Summary
-
1.
The effect of capsaicin injected into the superior mesenteric artery has been studied on the intestinal blood flow in dogs.
-
2.
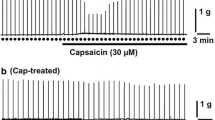
Capsaicin evoked a marked dose-dependent increase in mesenterial blood flow in the dose range of 0.1–7 μg/kg. The intestinal vasodilatatory effect of capsaicin could invariably be demonstrated after pretreatment with adrenoceptor and dopamine receptor antagonists, as well as with the ganglion blocking agent hexamethonium.
-
3.
Pretreatment with atropine significantly reduced, but did not abolish the increase in intestinal blood flow elicited by capsaicin.
-
4.
Concomitant administration of somatostatin significantly inhibited both the atropine-sensitive and the atropineresistant components of the effect of capsaicin injected into the superior mesenteric artery.
-
5.
Our results indirectly support the assumption that the intestinal vasodilatatory effect of capsaicin may be mediated by substance P release from capsaicin-sensitive paravascular nerve fibres associated with the blood vessels of the gastrointestinal tract. It is suggested that sensory substance P-containing nerve fibres may be involved in the regulation of the vascular reactions of the gut.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ault B, Evans H (1980) Depolarizing action of capsaicin on isolated dorsal root fibres of the rat. J Physiol (Lond) 306:22P
Baraz LA, Khayutin VM, Molnár J (1968) Analysis of the stimulatory action of capsaicin on receptors and sensory fibres of the small intestine in the cat. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung 33:225–235
Barja F, Mathison R, Huggel H (1983) Substance P-containing nerve fibres in large peripheral blood vessels of the rat. Cell Tiss Res 229:411–422
Barthó L, Holzer P, Lembeck F, Szolcsányi J (1982) Evidence that the contractile response of the guinea-pig ileum to capsaicin is due to release of substance P. J Physiol (Lond) 332:157–167
Björkroth U (1983) Inhibition of smooth muscle contractions induced by capsaicin and electrical transmural stimulation by a substance P antagonist. Acta Physiol Scand Supp 515:11–16
Brownlee KA (1965) Statistical theory and methodology in science and engineering. John Wiley and Sons, New York London Sydney
Bucsics A, Lembeck F (1981) In vitro release of substance P from spinal cord slices by capsaicin congeners. Eur J Pharmacol 71:71–77
Chahl LA (1982) Evidence that the contractile response of the guinea-pig ileum to capsaicin is due to substance P release. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 319:212–215
Dalsgaard C-J, Vincent SR, Hökfelt T, Lundberg JM, Dahlström A, Schultzberg M, Dockray GJ, Cuello AC (1982) Coexistence of cholecystokinin-and substance P-like peptides in neurons of the dorsal root ganglia of the rat. Neurosci Lett 33:159–163
Donnerer J, Barthó L, Holzer P, Lembeck F (1983) Peristalsis and release of substance P from the vascularly perfused small intestine of the guinea-pig. In: Skrabanek P, Powell D (eds) Substance P — Dublin 1983. Boole Press, Dublin, Ireland, pp 119–120
Furness JB, Papka RE, Della NG, Costa M, Eskay RL (1982) Substance P-like immunoreactivity in nerves associated with the vascular system of guinea-pigs. Neuroscience 7:447–459
Gamse R, Molnar A, Lembeck F (1979) Substance P release from spinal cord slices by capsaicin. Life Sci 25:629–639
Gamse R, Holzer P, Lembeck F (1980) Decrease of substance P in primary afferent neurones and impairment of neurogenic plasma extravasation by capsaicin. Br J Pharmacol 68:207–213
Gazelius B, Brodin E, Olgart L, Panopoulos P (1981) Evidence that substance P is a mediator of antidromic vasodilatation using somatostatin as a release inhibitor. Acta Physiol Scand 113:155–159
Grönstad KO, Yeo C, Ahlman H, Jaffe BM, Zinner MJ (1983) The effect of endoluminal substance P on jejunal blood flow. In: Skrabanek P, Powell D (eds) Substance P — Dublin 1983 Boole Press, Dublin, Ireland, pp 133–134
Holzer P, Bucsics A, Lembeck F (1982) Distribution of capsaicinsensitive nerve fibres containing immunoreactive substance P in cutaneous and visceral tissues of the rat. Neurosci Lett 31:253–257
Holzer P, Gamse R, Lembeck F (1980) Distribution of substance P in the rat gastrointestinal tract — lack of effect of capsaicin pretreatment. Eur J Pharmacol 61:303–307
Hökfelt T, Lundberg JM, Jancsó G, Kimmel J (1981) Avian pancreatic polypeptide (APP) immunoreactive neurons in the spinal cord and spinal trigeminal nucleus. Peptides 2:81–87
