Abstract
We compared the hyperglycaemic effect of intranasal and intramuscular (i.m.) administration of glucagon after insulin-induced hypoglycaemia.
Twelve healthy subjects were examined twice, receiving on both occasions an intravenous insulin bolus. Somatostatin and propranolol were administered to block endogenous glucose counterregulation, and glucose turnover was estimated by a 3-[3H]-glucose infusion. When hypoglycaemia was reached, the subjects received either i.m. glucagon of pancreatic extraction (1 mg) or intranasal genetically engineered glucagon (2 mg).
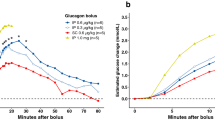
The incremental values for plasma glucose concentrations 15 min after intranasal and i.m. administration of glucagon differed marginally. However, after 5 min the glucose appearance rate, as well as the incremental values for plasma glucose, were significantly higher for the i.m. glucagon treatment. The mean time taken for incremental plasma glucose to exceed 3 mmol·l−1 was significantly shorter for i.m. glucagon. The mean plasma glucagon level increased faster after i.m. glucagon than after intranasal glucagon, and the levels remained higher throughout the study period.
We conclude that glucose recovery was significantly better after i.m. administration of glucagon than after intranasal administration. However, the differences between the incremental plasma glucose and the time for incremental plasma glucose to exceed 3 mmol·l−1 were not considered of major clinical importance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hvidberg A, Jørgensen S, Hilsted J (1992) The effect of genetically engineered glucagon on glucose recovery in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 34: 547–550
Samanta A, Burden AC, Feehally J, Walls J (1986) Awareness and use of glucagon in diabetics treated with insulin. BMJ 293: 367–368
Pontiroli A, Alberetto M, Pozza G (1983) Intranasal glucagon raises blood glucose concentrations in healthy volunteers. BMJ 287: 462–463
Jørgensen S, Sørensen AR, Kimer LL, Mygind N (1991) A powdery formulation of glucagon for nasal delivery-a phase 1 study. Diabetes 40 [Suppl A]: 2190
Steele R (1959) Influences of glucose loading and of injected insulin on hepatic glucose output. Ann N Y Acad Sci 82: 420–430
De Bodo RC, Steele R, Altszuler N, Dunn A, Bishop JS (1963) On the hormonal regulation of carbohydrate metabolism; studies with C14 glucose. Recent Prog Horm Res 19: 445–488
Cherrington AD, Vranic M (1973) Effect of arginine on glucose turnover and plasma free fatty acids in normal dogs. Diabetes 22: 537–543
Hills M, Armitage P (1979) The two-period cross-over clinical trial. Br J Clin Pharmacol 8: 7–20
Hirai S, Yashiki T, Mima H (1978) Nasal absorption of insulin in dogs. Diabetes 17: 296–299
Drejer K, Vaag A, Bech K, Hansen P, Mygind N (1992) Intranasal administration of insulin with phospholipid as absorption enhancer: pharmacokinetics in normal subjects. Diabetes Med 9: 335–340
Rosenfalck AM, Bendtson I, Jørgensen S, Binder C (1992) Nasal glucagon in the treatment of hypoglycaemia in type 1 (insulin dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 17: 43–50
Pontiroli A, Alberetto M, Pozza G (1985) Metabolic effects of intranasally administered glucagon: comparison with intramuscular and intravenous injection. Acta Diabetol Lat 22: 103–110
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hvidberg, A., Djurup, R. & Hilsted, J. Glucose recovery after intranasal glucagon during hypoglycaemia in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 46, 15–17 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195909
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195909