Abstract
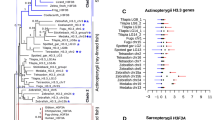
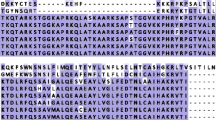
Phylogenetic analysis of histone H3 protein sequences demonstrates the independent origin of the replacement histone H3 genes in animals and in plants. Multiple introns in the replacement histone H3 genes of animals in a pattern distinct from that in plant replacement H3 genes supports this conclusion. It is suggested that replacement H3 genes arose at the same time that, independently, multicellular forms of animals and of plants evolved. Judged by the degree of invariant and functionally constrained amino acid positions, histones H3 and H4, which form together the tetramer kernel of the nucleosome, have co-evolved with equal rates of sequence divergence. Residues 31 and 87 in histone H3 are the only residues that consistently changed across each gene duplication event that created functional replacement histone H3 variant forms. Once changed, these residues have remained invariant across divergent speciation. This suggests that they are required to allow replacement histone H3 to participate in the assembly of nucleosomes in non-S-phase cells. The abundant occurrence of polypyrimidine sequences in the introns of all replacement H3 genes, and the replacement of an intron by a polypyrimidine motif upstream of the alfalfa replacement H3 gene, suggests a function. It is speculated that they may contribute to the characteristic cell-cycle-independent pattern of replacement histone H3 genes by binding nucleosome-excluding proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arents G, Moudrianakis EN (1993) Topography of the histone octamer surface: repeating structural motifs utilized in the docking of nucleosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10489–10493.
Arents G, Moudrianakis EN (1995) The histone fold: a ubiquitous architectural motif utilized in DNA compaction and protein dimerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:11170–11174
Arents G, Burlingame RW, Wang BC, Love WE, Moudrianakis EN (1991) The nucleosomal core histone octamer at 3.1 Å resolution. A tripartite protein assembly and a left-handed superhelix. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10138–10148
Bannon GA, Calzone FJ, BowenJK, Allis CD, Gorovsky MA (1983) Multiple, independently regulated, polyadenylated messages for histone H3 and H4 in Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res 11:3903–3917
Baxevanis AD, Landsman D (1996) Histone sequence database: a compilation of highly-conserved nucleoprotein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 24:245–247
Biggin MD, Tjian R (1988) Transcription factors that activate the ultrabithorax promoter in developmentally staged extracts. Cell 53: 699–711
Björkroth B, Ericsson C, Lamb MM, Daneholt B (1988) Structure of the chromatin axis during transcription. Chromosoma 96:333–340
Brocard MP, Rousseau D, Lawrence JJ, Khochbin S (1994) Two mRNA species encoding the differentiation-associated histone H1° are produced by alternative polyadenylation in mouse. Eur J Biochem 221:421–425
Chaboute ME, Chaubet N, Clement B, Gigot C, Philipps G (1988) Polyadenylation of histone H3 and H4 mRNAs in dicotyledonous plants. Gene 71:217–223
Chaboute ME, Chaubet N, Gigot C, Philipps G (1993) Histories and histone genes in higher plants: structure and genomic organization. Biochimie 75:523–531
Chaubet N, Chaboute ME, Clement B, Ehling M, Philipps G, Gigot C (1988) The histone H3 and H4 messenger RNAs are polyadenylated in maize. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1295–1304
Chaubet N, Clement B, Gigot C (1992) Genes encoding a histone H3.3-like variant in Arabidopsis contain intervening sequences. J Mol Biol 225:569–574
Desjardins E, Hay N (1993) Repeated CT elements bound by zinc-finger proteins control the absolute and relative activities of the two principal human c-myc promoters. Mol Cell Biol 13:5710–5724
Fabry S, Müller K, Lindauer A, Park PB, Cornelius T, Schmitt R (1995) The organization, structure and regulatory elements of Chlamydomonas histone genes reveal features linking plant and animal genes. Curr Genet 28:333–345
Fahmer K, Yarger J, Hereford L (1980) Yeast histone mRNA is polyadenylated. Nucleic Acids Res 8:5725–5737