Hökfelt T, Skirboll L, Dalsgaard C-J, Johansson O, Lundberg JM, Norell G, Jancsó G (1982) Peptide neurons in the spinal cord with special reference to descending systems. In: Sjölund B, Björklund A (eds) Brain strem control of spinal mechanisms. Elsevier Biomedical Press, pp 89–117
Jancsó G (1981) Chemosensitive primary sensory neurones: some morphological and functional characteristics. In: Brown AG, Réthelvi M (eds) Spinal cord sensations. Scottish Academic Press, Edinburgh, pp 55–56
Jancsó G, Király E, Jancsó-Gábor A (1977) Pharmacologically induced selective degeneration of chemosensitive primary sensory neurones. Nature 270:741–743
Jancsó G, Király E, Jancsó-Gábor A (1980) Chemosensitive pain fibres and inflammation. Int J Tiss Reac 2:57–66
Jancsó G, Hökfelt T, Lundberg JM, Király E, Halász N, Nilsson G, Terenius L, Rehfeld J, Steinbusch H, Verhofstad A, Elde RP, Said S, Brown M (1981) Immunohistochemical studies on the effect of capsaicin on spinal and medullary peptide and monoamine neurones using antisera to substance P, gastrin/CCK somatostatin, VIP, enkephalin, neurotensin and 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Neurocytol 10:963–980
Jancsó G, Such G (1983) Effects of capsaicin applied perineurally to the vagus nerve on cardiovascular and respiratory functions in the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 341:359–370
Jancsó N (1960) Role of the nerve terminals in the mechanism of inflammatory reactions. Bull Millard Filmore Hosp Buffalo NY 7:53–57
Lawson SN, Nickels SM (1980) The use of morphometric techniques to analyze the effect of neonatal capsaicin treatment on rat dorsal root ganglia and dorsal roots. J Physiol (Lond) 303:12P
Lembeck F, Donnerer J, Barthó L (1982) Inhibition of neurogenic vasodilatation and plasma extravasation by substance P antagonists, somatostatin and (d-met2, pro5) enkephalinamide. Eur J Pharmacol 35:171–176
Lembeck F, Holzer P (1979) Substance P as mediator of antidromic vasodilatation and nerogenic plasma extravasation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 310:175–183
Longhurst JC, Ashton JH, Iwamoto GA (1980) Cardiovascular reflexes resulting from capsaicin-stimulated gastric receptors in anesthetized dogs. Circ Res 46:780–788
Lundberg JM, Saria A (1983) Capsaicin-induced desensitization of airway mucosa to cigarette smoke, mechanical and chemical irritants. Nature 302:251–253
Miller ME, Christensen GC, Evans HE (1964) Anatomy of the dog. Saunders, Philadelphia London
Nagy JI, Vincent SR, Staines WA, Fibiger HC, Reisine TD, Yamamura HI (1980) Neurotoxic action of capsaicin on spinal substance P neurons. Brain Res 186:435–444
Nagy JI, Iversen LL, Goedert M, Chapman D, Hunt SP (1983) Dose-dependent effects of capsaicin on primary sensory neurons in the neonatal rat. J Neurosci 3:399–406
Porszász J, György L, Porszász-Gibiszer K (1955) Cardiovscular and respiratory effects of capsaicin. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung 8:61–76
Priestley JV, Bramwell S, Butcher LL, Cuello AC (1982) Effect of capsaicin on neuropeptides in areas of termination of primary sensory neurones. Neurochem Internat 4:57–65
Rózsa Zs, Varró V (1984) Effects of somatostatin on the circulation of the small intestine in dogs. Regul Pep (in press)
Saria A, Lundberg JM, Hua X, Lembeck F (1983) Capsaicin-induced substance P release and sensory control of vascular permeability in the guinea-pig ureter. Neurosci Lett 41:167–172
Scadding JW (1980) The permanent anatomical effects of neonatal capsaicin on somatosensory nerves. J Anat 131:473–484
Schrauwen E, Houvenaghel A (1980) Substance P: a powerful intestinal vasodilator in the pig. Pflügers Arch 386:281–284
Yaksh TL, Jessel TM, Gamse R, Mudge AW, Leeman SE (1980) Intrathecal morphine inhibits substance P release from mammalian spinal cord in vivo. Nature 286:155–157
Yanagisawa M, Nakano S, Otsuka M (1980) Capsaicin-induced depolarization of primary afferent fibres and the release of substance P from isolated rat spinal cord. Biomed Res 1:88–90
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rózsa, Z., Jancsó, G. & Varró, V. Possible involvement of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves in the regulation of intestinal blood flow in the dog. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 326, 352–356 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501442
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501442