Abstract
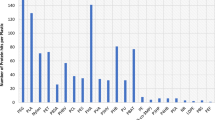
The present study demonstrates the potential hydrolytic activities in the symbiont-containing tissues of the vent invertebrates Riftia pachyptila, Bathymodiolus thermophilus (collected in 1991 at the East Pacific Rise) and the shallow-water bivalve Lucinoma aequizonata (collected in 1991 from the Santa Barbara Basin). Activities of phosphatases, esterases, β-glucuronidase and leucineaminopeptidase were comparable to those of digestive tract tissues of other marine invertebrates. A lack in most glycosidases as well as in trypsin and chymotrypsin was observed. Activities of lysozyme and chitobiase were rather high. In all vent invertebrates with symbionts and in L. aequizonata, the symbiont-containing tissues and the symbiont-free tissues had similar levels of enzymatic activities, indicating that polymeric nutrients could be hydrolysed after release from the symbionts and cellular uptake. The high activities of α-fucosidase in all vent invertebrates as well as in the shallow-water bivalve L. aequizonata could point to the existence of a yet undescribed substrate available to hydrolysation. The ectosymbionts-carrying polychaete Alvinella pompejana (collected in 1991 at the East Pacific Rise, EPR) shows high lysozyme activities in its gut, consistent with the proposed food source of bacteria. For the vent crab Bythogrea thermydron (also collected in 1991 at the EPR) hydrolytic activities were highest in the gut, dominated by esterase and peptidase activities which support their proposed carnivorous food source. A snail and a limpet collected from R. pachyptila tubes showed high levels of chitobiase suggesting a food source of grazed bacteria or ingested R. pachyptila tube.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alayse-Danet AM, Desbruyères D, Gaill F (1987) The possible nutritional or detoxification role of the epibiotic bacteria of Alvinellid polychaetes: review of current data. Symbiosis 4:51–62
Allen JA (1958) On the basic form and adaptation to habitat in the Lucinacea (Eulamellibranchiata). Phil Trans R Soc Lond 241: 421–484
Anderson AE, Childress JJ, Favuzzi JA (1987) Net uptake of CO2 driven by sulfide and thiosulfate oxidation in the bacterial symbiont-containing clam Solemya reidi. J exp Biol 133:1–31
Angeles de Pedro M, Reglero A, Cabezas J (1978) Purification and some properties of α-fucosidase from Littorina littorea L. Comp Biochem Physiol 60B:379–382
Bärlocher F, Arsuffi TL, Newell SY (1989) Digestive enzymes of the saltmarsh periwinkle Littorina irrorata (Mollusca: Gastropoda). Oecologia 80:39–43
Bosch C, Grassé PP (1984) Cycle partiel des bacteries chimioautotrophes symbiotiques et leurs rapports avec les bacteriocytes chez Riftia pachyptila Jones (Pogonophore Vestimentifère). I. Le trophosome et les bacteriocytes. C r hebd Séanc Acad Sci, Paris 299:413–419
Boss KJ, Turner RD (1980) The giant white clam from the Galapagos rift, Calyptogena magnifica spec. n. Malacologia 20:161–194
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye-binding. Analyt Biochem 72:248–254
Calow P, Calow LJ (1975) Cellulase activity and niche separation in freshwater gastropods. Nature Lond 255:478–480
Cary SC, Vetter RD, Felbeck H (1989) Habitat characterization and nutritional strategies of the endosymbiont-bearing bivalve Lucinoma aequizonata. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 55:31–45
Childress JJ, Fisher CR (1992) The biology of hydrothermal vent animals: physiology, biochemistry and autotrophic symbioses. Oceanogr mar Biol A Rev 30:337–441
Desbruyères D, Gaill F, Laubier L, Fouquet Y (1985) Polychaetous annelids from hydrothermal vent ecosystems: an ecological overview. Bull biol Soc Wash 6:103–116
Desbruyères D, Gaill F, Laubier L, Prieur D, Rau GH (1983) Unusual nutrition of the Pompei worm Alvinella pompejana (Polychaetous Anellid) from a hydrothermal vent environment: SEM, TEM 13C and 15N evidence. Mar Biol 75:201–205
