Summary
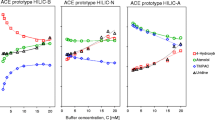
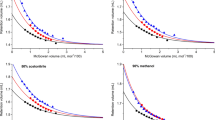
One hundred and one sets of retention data obtained from twenty types of chromatographic systems with seventeen kinds of biopolymers in both reversed-phase and hydrophobic interaction chromaoography were used to test the broad applications of stoichiometric displacement model of retention. We also investigated the linear relationship between the stoichiometric displacement parameter Z and molecular weight of proteins and found out that it really depends on the changes in the molecular conformation or the completeness of losing quarternary or tertiary structure of proteins during the chromatographic process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jianhua Chang, Xindu Geng, J. Northwest Univ., Nature Sci.4, 103 (1989).
Xindu Geng, Wenke Feng, Jianhua Chang, Xiaoqing Chang, Feng Ma, Jianning Yin, Huaru Li, Liujiao Biao, High Technology Letters7, 1–4 (1991).
Xindu Geng, Xiaoqing Chang, J. Chromatogr.599, 185 (1992).
J. J. Kirkland, J. Chromatogr. Sci.9, 206 (1971).
J. H. Knox, A. Pryde, J. Chromatogr.112, 17 (1975).
L. R. Snyder, J. J. Kirkland, “Introduction to Modern Liquid Chromatography”, Wiley-Interscience, New York, 2nd Ed., 1979.
R. R. Drager, F. E. Regnier, J. Chromatogr.406, 237 (1987).
J. L. Fausnaugh, L. A. Kennedy, F. E. Regnier, J. Chromatogr.317, 141 (1984).
H. P. Jennissen, G. Botzer, J. Biol. Macromol.1, 171 (1979).
H. P. Jennissen, J. Chromatogr.248, 101 (1978).
T. Arkawa, Arch. Biochem. Biophys.248, 101 (1986).
W. R. Melander, D. Corradim, Cs. Horvath, J. Chromatogr.317, 67 (1984).
O. Sinanoglu, S. Abdulnur, Fed. Proc. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Btol.24, 12 (1965).
Xindu Geng, F. E. Regnier, J. Chromatogr.296, 15 (1984).
Xindu Geng, F. E. Regnier, J. Chromatogr.332, 147 (1985).
Xindu Geng, Li'an Guo, Jianhua Chang, J. Chromatogr.507, 1 (1990).
Xindu Geng, Yali Shi, Sci. China, ser. B32, 11 (1989).
Xindu Geng, Liujiao Bian, Sci. China, ser. B35, 262 (1992).
Xindu Geng, J. Northwest Univ., Nature sci.4, 38 (1991).
Yali Shi, Xindu Geng, chem. J. Chinese Univ. (English Ed.) in press.
M. Kunitani, D. Johnson, L. R. Snyder, J. Chromatogr.,371, 313 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, J., Guo, L., Feng, W. et al. Studies on the correlation of chromatographic behaviour of biopolymers between reversed-phase and hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Testing the stoichiometric displacement between biopolymer and displacing agent. Chromatographia 34, 589–596 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02269868
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02269868