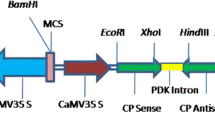
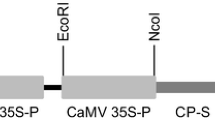
Abstract
Soybean (Glycine max. Merrill. cv. Fayette) cotyledonary nodes were transformed with bean pod mottle virus (BPMV) coat protein precursor (CP-P) gene via Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. The transformation rate was low, and only five primary transformants derived from five different cotyledons were obtained from 400 original cotyledons. Southern blot hybridization verified the integration of the BPMV CP-P gene. Inheritance and expression of this gene in R1 plants were also demonstrated. About 30% of R2 plants derived from one transgenic line showed complete resistance to BPMV infection, as assessed by symptomatology and ELISA, suggesting that homozygous, but not hemizygous, plants exhibit the resistant phenotype.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAP:
-
6-benzyladenine phosphate
- BPMV:
-
bean pod mottle virus
- CP-P:
-
coat protein-precursor
- CTAB:
-
hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide
- DAS-ELISA:
-
double antibody sandwich-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- IBA:
-
indole-butyric acid
- kbp:
-
kilobase pairs
- MES:
-
2-(N-Morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid
- NOS:
-
nopaline synthase
- NPTII:
-
neomycin phosphotransferase II
- NTP:
-
nucleoside triphosphate
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- PVP:
-
polyvinyl pyrrolidone
- VPg:
-
viral genome-linked protein
References
An G, Ebert PR, Mitra A, Ha SB (1988) Plant Mol Biol Manual A3:1–19
Anjos RJ, Jarlfors U, Ghabrial SA (1992) Phytopathology 82:1022–1027
Bennett MD, Smith JB (1976) Phil Trans R Soc London Ser. B. 274:227–274
Calvert LA, Ghabrial SA (1983) Phytopathology 73:992–997
Chee PP, Drong R F, Slightom JL (1991) Plant Mol Biol Manual C3:1–28
Christou P, Murphy JE, Swain WF (1987) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3962–3966
Christou P (1990) Ann Bot 66:379–386
Christou P, McCabe DE (1992) Plan J 2:283–290
Christou P, McCabe DE, Swain WF (1988) Plant Physiol 87:671–674
Christou P, Swain WF, Yang NS, McCabe DE (1989) Proc.Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 86:7500–7504
Finer JJ, McMullen MD (1991) In vitro Cell Dev Biol 27P:175–182.
Fitchen JH, Beachy RN (1993) Ann Rev Microbiol 27:739–763.
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
Ghabrial SA (1992) Rice Biotech Quart 12:23–24
Ghabrial SA, Schultz FJ (1983) Phytopathology 73:480–483
Ghabrial SA, Hershman DE, Johnson DW, Yan D (1990) Plant Dis 74:132–134
Goldbach R, Martelli GP, Milne RG (1995) In: Murphy FA, Fauquet CM, Bishop DHL, Ghabrial SA, Jarvis, AW, Martelli, GP, Mayo MA, Summers MD (eds), Virus Taxonomy, Springer-Verlag, Wien New York, pp 341–347.
Hepburn AG, White j, Pearson L, Maunders MJ, Clarke LE, Prescott AG, Blundy KS (1985) J Gen Microbiol 131:2961–2969
Hinchee MA, Connor-Ward DV, Newell CA, McDonell RE, Sato SJ, Gasser CS, Fischhoff DA, Re DB, Fraley RT, Horsch RB (1988) Bio/Tech 6:923–928
Lin W, Odell JT, Schreiner RM (1987) Plant Physiol 84:856–861
MacFarlane SA, Shanks M, Davies JW, Zlotnick A, Lomonossoff GP (1991) Virology 183:405–409
Matthysse AG, Gurlitz RHG (1982) Physiol Plant Path 21:381–387
McCabe DE, Swain WF, Martinelli BJ, Christou P (1988) Bio/technology 6:923–926
Nida DL, Anjos RJ, Lomonossoff GP, Ghabrial SA (1992) J Gen Virol 73:157–163
Pasternak JJ (1993) In: Glick BR, Thompson JE, (eds), Methods in Plant Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL., pp 29–36
Rogers SG, Klee HJ, Horsch RB, Fraley RT (1987) Meth Enzymol 153:253–277
Ross OP (1968) Plant Dis Rep 52:344–348
Ross OP, Butler AK (1985) Plant Dis 69:101–103
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning, a Laboratory Manual, 2nd edition, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Sato S, Newell C, Kolacz K, Tredo L, Finer J, Hinchee M (1993) Plant Cell Rep 12:408–413
Sinclair JB, Packman PA (1989) Compendium of soybean diseases, 3rd edition, American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul, MN, pp 106
Torisky RS, Griffin JD, Yenofsky RL, Polacco JC (1994) Mol Gen Genet 242:404–414.
Wright M S, Koehler SM, Hinchee MA, Carnes MG (1986) Plant Cell Rep 5:150–154
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by W. A. Parrott
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di, R., Purcell, V., Collins, G.B. et al. Production of transgenic soybean lines expressing the bean pod mottle virus coat protein precursor gene. Plant Cell Reports 15, 746–750 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232220
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232220