Abstract
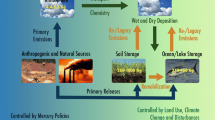
A model of the global Hg cycle is presented and applied to analyze modern Hg budgets and historical changes in deposition. Our modeling suggests that mixing into the ocean interior is a significant sink of Hg and likely has limited any anthropogenically-caused increase in surface ocean Hg concentrations to about 50% above natural levels rather than 200% as has recently been argued. Additionally, both the increase in air pollutants during the industrial era and their recent decrease in North America likely have affected atmospheric Hg scavenging and the resulting records of Hg deposition rates in lake and bog sediments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benoit, J.M., Fitzgerald, W.F. and Damman, A.W.H.: 1994, inMercury Pollution: Integration and Synthesis, C.J. Watras and J.H. Huckabee, Eds., in press.
Engstrom, D.R., Swain, E.B., and Brigham, M.E.: 1994, inAbstracts of International Conference on Mercury as a Global Pollutant, July, 1994, Whistler, B.C., Electric Power Research Institute, Palo Alto, CA.
Fitzgerald, W.F.: 1986, inThe Role of Air-Sea Exchange in Geochemical Cycling, p 363, Buat-Menard, P., Ed., NATO ASI Series, Series C, Mathematical and Physical Sciences; no. 185, D. Reidel, Boston.
Hudson, R.J.M., S.A. Gherini, and Goldstein, R.A.: 1994,Global Biogeochem. Cycles,8, 307–333.
Keeling, C.D.: 1990, inTRENDS '90: A Compendium of Data on Global Change, pp. 90–91, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tenn.
Lindquist, O.: 1991,Wat., Air, and Soil, Pollut.,55, 65–71.
Liss, P.S.: 1983, inAir-Sea Exchange of Gases and Panicles, Liss, P.S. and Slinn, G.N., Eds., NATO ASI Series. Series C, Mathematical and Physical Sciences; no. 108, D. Reidel, Boston.
Marland, G.: 1990, inTRENDS '90: A Compendium of Data on Global Change, pp. 92–93, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tenn.
Mason, R.P. and W.F. Fitzgerald: 1993,Deep-Sea Res.,40, 1897–1924.
Mason, R.P., W.F. Fitzgerald and Morel, F.M.M.: 1994,Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,58, 3191–3198.
Milward, G.E.: 1982,J. Geophys. Res.,87, 8891–8897.
Munthe, J. and McElroy, W.J.: 1992,Atmos. Environ.,26A, 533.
Nriagu, J.O.: 1989,Nature,338, 47–49.
Nriagu, J.O.: 1994,Sci. Tot. Environ.,154, 1–8.
Slemr, F. and Langer, E.: 1992,Nature,355, 434–437.
Swain, E.B., Engstrom, D.R., Brigham, M.E., Henning, T.A., and Brezonik, P.L.: 1992,Science,257, 784–787.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hudson, R.J.M., Gherini, S.A., Fitzgerald, W.F. et al. Anthropogenic influences on the global mercury cycle: A model-based analysis. Water Air Soil Pollut 80, 265–272 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01189676
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01189676