Summary
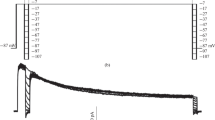
Superfusion with Pb2+ induces a slow, noninactivating and reversible inward current in voltage-clamped N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells. The amplitude of this inward current increases in the range of 1–200 μm Pb2+. Single-channel patch-clamp experiments have revealed that this inward current is mediated by discrete ion channels. Reversal potentials from linearI–V relationships are close to 0 mV for whole-cell and single-channel currents and the single-channel conductance amounts to 24 pS. The Pb2+-induced membrane current is not mediated by various known types of ion channels, since it is not blocked by external tetrodotoxin, tetraethylammonium,d-tubocurarine, atropine, ICS 205-930 and by internal EGTA. In Na+-free solutions superfusion with Pb2+ neither evokes a whole-cell inward current, nor single-channel openings. At −80 mV the open-time distribution of the single channels activated by 1μm Pb2+ is dual exponential with time constants of 17 and 194 msec. When the Pb2+ concentration is increased from 1 to 20 μm these time constants decrease to 2 and 13 msec, but the amplitude of single-channel currents remains −1.9 nA. Cd2+ and Al3+ induce inward currents and single-channel openings similar to Pb2+. Time constants fitted to the open-time distribution of single channels are 14 and 135 msec in the presence of 1 μm Cd2+ and 15 and 99 msec in the presence of 50 μm Al3+. Conversely, Cu2+ induces an irreversible inward current in neuroblastoma cells. Single-channel openings are undetected in the presence of Cu2+ and in Na+-free solutions Cu2+ is still able to induce an inward current. It is concluded that Pb2+, Cd2+ and possibly Al3+ activate a novel type of metal ionactivated (MIA) channel in N1E-115 cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amano, T., Richelson, E., Nirenberg, P.G. 1972. Neurotransmitter synthesis by neuroblastoma clones.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 6:258–263
Bendat, J.S., Piersol, A.G. 1971. Random data: Analysis and measurement procedures. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Blatz, A.L., Magleby, K.L. 1987. Calcium-activated potassium channels.Trends Neurosci. 10:463–467
Diem, K., Lentner, C. 1968.Wissenschaftliche Tabellen. Ciba-Geigy AG, Basle
Gorman, A.L.F., Hermann, A. 1979. Internal effects of divalent cations on potassium permeability in molluscan neurones.I. Physiol. (London) 296:393–410
Hagiwara, S., Byerly, L. 1981. Calcium channel.Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 4:69–125
Hamill, O.P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., Sigworth, F.J. 1981. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches.Pfluegers Arch. 391:85–100
Marquardt, D.W. 1963. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of non-linear parameters.J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 11:431–441
Narahashi, T., Tsunoo, A., Yoshii, M. 1987. Characterization of two types of calcium channels in mouse neuroblastoma cells.J. Physiol. (London) 383:231–249
Neijt, H.C., te Duits, I.J., Vijverberg, H.P.M. 1988. Pharmacological characterization of serotonin 5-HT3 receptor-mediated electrical response in cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells.Neuropharmacology 27:301–307
Oortgiesen, M., Van Kleef, R.G.D.M., Bajnath, R.B., Vijverberg, H.P.M. 1989. Nanomolar concentrations of lead selectively block neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine responses in mouse neuroblastoma cells.Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. (in press)
Owen, D.G., Segal, M., Barker, J.L. 1986. Voltage-clamp analysis of a Ca2+ and voltage-dependent chloride conductance in cultured mouse spinal neurons.J. Neurophysiol. 55:1115–1135
Partridge, L.D., Swandulla, D. 1988. Calcium-activated non-specific cation channels.Trends Neurosci. 11:69–72
Quandt, F.N. 1988. Three kinetically distinct potassium channels in mouse neuroblastoma cells.J. Physiol. (London) 395:401–418
Romey, G., Hugues, M., Schmid-Antomarchi, H., Lazdunski, M. 1984. Apamin: A specific toxin to study a class of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels.J. Physiol. (Paris) 79:259–264
Shields, M., Grygorczyk, R., Fuhrmann, G.F., Schwarz, W., Passow, H. 1985. Lead-induced activation and inhibition of potassium-selective channels in the human red blood cell.Biochim Biophys. Acta 815:223–232
Weinreich, D., Wonderlin, W.F. 1987. Copper activates a unique inward current in molluscan neurones.J. Physiol. (London) 394:429–443
Yellen, G. 1982. Single Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channels in neuroblastoma.Nature (London) 296:357–359
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oortgiesen, M., van Kleef, R.G.D.M. & Vijverberg, H.P.M. Novel type of ion channel activated by Pb2+, Cd2+, and Al3+ in cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells. J. Membrain Biol. 113, 261–268 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870077
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870077