Abstract
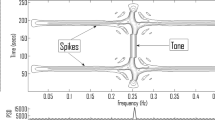
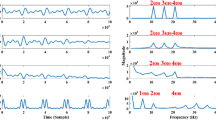
Spikes such as QRS complex in ECG, epileptic seizures in EEG, fine crackles in vesicular sound and glottal closure instants in voiced sound are of diagnostic importance. Various methods of spike detection use the amplitude and frequency characteristics of the spikes. Because of the high frequency content, the spikes appear in the error signal when a linear prediction filtering scheme is used. The authors use the method of midprediction filtering for the detection of the spikes. In this method, the present sample is predicted as a weighted average of p recent past and p immediate future samples. The symmetrical nature of midprediction causes the spikes to appear in the error signal with their original basewidths. This can help in improving the reliability of spike detection, as both the amplitude and the duration of the spike can be considered as decision making parameters. It is observed that the high frequency gain of the midprediction filter is higher compared to the high frequency gain of the LPC or endprediction filter. As a result, this method works better than linear prediction for the detection of spikes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arakawa, K., Fender, D. H., Harashima, H., Miyakawa, H., andSaito, Y. (1986): ‘Separation of nonstationary component from EEG by a nonlinear digital filter’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,33, pp. 724–726
Birkemeier, W. P., Frontaine, A. B., Celesia, G. G., andMa, K. M. (1978): ‘Pattern recognition techniques for the detection of epileptic transients in EEG’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,25, pp. 213–217
Bodenstein, G., andPraetorius, H. M. (1977): ‘Feature extraction from the electroencephalogram by adaptive segmentation’,Proc. IEEE,65, pp. 642–652
Dandapat, S., andRay, G. C. (1994): ‘Midprediction filter for biomedical applications’.Proc. International Conference on Recent Advances in Biomedical Engineering, Hyderabad, India, pp. 16–19
David, S., andRamamurthi, B. (1991): ‘Two sided filters for frame based prediction’,IEEE Trans. Signal Process.,39, pp. 789–794
Frost, J. D. Jr. (1985): ‘Automatic recognition and characterization of epileptoform discharges in the human EEG’,J. Clin. Neurophysiol.,2, pp. 231–249
Gotman, J., andGloor, P. (1976): ‘Automatic recognition of interictal epileptic activity in prolonged EEG recordings’,Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,41, pp. 513–529
Guyton, A. C. (1991): ‘Text book of medical physiology’ (Prism books (pvt.) Ltd., Eastern Press, Bangalore, India)
Hsue, J. J., andYagle, A. E. (1993): ‘Fast algorithms for close-to-Toeplitz-plus-Hankel systems and two sided linear prediction’,IEEE Trans. Signal Process.,41, pp. 2349–2361
Kadambe, S., Murray, R., andBoudreaux-Bartels, G. F. (1992): ‘The dyadic wavelet transform based QRS detector’.Proc. 26th Asimolar conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, California, pp. 130–133
Khansari, M. R. K., andGarcia, A. L. (1993): ‘A fast algorithm for optimal linear interpolation’,IEEE Trans. Signal Process.,41, pp. 2934–2937
Lin, R. P., andChang, W. H. (1989): ‘QRS feature extraction using linear prediction’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,36, pp. 1050–1055
Ono, M., Arakawa, K., Mori, M., Sigimoto, T., andHarashima, H. (1989): ‘Separation of fine crackles from vesicular sounds by a nonlinear digital filter’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,36, pp. 286–291
Qian, J., Barlow, J. S., andBeddoes, M. P. (1988): ‘A simplified arithmatic detector for EEG sharp transients—preliminary results’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,35, pp. 11–18
Rabiner, L. R., andSchafer, R. W. (1978): ‘Digital processing of speech signals’ (Prentice-Hall)
Ray, G. C. (1991): ‘A new technique to separate the nonstationary component of a signal and its application in biomedical engineering’.Proc. Conference on Technology Scenario for the Nineties, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India
Ray, G. C. (1994): ‘An algorithm to separate nonstationary part of a signal using midprediction’,IEEE Trans. Signal Process.,42, pp. 2276–2279
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dandapat, S., Ray, G.C. Spike detection in biomedical signals using midprediction filter. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 35, 354–360 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02534090
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02534090