Fodinger M, Ortner S, Plaimauer B, Wiedermann G, Scheiner O, Duchene M (1993) Pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica: cDNA cloning of a histone H3 with a divergent primary structure. Mol Biochem Parasitol 59:315–322
Heintz N (1991) The regulation of histone gene expression during the cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta 1088:327–340
Hillis DM, Huelsenbeck JP, Cunningham CW (1994) Application and accuracy of molecular phylogenies. Science 264:671–677
Kapros T, Bögre L, Németh K, Bakó L, Györgyey J, Wu S-C, Dudits D (1992) Differential expression of histone H3 gene variants during cell cycle and somatic embryogenesis in alfalfa. Plant Physiol 98: 621–625
Kapros T, Robertson AJ, Waterborg JH (1995) Histone H3 transcript stability in alfalfa. Plant Mol Biol 28:901–914
Kirsh AL, Groudine M, Challoner PB (1989) Polyadenylation and U7 snRNP-mediated cleavage—alternative modes of RNA 3' processing in two avian histone Hl genes. Genes Dev 3:2172–2179
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (1993) MEGA: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis, version 1.0. The Pennsylvania University,University Park, PA
Laner M, de Bruin D, Wertheimer SP, Ravetch JV (1994) Transcriptional and nucleosomal characterization of a subtelomeric gene cluster flanking a site of chromosomal rearrangements in Plasmodium falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4176–4182
Li B, Adams CC, Workman JL (1994) Nucleosome binding by the constitutive transcription factor Spl. J Biol Chem 269: 7756–7763
Lu Q, Wallrath LL, Granok H, Elgin SC (1993) (CT)n (GA)n repeats and heat shock elements have distinct roles in chromatin structure and transcriptional activation of the Drosophila hsp26 gene. Mol Cell Biol 13:2802–2814
Mannironi C, Bonner WM, Hatch CL (1989) H2A.X, a histone isoprotein with a conserved C-terminal sequence, is encoded by a novel mRNA with both DNA replication type and polyA 3′ processing signals. Nucleic Acids Res 17:9113–9126
Marzluff WF (1989) Histone gene expression not coupled to DNA synthesis. In: Hnilica LS, Stein GS, Stein JL (eds) Histones and other basic proteins. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Marzluff WF (1992) Histone 3' ends: essential and regulatory functions. Gene Expr 2:93–97
Matthews HR, Waterborg JH (1985) Reversible modifications of nuclear proteins and their significance. In: Freedman RB, Hawkins HC (eds) The enzymology of post-translational modification of proteins, vol 2. Academic Press, London
Michalon P, Couturier R, Bender K, Hecker H, Marion C (1993) Structural analysis of Trypanosoma brucei brucei chromatin by limited proteolysis. An electrical birefringence study. Eur J Biochem 216: 387–394
Muller SB, Reusing SA, Maier UG (1994) The cryptomonas histone H4-encoding gene: structure and chromosomal location. Gene 150: 299–302
O'Brien T, Wilkins RC, Giardina C, Lis JT (1995) Distribution of GAGA protein on Drosophila genes in vivo. Genes Dev 9:1098–1110
O'Donnell KH, Wensink PC (1994) GAGA factor and TBF1 bind DNA elements that direct ubiquitous transcription of the α1-tubulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4712–4718
O'Donnell KH, Chen CT, Wensink P (1994) Insulating DNA directs ubiquitous transcription of the Drosophila melanogaster αl-tubulin gene. Mol Cell Biol 14:6398–6408
Old RW, Woodland HR (1984) Histone genes: not so simple after all. Cell 38:624–626
Osley MA (1991) The regulation of histone synthesis in the cell cycle. Annu Rev Biochem 60:827–861
Peltz SW, Brewer G, Bernstein P, Hart PA, Ross J (1991) Regulation of mRNA turnover in eukaryryotec cells. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 1:99–126
Puerta C, Martin J, Alonso C, Lopez MC (1994) Isolation and characterization of the gene encoding histone H2A from Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol 64:1–10
Robertson AJ, Kapros T, Dudits D, Waterborg JH (1995) Identification of the three highly expressed replacement histone H3 genes of alfalfa. DNA Seq (in press)
Sadler LA, Brunk CF (1992) Phylogenetic relationships and unusual diversity in histone H4 proteins within the Tetrahymena pyriformis complex. Mol Biol Evol 9:70–84
Saint-Guily A, Schantz ML, Schantz R (1994) Structure and expression of a cDNA encoding a histone H2A from Euglena gracilis. Plant Mol Biol 24:941–948
