Abstract
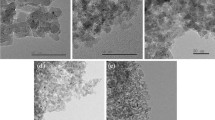
Initially reduced ≈ 100 Å diameter Rh metal particles on SiO2 are found by TEM to be dispersed into an amorphous metal film by treatment in 5% NO + 5% CO in He at 260 °C, leaving thin rings around the perimeter of the original particles. Electron diffraction shows that Rh is amorphous while XPS shows that the Rh is approximately zero valent in the dispersed state. Continued heating in this mixture resulted in irreversible volatilization of the Rh even at these low temperatures. Subsequent heating in H2 at 650 °C caused sintering and the reformation of crystalline Rh particles, but with a lower loading than observed initially. Treatment of Rh particles in 5% NO at 260 °C causes Rh particles to shrink in diameter and to form thin shells around their perimeters. The only change observed after treatment in 5% CO alone at 260 °C was slight sintering of adjacent Rh particles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.C. Taylor, in:Catalysis: Science and Technology, Vol. 5, eds. J.R. Anderson and M. Boudart (Springer, Berlin, 1984) p. 119.
T.W. Root, L.D. Schmidt and G.B. Fisher, Surf. Sci. 134 (1983) 30.
S.H. Oh, J. Catal. 124 (1990) 477.
S.H. Oh and C.C. Eickel, J. Catal. 128 (1991) 526.
B.K. Cho, B.H. Shanks and J.E. Bailey, J. Catal. 115 (1989) 486.
A.C. Yang and C.W. Garland, J. Phys. Chem. 61 (1957) 1504.
F. Solymosi and M. Pásztor, J. Phys. Chem. 89 (1985) 4789.
F. Solymosi and M. Pásztor, J. Phys. Chem. 90 (1986) 5312.
J.T. Yates Jr., T.M. Duncan, S.D. Worley and R.W. Vaughan, J. Chem. Phys. 70 (1979) 1219.
J.T. Yates Jr., T.M. Duncan and R.W. Vaughan, J. Chem. Phys. 71 (1979) 3908.
H.F.J. van't Blik, J.B.A.D. van Zon, T. Huizinga, J.C. Vis, D.C. Koningsberger and R. Prins, J. Phys. Chem. 87 (1983) 2264.
H.F.J. van't Blik, J.B.A.D. van Zon, T. Huizinga, J.C. Vis, D.C. Koningsberger and R. Prins, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 107 (1985) 3139.
F. Solymosi, T. Bánsági and E. Novák, J. Catal. 112 (1988) 183.
F. Solymosi, M. Pásztor and G. Rákhely, J. Catal. 110 (1988) 413.
J.L. Robbins, J. Catal. 115 (1989) 120.
F. Solymosi and J. Raskó, J. Catal. 15 (1989) 107.
T. Mizushima, K. Tohji, Y. Udagawa and A. Ueno, J. Phys. Chem. 94 (1990) 4980.
S.L. Anderson, T. Mizushima and Y. Udagawa, J. Phys. Chem. 95 (1991) 6603.
T. Wang and L.D. Schmidt, J. Catal. 70 (1981) 187.
K.R. Krause, P.S. Schabes-Retchkiman and L.D. Schmidt, J. Catal. 134 (1992) 204.
J. Schwartz and L.D. Schmidt, J. Catal. (1992), submitted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was sponsored by NSF under Grant CBT-882745 and by a grant from Ford Motor Company.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krause, K.R., Schmidt, L.D. Catalytic disruption and volatilization of rhodium particles on silica in NO + CO. Catal Lett 14, 141–148 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00765228
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00765228