DeBurgh ME (1986) Evidence for a physiological gradient in the vestimentiferan trophosome: size-frequency analysis of bacterial populations and trophosome chemistry. Can J Zool 64:1095–1103
Diez T, Cabezas JA (1979) Properties of two molecular forms of β-glucuronidase from the mollusc Littorina littorea L. Eur J Biochem 93:301–311
Distel DL, Felbeck H (1987) Bacteria-bearing in the lucinid clams Lucinoma aequizonata, Lucinoma annulata and Lucina floridana: the functional morphology of an endosymbiotic system. Mar Biol 96:79–86
Fiala-Médioni A, Felbeck H (1990) Autotrophic processes in invertebrate nutrition: bacterial symbiosis in bivalve molluscs. In: Mellinger J (ed) Animal nutrition and transport processes. 1. Nutrition in wild and domestic animals, Vol 5. Comp Physiol, Basel, Karger, pp 49–69
Fiala-Médioni A, Métivier C, Herry A, Le Pennec M (1986) Ultrastructure of the gill filament of a hydrothermal vent Mytilidae. Mar Biol 92:65–72
Fiala-Médioni A, Michalski JC, Jollès J, Alonso C, Montreuil J (1994) Lysosomic and lysozyme activities in the gill of bivalves from deep hydrothermal vents. C r hebd Séanc Acad Sci Paris 317:239–244
Fisher CR (1990) Chemoautotrophic and methanotrophic symbiosis in marine invertebrates. Rev aquat Sciences 2 (3–4):399–436
Fisher CR, Childress JJ (1986) Translocation of fixed carbon from symbiotic bacteria to host tissues in the gutless bivalve Solemya reidi. Mar Biol 93:59–68
Fisher CR, Childress JJ, Oremland RS, Bidigare RR (1987) The importance of methane and thiosulfate in the metabolism of the symbionts of two deep-sea mussels. Mar Biol 96:59–71
Fisher CR, Childress JJ, Sanders NK (1988) The role of vestimentiferan hemoglobin in providing an environment suitable for chemoautotrophic sulfide oxidizing endosymbiosis. Symbiosis 5:229–246
Gage JD, Tyler PA (1991) Deep-sea biology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gaill F, Hunt S (1986) Tubes of hydrothermal vent worms Riftia pachyptila (Vestimentifera) and Alvinella pompejana (Annelida). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 34:267–274
Gianfreda L, Imperato A, Palescandolo R, Scardi V (1979) Distribution of β-1,4-glucanase and β-glucosidase acitivities among marine molluscs with different feeding habits. Comp Biochem Physiol 63B:345–348
Grossmann S, Reichardt W (1991) Impact of Arenicola marina on bacteria in intertidal sediments. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 77:85–93
Gonzales JM, Sherr BF, Sherr EB (1993) Digestive enzyme activity as a quantiative measure of protistan grazing: the acid lysozyme assay for bacterivory. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 100:197–206
Hand SC (1987) Trophosome ultrastructure and the characterization of isolated bacteriocytes from invertebrate-sulfur bacteria symbioses. Biol Bull mar biol Lab, Woods Hole 173:260–276
Head EJH, Wang R, Conover RJ (1984) Comparison of diurnal feeding rhythms in Temora longicornis and Centropages hamatus with digestive enzyme activity. J Plankton Res 6:543–550
Hugon J, Borgers M (1968) Fine structural association of acid and alkaline phosphatase activities in the absorbing cells of the duodenum of rodents. Histochemie 12:42–66
Hylleberg J (1976) Resource partitioning on basis of hydrolytic enzymes in deposit-feeding mud snails (Hydrobiidae). Oecologia 23:15–125
Köster M, Jensen P, Meyer-Reil LA (1991) Hydrolytic activities of organisms and hiogenic structures in deep-sea sediments. In: Chróst RJ (ed) Microbial enzymes in aquatic environments. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 298–310
Kristensen JH (1972) Carbohydrases of some marine invertebrates with notes on their food and on the natural occurrence of the carbohydrates studied. Mar Biol 14:130–142