Schlimme W, Burri M, Bender K, Betschart B, Hecker H (1993) Trypanosoma brucei brucei: differences in the nuclear chromatin of bloodstream forms and procyclic culture forms. Parasitology 107: 237–247
Soto M, Requena JM, Jimenez-Ruiz A, Alonso C (1991) The messenger RNA coding for the nucleosomal protein H2A of Leishmania is polyadenylated and has stem-loops at the 3′ end. Nucleic Acids Res 19:4554
Soto M, Requena JM, Morales G, Alonso C (1994) The Leishmania infantum histone H3 possesses an extremely divergent N-terminal domain. Biochem Biophys Acta 1219:533–535
Standart N, Dale M (1993) Regulated polyadenylation of clam maternal mRNAs in vitro. Dev Genet 14:492–499
Swofford DL (1993) PAUP: Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony, version 3.1.1. Illinois Natural History Survey, Campaign, IL
Thatcher TH, MacGaffey J, Bowen J, Horowitz S, Shapiro DL, Gorovsky MA (1994) Independent evolutionary origin of histone H3.3-like variants of animals and Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res 22: 180–186
Tsukiyama T, Becker PB, Wu C (1994) ATP-dependent nucleosome disruption at a heat-shock promoter mediated by binding of GAGA transcription factor. Nature 367:525–532
Urban MK, Zweidler A (1983) Changes in nucleosomal core histone variants during chicken development and maturation. Dev Biol 95: 421–428
VanDaal A, White EM, Elgin SC, Gorovsky MA (1990) Conservation of intron position indicates separation of major and variant H2As is an early event in the evolution of eukaryotes. J Mol Evol 30: 449–455
Vanfleteren JR, VanBun SM, VanBeeumen JJ (1989) The histones of Caenorhabditis elegans. No evidence of stage specific isoforms—an overview. FEBS Lett 257:233–237
Van Holde KE (1989) Chromatin. In: Chromatin. Springer Verlag, New York
Wall G, Varga-Weisz PD, Sandaltzopoulos R, Becker PB (1995) Chromatin remodeling by GAGA factor and heat shock factor at the hypersensitive Drosophila hsp26 promoter in vitro. EMBO J 14: 1727–1736
Waterborg JH (1990) Sequence analysis of acetylation and methylation of two histone H3 variants of alfalfa. J Biol Chem 265:17157–17161
Waterborg JH (1991) Multiplicity of histone H3 variants in wheat, barley, rice and maize. Plant Physiol 96:453–458
Waterborg JH (1992) Existence of two histone H3 variants in dicotyledonous plants and correlation between their acetylation and plant genome size. Plant Mol Biol 18:181–187
Waterborg JH (1993) Histone synthesis and turnover in alfalfa. Fast loss of highly acetylated replacement histone H3.2. J Biol Chem 268:4912–4917
Waterborg JH, Robertson AJ, Tatar DL, Borza CM, Davie JR (1995) Histones of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Synthesis, acetylation and methylation. Plant Physiol 109:393–407
Wells JRE, Coles LS, Robins AJ (1989) Organization of histone genes and their variants. In: Hnilica LS, Stein GS, Stein JL (eds) Histones and other basic proteins. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Wilhelm ME, Toublan B, Fujita RA, Wilhelm FX (1988) Histone H4 messenger RNA is stored as a small cytoplasmic rnp during the G2 phase in Physarum polycephalum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 153:162–171
Williams AS, Ingledue TC, Kay BK, Marzluff WF (1994) Changes in the stem-loop at the 3′ terminus of histone mRNA affect its nucleoplasmic transport and cytoplasmic regulation. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4660–4666
Wu S-C, Györgyey J, Dudits D (1989) Polyadenylated H3 histone transcripts and H3 histone variants in alfalfa. Nucleic Acids Res 17:3057–3063
Zhong R, Roeder RG, Heintz N (1983) The primary structure and expression of four cloned human histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res 11:7409–7425
Zweidler A (1984) Core histone variants of the mouse: primary structure and differential expression. In: Stein GS, Stein JL, Marzluff WF (eds) Histone genes: structure, organization and regulation. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: J. H. Waterborg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waterborg, J.H., Robertson, A.J. Common features of analogous replacement histone H3 genes in animals and plants. J Mol Evol 43, 194–206 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02338827
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02338827