Abstract
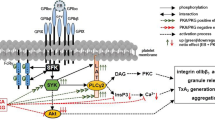
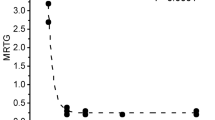
Four chemically distinct PAF-acether antagonists were used to test the hypothesis that the cyclooxygenase and ADP-independent thrombin-induced aggregation of human platelets is due to PAF-acether. The compouds 48740 RP, CV-3988, BN 52021 and Ro 19-3704 inhibited aggregation by PAF-acether whereas 48740 RP also interfered with aggregation by arachidonic acid, U 46619, collagen and thrombin. Aspirin-treated platelets aggregated in response to PAF-acether and to 0.25 U/ml thrombin as much as control platelets in absence of detectable thromboxane A2, and were less responsive to 0.05–0.1 U/ml. Thrombin-induced aggregation of aspirin-treated platelets was unaffected by the PAF-acether antagnists BN 52021, CV-3988 and Ro 19-3704. In separate experiments, platelets were exposed for five min to convulxin, a glycoprotein extracted from a snake venom which depletes granular ADP and ATP. A combination of PGI2, aspirin and anticrotalid serum used to disaggregate allowed the recovery of approximately 80% free platelets, which failed to respond to PAF-acether but still aggregated in presence of thrombin. This residual ADP and cyclooxygenase-independent aggregation is not accountable for by the platelet formation of PAF-acether, since it was not modified by the latters' antagonists nor by platelet exposure to convulxin. Our results do not support the proposal that PAF-acether mediates a third pathway of human platelet aggregation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Benveniste, P. M. Henson and C. G. Cochrane,Leukocyte-dependent histamine release from rabbit platelets: the role of IgE, basophils and platelet-activating factor. J. exp. Med.136, 1356–1376 (1972).
B. B. Vargaftig,Carrageenan and thrombin trigger prostaglandin synthetase-independent aggregation of rabbit platelets: inhibition by phospholipase A2 inhibitors. J. Pharm. Pharmacol.29, 222–228 (1977).
E. G. Lapetina, K. A. Chandrabose and P. Cuatreacasas,Ionophore A23187 and thrombin-induced platelet aggregation: independence from cyclooxygenase products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA75, 818–822 (1978).
R. M. L. Kinlough-Rathbone, P. A. Packham, H. J. Reimers, J. P. Cazenave and J. F. Mustard,Mechanisms of platelet shape change, aggregation and release induced by collagen, thrombin, or A23187. J. Lab. Clin. Med.90, 707–719 (1977).
M. Chignard, J. P. Le Couedic, M. Tence, B. B. Vargaftig and J. Benveniste,The role of platelet-activating factor in platelet aggregation. Nature279, 788–800 (1979).
M. Chignard, J. P. Le Couedic, M. Tence, B. B. Vargaftig and J. Benveniste,Platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) secretion from platelets: effects of aggregating agents. Brit. J. Haematol.46, 455–464 (1980).
L. Touqui, M. Hatmi and B. B. Vargaftig,Human platelets stimulated by thrombin produce PAF-acether (1-0-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) when the degradating enzyme acetyl hydrolase is blocked. Biochem. J.230, 811–816 (1985).
Z. I. Terashita, S. Tsushima, Y. Yoshioka, H. Nomura, Y. Inada and K. Nishikawa,CV-3988, a specific antagonist of platelet-activating factor. Life Sci.32, 1957–1982 (1983).
K. Burri, B. Barner, J. M. Cassal, P. Hadvary, G. Hirth and K. Muller,PAF: from agonists to antagonists by synthesis. Prostaglandins30, 691 (1985).
P. Sédivy, C. G. Caillard, A. Floch, F. Folliard, S. Mondot, C. Robaut and B. Terlain,48740 RP: a specific PAF-acether antagonist. Prostaglandins30, 688 (1985).
P. Braquet, GB Patent 8, 418, 424, July 19 (1984).
G. Marlas,Purification and preliminary structure of a potent platelet aggregating glycoprotein isolated from the venom of Crotalus durissus cascavella. Toxicon20, n° 1, 289–290 (1982).
B. B. Vargaftig, D. Joseph, F. Wal, G. Marlas, M. Chignard and L. G. Chevance,Convulxin-induced activation of intact and of thrombin-degranulated rabbit platelets: specific crossed desensitization with collagen. Eur. J. Pharmac.92, 57–68 (1983).
H. J. Reimers, R. L. Kinlough-Rathbone, J. P. Cazenave, A. F. Senyi, J. Hirsh, A. Packham and J. F. Mustard,In vitro and in vivo functions, of thrombin-treated platelets.Thromb. Haemostas. 35, 151–165 (1976).
F. Fouque and B. B. Vargaftig,Triggering by platelet-activating factor and adrenaline of cyclooxygenase-independent platelet aggregation. Br J. Pharmac.83, 625–633 (1984).
C. Lalau-Keraly and J. Benveniste,Specific desensitization of rabbit platelets by platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) and derivatives. Br. H. Haematol.,51, 313–322 (1982).
F. Wal, D. Joseph, L. Touqui and B. B. Vargaftig,PAF-acether may not mediate the third pathway of platelet aggregation since self-desensitization reduces the effects of low thrombin but enhances those of convulxin. Thromb. Haemost.53, 99–104 (1985).
L. Touqui, M. Chignard, C. Jacquemin, F. Wal and B. B. Vargaftig,Dissociation between inhibition of phospholipid methylation and production of PAF-acether by rabbit platelets. Experientia,40, 374–377 (1984).
J. Westwick, G. Mark and V. V. Kakkar,The role of platelet-activating factor (PAF) in cyclo-oxygenase independent thrombin and collagen-induced platelet activation. J. Pharmacol. (Paris)14, 61 Abst (1985).
T. J. Hallam, M. C. Scrutton and R. B. Wallis,The role of 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholine (AcGEPC) and palmitoyl-lysophosphatidate in the responses of human blood platelets to collagen and thrombi. FEBS Letters162, 142–146 (1983).
E. Kloprogge, G. H. de Hass, G. Gorter and J. W. N. Akkerman,Stimulus-response coupling in human platelets. Evidence against a role of PAF-Acether in the “Third Pathway”. Thromb. Res.30, 107–112 (1983).
B. B. Vargaftig, M. Chignard, J. Benveniste, J. Lefort and F. Wal,Background and present status of research on platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether). Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.370, 119–137 (1981).
J. Benveniste and B. B. Vargaftig,Platelet activating factor: an, ether lipid with biological activity. In:Ether Lipids: biochemical and biomedical aspects. (Eds. H. K. Mangold and F. Pantolf), Amsterdam, Elsevier 1983, pp. 355–373.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adnot, S., Joseph, D. & Vargaftig, B.B. Antagonists of PAF-acether do not suppress thrombin-induced aggregation of ADP-deprived and aspirin-treated human platelets. Agents and Actions 21, 195–202 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01974942
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01974942