaB, survivin, Bcl-2 and caspase3 on apoptosis of gastric cancer cells induced by tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis inducing ligand. World J Gastroenterol 10:22–25, 2004
Bortul R, Tazzari PL, Cappellini A, et al: Constitutively active Akt1 protects HL60 leukemia cells from TRAIL-induced apoptosis through a mechanism involving NF-kappaB activation and cFLIP(L) up-regulation. Leukemia 17:379–89, 2003
Ehrhardt H, Fulda S, Schmid I, et al: TRAIL induced survival and proliferation in cancer cells resistant towards TRAIL-induced apoptosis mediated by NF-kappaB. Oncogene 22:3842–3852, 2003
Franco AV, Zhang XD, Van Berkel E, et al: The role of NF-kappa B in TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis of melanoma cells. J Immunol 166:5337–5345, 2001
Jeremias I, Kupatt C, Baumann B, et al: Inhibition of nuclear factor kappaB activation attenuates apoptosis resistance in lymphoid cells. Blood 91:4624–4631, 1998
Johnson TR, Stone K, Nikrad M, et al: The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 overcomes TRAIL resistance in Bax and cas-pase 9-negative or Bcl-xL overexpressing cells. Oncogene 22:4953–4963, 2003
Zhu H, Guo W, Zhang L, et al: Proteasome inhibitors-mediated TRAIL resensitization and Bik accumulation. Cancer Biol Ther 4:781–786, 2005
Zhu H, Zhang L, Dong F, et al: Bik/NBK accumulation correlates with apoptosis-induction by bortezomib (PS-341, Velcade) and other proteasome inhibitors. Oncogene 24:4993–4999, 2005
Nikrad M, Johnson T, Puthalalath H, et al: The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib sensitizes cells to killing by death receptor ligand TRAIL via BH3-only proteins Bik and Bim. Mol Cancer Ther 4:443–449, 2005
Schneider P: Production of recombinant TRAIL and TRAIL receptor: Fc chimeric proteins. Methods Enzymol 322:325–3245, 2000
Leverkus M, Sprick MR, Wachter T, et al: Proteasome inhibition results in TRAIL sensitization of primary keratinocytes by removing the resistance-mediating block of effector caspase maturation. Mol Cell Biol 23:777–790, 2003
Chauhan D, Li G, Podar K, et al: Targeting mitochondria to overcome conventional and bortezomib/proteasome inhibitor PS-341 resistance in multiple myeloma (MM) cells. Blood 104:2458–2466, 2004
La Vallee TM, Zhan XH, Johnson MS, et al: 2-methoxyestradiol up-regulates death receptor 5 and induces apoptosis through activation of the extrinsic pathway. Cancer Res 63:468–475, 2003
Creagh EM, Murphy BM, Duriez PJ, et al: Smac/Diablo antagonizes ubiquitin ligase activity of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. J Biol Chem 279:26906–26914, 2004
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, et al: Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell 102:33–42, 2000
Ni H, Ergin M, Huang Q, et al: Analysis of expression of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B) in multiple myeloma: downregulation of NF-kappa B induces apoptosis. Br J Haematol 115:279–286, 2001
Berenson JR, Ma HM, Vescio R: The role of nuclear factor-kappaB in the biology and treatment of multiple myeloma. Semin Oncol 28:626–633, 2001
Tillman DM, Izeradjene K, Szucs KS, et al: Rottlerin sensitizes colon carcinoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis via uncoupling of the mitochondria independent of protein kinase C. Cancer Res 63:5118–5125, 2003
Ganten TM, Koschny R, Haas TL, et al: Proteasome inhibition sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells, but not human hepatocytes, to TRAIL. Hepatology 42:588–597, 2005
Lashinger LM, Zhu K, Williams SA, et al: Bortezomib abolishes tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance via a p21-dependent mechanism in human bladder and prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 65:4902–4908, 2005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagy, K., Székely-Szüts, K., Izeradjene, K. et al. Proteasome inhibitors sensitize colon carcinoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via enhanced release of smac/DIABLO from the mitochondria. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 12, 133–142 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02893359
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02893359