Laubier L, Desbruyères D, Chassard-Bouchaud C (1983) Microanalytical evidence of sulfur accumulation in a polychaete from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Mar Biol Lett 4:113
Le Pennec M, Henry A, Lutz R, Fiala-Médioni A (1988) Premières observations ultrastructurales de la branchie d'un bivalve Pectriuidae hydrothermal profond. C r hebd Séanc Acad Sci Paris 307:627–633
Le Pennec M, Fiala-Médioni A (1988) The role of the digestive tract of Calyptogena laubieri, vescomid bivalves of the subduction zones of Japan. Oceanol Acta 11:193–199
Le Pennec M, Martinez JC, Donval A, Herry A, Beninger P (1992) Enzymologie du tractus digestif de la modiole hydrothermale Bathymodiolus thermophilus (Mollusque Bivalve). Can J Zool 70:2298–2302
Le Pennec M, Prieur D (1984) Observations sur la nutrition d'un Mytilidae d'un site hydrothermal actif de la dorsale du Pacific Oriental. C r hebd Séanc Sci, Paris 29:493–498
Mathers NF (1973) A comparative histochemical survey of enzymes associated with the process of digestion in Ostra edulis and Crassostrea angulata (Mollusca: Bivalvia). J Zool Lond 169:169–179
Mayasich SA, Smucker RA (1986) Glycosidases in the American oyster Crassostrea virginica Gmelin, digestive tract. J exp mar Biol Ecol 95:95–98
McHenery JG, Allen JA, Birkbeck TH (1986) Distribution of lysozyme-like activity in 30 bivalve species. Comp biochem Physiol 85B 3:581–584
McHenery JG, Birkbeck TH, Allen JA (1979) The occurence of lysozyme in marine bivalves. Comp Biochem Physiol 63B:25–28
Morton B (1983) Feeding and digestion in Bivalvia. In: Saleuddin ASM, Wilbur KM (eds) Mollusca, 5. Physiology (II). Academic Press, New York, pp 65–174
Morton B (1986) The functional morphology of the organs of feeding and digestion of the hydrothermal vent bivalve Calptogena magnifica (Vesicomyidae). J Zool Lond (Ser A) 208:83–98
Onishi T, Suzuki M, Kikuchi R (1984) The distribution of polysaccharide hydrolase activity in gastropods and bivalves. Tokyo Reg Fish Res Lab 744:301–308
Page HM, Fiala-Médioni A, Fisher CR, Childress JJ (1991) Experimental evidence for filter-feeding by the hydrothermal vent mussel, Bathymodiolus thermophilus. Deep-Sea Res 38A:1455–1461
Powell MA, Somero GN (1986) Adaptation to sulfide by hydrothermal vent animals: sites and mechanisms of detoxification and metabolism. Biol bull mar biol Lab, Woods Hole 171:274–290
Reid RGB (1966) Digestive tract enzmyes in the bivalves Lima hinas (Gmelin) and Mya arenaria (L.). Comp biochem Physiol 17:417–433
Reid RGB, Bernard FR (1980) Gutless bivalves. Science, NY 208:609–610
Somero GN, Childress JJ, Anderson AE (1989) Transport, metabolism and detoxification of hydrogen sulfide in animals from sulfide-rich marine environments. CRC critical Rev aquat Sci 1:591–614
Sova VV, Elyakova LA, Vaskovsky VE (1970) The distribution of laminarases in marine invertebrates. Comp biochem Physiol 32:459–464
Stuart V, Head EJH, Mann KH (1985) Seasonal changes in the digestive enzyme levels of the amphipod Corophium volutator Pallas in relation to diet. J exp mar Biol Ecol 88:243–256
Tuttle JH (1985) The role of the sulfur-oxidizing bacteria at deepsea hydrothermal vents. Bull Biol Soc Wash 6:335–343
Warén A, Bouchet P (1989) New gastropods from East Pacific hydrothermal vents. Zool Scr 18:67–102
Weel PB van (1961) The comparative physiology of digestion in molluscs. Am Zool 1:245–252
Weisner B (1984) Lysozyme (Muramidase). In: Bergmeyer HU, Bergmeyer J, Grassl M (eds) Methods of enzymatic analysis, Vol. IV. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 189–195
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boetius, A., Felbeck, H. Digestive enzymes in marine invertebrates from hydrothermal vents and other reducing environments. Marine Biology 122, 105–113 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349283
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349283