Abstract
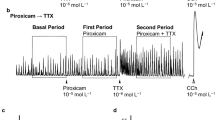
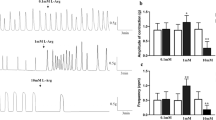
The effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5HT) was studied in circular and longitudinal muscle from the proximal and distal colon of New Zealand white rabbits. 5HT stimulated a dose-dependent isometric contraction of distal and proximal circular muscle that was greater than in distal longitudinal muscle (P<0.01). 5HT did not stimulate taenia coli longitudinal muscle. The EC50 for 5HT stimulation of distal circular muscle (−7.0±0.1), distal longitudinal muscle, and proximal circular muscle was similar. Methysergide dose-dependently inhibited the 5HT stimulation of both proximal and distal circular muscle. The IC50 for methysergide inhibition of 5HT (5×10−7 M) stimulation was −5.5±0.2. Ketanserine and ICS 205-930 did not inhibit 5HT stimulation of colonic muscle. Tetrodotoxin (TTX) decreased the potency, but not the efficacy of 5HT stimulation of proximal and distal circular muscle. Atropine decreased the potency (EC50=−6.6±0.1) (P<0.05) and the efficacy by 40%. Electrical field stimulation (EFS) caused an on-contraction and off-contraction of distal circular muscle and an on-contraction of proximal circular muscle. 5HT decreased the off-contraction of the distal circular muscle but did not affect the on-contraction of the other muscle strips. 5HT receptor antagonists did not affect EFS of the tissue. The studies suggest: (1) 5HT stimulates circular colonic muscle with greater efficacy than longitudinal muscle, (2) 5HT stimulates circular muscle through a 5HT1 receptor, (3) there is atropine-sensitive and atropine-insensitive 5HT stimulation of circular colonic muscle, (4) 5HT inhibits neurons responsible for the off-contraction in distal circular muscle without affecting the on-contraction. Thus, 5HT affects colonic contraction by a direct effect on muscle and indirectly through the enteric nerves.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Snape WJ Jr. Kim BH, Willenbucher R, Koelbel C, Mayer EA, Walsh JH: The response of proximal and distal rabbit colonic muscle after electrical field stimulation. Gastroenterology 96:321–326, 1989
Costa M, Furness JB, Cuello AC, Verhofstad AAJ, Steinbusch HWJ, Elde RP: Neurons with 5-hydroxytryptamine-like immunoreactivity in the enteric nervous system: Their visualization and reactions to drug treatment. Neuroscience 7:351–363. 1982
Furness JB, Costa M: Neurons with 5-hydroxytryptamine-like immunoreactivity in the enteric nervous system: Their projections in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience 7:341–345, 1982
Griffith S, Burnstock G: Serotonergic neurons in human fetal intestine: An immunohistochemical study. Gastroenterology 85:929–937, 1983
Bulbring E, Crema A: Observation concerning the action of 5-hydroxytryptamine on the peristaltic reflex. Br J Pharmacol 13:444–457, 1958
Gershon MD, Erde SM: The nervous system of the gut. Gastroenterology 80:1517–1594, 1981
Gaddum JH, Picarelli ZP: Two kinds of tryptamine receptors. Br J Pharmacol 9:240–248, 1956
Gronstad K, Dahlstrom A, Florence L, Zinner MJ, Ahlman J, Jaffe BM: Regulatory mechanisms in endoluminal release of serotonin and substance P from feline jejunum. Dig Dis Sci 32:393–400, 1987
Costa M, Furness JB: The sites of action of 5-hydroxytryptamine in nerve-muscle preparations from the guinea-pig small intestine and colon. Br J Pharmacol 65:237–248
Pairet M, Merieu O, Bardon T, Ruckebusch Y: Cholinergic modulation of the release of serotonin in the gastric interstitial fluids: An in vivo study in rabbits. Gastroenterology 91:1250–1257, 1986
Horita A, Carino MA: Centrally administered thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) stimulates colonic transit and diarrhea production by a vagally mediated serotonergic mechanism in the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 222:367–371, 1982
LaHann TR, Horita A: Thyrotropin releasing hormone: Centrally mediated effects in gastrointestinal motor activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 222:66–70, 1982
Belai A, Lincoln J, Milnet P, Burnstock G: Progressive changes in adrenergic, serotinergic and peptidergic nerves in proximal colon of streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Gastroenterology 95:1234–1241, 1988
Gore S, Gilmore IT, Haigh CG, Brownlens SM, Stockdale H, Morris AI: Colonic transit in man is slowed by ordansetrun (GR38032F), a selective 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor (type 3) antagonist. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 4:135–144, 1990
