Abstract
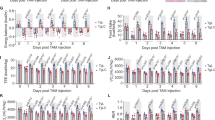
Cachexia frequently occurs in the late stages of cancer, and is difficult to manage. We previously reported that interleukin-6 (IL-6) cDNA transfection into Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC-IL6) induced cachexia-like symptoms in C57BL/6 mice. This was thought to be a useful experimental model of cancer cachexia. We have examined the effects of two eicosanoids, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), in order to evaluate whether they could relieve cachexia. LLC-IL6-bearing animals were divided into three treatment groups receiving DHA, EPA or water as the control; 80-μl samples of these compounds (purity>95%) were administered orally by catheter daily starting 7 days after tumor transplantation. Tumor growth curves were similar in the three groups. There were no differences in water or food intake in the three groups. However, body weight, a marker of cachexia, was significantly higher in treated mice than in the control group. Sixteen days after tumor transplantation, the mean body weight was 17.45 g (P<0.05), 17.2 g and 16.41 g in the groups receiving DHA, EPA and water respectively. The eicosanoids did not affect serum levels of IL-6. Ubiquitination of muscle protein, a marker of proteolysis coupled to cachexia, was compared in LLC-IL6-and LLC-transplanted mice. The eicosanoids prevented the ubiquitination of approximately 180 kDa protein. These results suggest that eicosanoids may prevent the cachexia mediated by IL-6.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DHA :
-
docosahexaenoic acid
- EPA :
-
eicosapentaenoic acid
- LLC :
-
Lewis lung carcinoma
- IL :
-
interleukin
References
Beck SA, Smith KL, Tisdale MJ (1991) Anticachectic and antitumor effect of eicosapentaenoic acid and its effect on protein turnover. Cancer Res 51:6089–6093
Beutler BA, Cerami A (1985) Recombinant interleukin 1 suppresses lipoprotein lipase activity in 3T3-L1 cells. J Immunol 135:3969–3971
Black K, Carrett IF, Mundy GR (1991) Chinese hamster ovarian cells transfected with the murine interleukin-6 gene cause hypercalcemia as well as cachexia, leukocytosis and thrombocytosis in tumor-bearing nude mice. Endocrinology 128:2657–2659
Brouckaert P, Spriggs DR, Demetri G, Kufe DW, Fiers W (1989) Circulating interleukin 6 during a continuous infusion of tumor necrosis factor and interferon. J Exp Med 6:2257–2262
Garcia Martinez C, Agell N, Llovera M, Lopez Soriano Fj, Argiles JM (1993) Tumour necrosis factor-alpha increases the ubiquitinization of rat skeletal muscle proteins. FEBS Lett 323:211–214
Gelin J, Moldawer LL, Lonnroth C, Sherry B, Chizzonite R, Lundholm K (1991) Role of endogenous tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 for experimental tumor growth and the development of cancer cachexia. Cancer Res 51:415–421
Hill RJ, Warren MK, Levin J (1990) Stimulation of thrombopoiesis in mice by human recombinant interleukin 6. J Clin Invest 85:1242–1247
Jeevanandam M, Horowitz GD, Lowry SF, Brennan MF (1984) Cancer cachexia and protein metabolism. Lancet 1:1423–1426
Karasuyama H, Melchers F (1988) Establishment of mouse cell lines which constitutively secrete large quantities of interleukin 2, 3, 4 or 5, using modified cDNA expression vectors. Eur J Immunol 18:97–104
Karmali RA, Marsh J, Fuchs C (1984) Effect of omega-3 fatty acids on growth of a rat mammary tumor. J Natl Cancer Inst 73:457–461
Karmali RA, Reichel P, Cohen LA, Terano T, Hirai A, Tamura Y, Yoshida S (1987) Modulation of prostaglandin synthesis in mouse peritoneal macrophages by enrichment of lipids with either eicosapentaenoic or docosahexaenoic acid in vitro. Immunobiology 175:406–419
Kern AK, Norton JA (1988) Cancer cachexia, Parenteral Enternal Nutr 12:286–298
Kitahara M, Kishimoto S, Hirano T, Kishimoto T, Okada M (1990) The in vivo anti-tumor effect of human recombinant interleukin-6. Jpn J Cancer Res 81:1032–1038
Langstein HN, Doherty GM, Fraker DL, Buresh CM, Norton JA (1991) The roles of gamma-interferon and tumor necrosis factor alpha in an experimental rat model of cancer cachexia. Cancer Res 51:2302–2306
Lonnroth C, Moldawer LL, Gelin J, Kindblom L, Sherry B, Lundholm K (1990) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 alpha production in cachectic, tumor-bearing mice. Int J Cancer 46:889–896
Mulé JJ, McIntosh JK, Jablons DM, Rosenberg SA (1990) Antitumor activity of recombinant interleukin 6 in mice. J Exp Med 171:629–636
Nishio K, Morikage T, Ohmori T, Kubota N, Takeda Y, Ohta S, Yazawa K, Saijo N (1993) Novel water-soluble derivatives of docosahexaenoic acid increase diacylglycerol production mediated by phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 203:200–208
Norton JA, Stein TP, Brennan MF (1981) Whole body protein synthesis and turnover in normal man and malnourished patients with and without cancer. Ann Surg 194:123–128
Ohe Y, Podack ER, Olsen KJ, Miyahara Y, Miura K, Saito H, Koishihara Y, Ohsugi Y, Ohira T, Nishio K, Saijo N (1993) Interleukin-6 cDNA transfected Lewis lung carcinoma cells show unaltered net tumour growth rate but cause weight loss and shorten survival in syngenic mice. Br J Cancer 67:939–944
Price MG, Gomer RH (1993) Skelemin, a cytoskeletal M-disc periphery protein, contains motifs of adhesion/recognition and intermediate filament proteins. J. Biol Chem 268:21 800–21 810
Temparis S, Asensi M, Taillandier D, Aurousseau E, Obled A, Bechet D, Ferrara M, Estrela JM, Attaix D (1994) Increased ATP-ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis in skeletal muscles of tumor-bearing rats. Cancer Res 54:5568–5573
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohira, T., Nishio, K., Ohe, Y. et al. Improvement by eicosanoids in cancer cachexia induced by LLC-IL6 transplantation. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 122, 711–715 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209117
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209117