Abstract
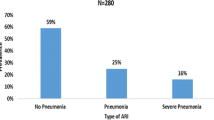
A prospective study was conducted in rural areas of Ballabgarh Block, Haryana by following 5,078 children for a period of 1 year in 1986. The morbidity due to ARI was 3.67 attacks/child/year with lowest attack rates in summer (2.1 in June), and highest in winter (4.78 in January). The moderate and severe cases constituted 14.7% of all cases. Proportional mortality rate due to ARI was 22.6% in these children. 66.5% of deaths were in infants. But the case fatality was 1.31% and the ARI related mortality was 6.3/1000 children and underfives mortality was 26.0/1000 children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kielmnan AA, Taylor CE, Mc Sweemer C, et al. The Narangwal experiment on interaction of nutrition and infections-II. Morbidity, mortality and effects.Indian J Med Res 1978;68:21–41
Gupta KB, Walia SMS. A longitudinal study of morbidity in children in a rural area of Punjab.Indian J Pediatr 1980;47: 297–301
Kamath KR, Feldman RA, Sunder Rao PSA, Web JKB. Infection and diseases in group of South Indian families-II. General morbidity patterns in families and family members.Am J Epidemiol 1969;89: 375–383
Banik ND, Krishna R, Mane SIS, Raj L. A longitudinal study of morbidity and mortality pattern of children under the age of 5 years in an urban community.Indian J Med Res 1969;57: 948–957
Monto AS, Ullman BM. Acute respiratory illnesses in an American community.J Am Med Assoc 1974;227: 164–169
Venkatash S. and Bansal RD. A longitudinal study of morbidity among underfive children in a semi-urban area.Indian J Comm Med 1986;10:11–20
Gulati PV. Thesis submitted in Faculty of AIIMS, New Delhi for M.D. Degree in Preventive & Social Medicine 1965
Bhargava SK, Banerjee SK, Choudhury P, Kumari S. A longitudinal study of morbidity and mortality pattern from birth to 5 years of age in infants of varying birth weight.Indian Pediatr 1979;16: 967–973
Sinclair S. Vital statistics of India. Report on causes of death. Model Registration. 1969.Indian Pediatr 1974;11: 69–73
WHO Scientific Working Group Meeting on Acute Respiratory infections. SEA/CD/83. New Delhi 25–28, July 1983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddaiah, V.P., Kapoor, S.K. Acute respiratory infections in rural underfives. Indian J Pediatr 55, 424–426 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02810367
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02810367