Snape WJ Jr, Yoo S: Effect of amino acids on isolated colonic smooth muscle from the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 235:690–695, 1985
Dixon WJ Ed. BMDP Statistical Software. San Francisco. University of California Press. 1985
Ormsbee III, HS, Fondacaro JD: Action of serotonin on the gastrointestinal tract. Proc Exp Biol Med 178:333–338, 1985
Bennett A, Whitney B: A pharmacological study of the motility of the human gastrointestinal tract. Gut 7:307–316, 1966
Misiewicz JJ, Walker SL, Eisner M: Motor responses of human gastrointestinal tract to 5-hydroxytryptaminein vivo andin vitro. Gut 7:208–216, 1966
Burleigh DE: Evidence for more than one type of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the human colon. J Pharm Pharmacol 20:538–541, 1977
Humphrey PA: Peripheral 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors and their classification. Neuropharmacology 23:1503–1510, 1984
Cohen ML, Schenck KW, Colbert W, Wittenaner L: Role of 5-HT2 receptors in serotonin induced contractions of non-vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 232:770–774, 1985
Bradley PB, Engle G, Feniuk W, Fozard JR, Humphrey PPA, Middlemiss DN, Mylecharane EJ, Richardson BP, Saxena PR: Proposals for the classification and nomenclature of functional receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine. Neuropharmacology 25:563–576, 1986
Niemegeers CJ, Van Nueten JM: Serotonin-S2 receptor binding sites and functional correlates. Neuropharmacology 23:1493–1501, 1984
Leysen JE, Niemegeers CJE, Van Nueten JM, Lanron PM: [3H]ketanserine (R41 468), a selective3H-ligand for serotonin-2 receptor binding sites: Binding properties, brain distribution, and functional role. Mol Pharmacol 21:301–314, 1982
Richardson BP, Engel G, Donatsch P, Staddler PA: Identification of serotonin M-receptor subtypes and their specific blockade by a new class of drug. Nature 316:126–131, 1985
Lidberg P: On the role of substance P and serotonin in the pyloric motor control. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 538:5–69, 1985
Feniuk W: An analysis of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors mediating contraction of isolated smooth muscle. Neuropharmacology 23:1461–1472. 1984
Akkerman LMA, Vos A, Hoekstra A, Rollafs JMM, Horowitz M. Effect of ICS205-90 (a specific 5-HT3 receptor antagonist) on gastric emptying of a solid meal in normal subjects. Gut 29:1249–1252, 1988
Gershon MD, Tamir H: Release of endogenous 5-hydroxytryptamine from resting and stimulated enteric neurons. Neuroscience 11:2277–2286, 1981
Misiewicz JJ, Waller SL, Eisner M: Motor response of human gastrointestinal tract to 5-hydroxytryptaminein vivo andin vitro. Gut 7:208–216, 1966
Costa M, Furness JB: The sites of action of 5-hydroxytryptamine in nerve-muscle preparation from the guinea-pig small intestine and colon. Br J Pharmacol 65:237–248. 1979
Behar J, Biancani P: Neural control of the sphincter of Oddi. A physiological role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the regulation of bowel sphincter of oddi motor activity in the cat. J Clin Invest 72:551–559, 1983
Buchheit KH, Engel G, Mulschler E, Richardson B: Study of the contractile effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) in the isolated longitudinal muscle strip from guinea-pig ileum: Evidence for two distinct release mechanism. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 329:36–41, 1985
Vizi VA, Vizi ES: Direct evidence of acetylcholine releasing effect of serotonin in the auerbach plexus. J Neural Transmission 42:127–138, 1978
Wallis D: Neuronal 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors outside the central nervous system. Life Sci 29:2345–2355, 1981
Kilbinger H, Wessler II: The variation of acetylcholine release from myenteric neurons with stimulation frequency and train length. Role of presynaptic muscarinic receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 324:130–133, 1983
Koelbel CB, Patel A, Ennes HM, Snape WJ Jr, Mayer EA: Evidence for the involvement of substance P in noncholinergic excitation of rabbit colonic muscle. Am J Physiol 256:G246-G253, 1989
Gonella J: The physiological role of peripheral serotonergic neurones. A review. J Physiol (Paris) 77:515–519, 1981
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ng, W.W., Jing, J., Hyman, P.E. et al. Effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine and its antagonists on colonic smooth muscle of the rabbit. Digest Dis Sci 36, 168–173 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01300751
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01300751