Abstract
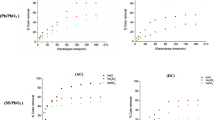
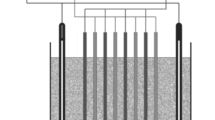
The performance of highly doped SnO2 anodes for the oxidative treatment of biologically refractory waste water was compared with PbO2 and Pt. The oxidation of a wide range of organic compounds proceeds with an efficiency which is about 5 times higher than with platinum anodes. The oxidation efficiency was found to be independent of the pH of the water. In chloride containing media, SnO2 anodes produce less chlorine gas than platinum anodes and hence show less potential to form hazardous chlorinated organic by-products. The design of a simple plate-and-frame reactor with undivided cells for waste water treatment using SnO2 anodes was based on two experimental findings: (a) no interference of the cathode with the oxidation has been found: (b) the rate of oxidation is not limited by mass transfer, indicating the participation of homogeneous reactions in the overall oxidation. The new anode material reduces the specific energy requirement of electrochemical oxidation of organics in waste water to 30 to 50 kWh kg−1 of COD removed. This makes the process an interesting alternative to chemical oxidation using oxidants such as ozone and hydrogen peroxide, or wet oxidation using oxygen at elevated temperature and pressure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Plattner and C. Comninellis, in ‘Process Technologies for Water Treatment’ (edited by S. Stucki). Plenum, New York (1988) p. 205.
C. Comninellis and E. Plattner,Chimia 42 (1988) 250.
G. Kreysa, in ‘Process Technologies for Water Treatment’ (edited by S. Stucki). Plenum, New York (1988) p. 65.
D. Wabner and C. Grambow,J. Electroanal. Chem. 195 (1985) 95.
J. Hoigne and H. Bader,Water Res. 17 (1983) 173.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stucki, S., Kötz, R., Carcer, B. et al. Electrochemical waste water treatment using high overvoltage anodes Part II: Anode performance and applications. J Appl Electrochem 21, 99–104 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01464288
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01464288