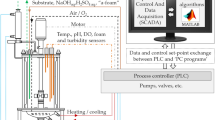
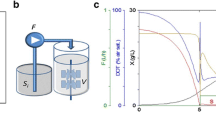
Summary
A recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae producing hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) exhibited growth-assciated product formation. By controlling the medium feed rate, based on the calculated amount of medium required for 1 h, a constant specific growth rate was obtained in the range of 1.12-0.18 h−1. In order to prolong the exponential growth phase, the medium feed rate was increased exponentially. A fedbatch cultivation method based on the production kinetics of batch culture enhanced HBsAg production ten times more than in batch culture. The reason for the increase can be explained by the fact that the production of HBsAg is expressed as an exponential function of time when the specific growth rate is controlled to a constant value in growth-associated product fromation kinetics. In the scale-up of this culture to 91, the specific growth rate could also be maintained constant and the HBsAg production trend was similar to that in a 1-l culture. However, ethanol accumulation occurred at a late stage in fed-bach culture. Ethanol produced was not reutilized and inhibited further cell growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiba S, Nagai S, Nishizawa Y (1976) Fed batch culture of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a perspective of computer control to enhance the productivity in baker's yeast cultivation. Biotechnol Bioeng 1:1001–1006
Bitter GA, Egan KM, Burnette WN, Samal B, Fieschko JC, Peterson DL, Downing MR, Wypych J, Langley KE (1988) Hepatitis B vaccine produced in yeast. J Med Virol 25:123–140
Fieschko JC, Egan KM, Ritch T, Koski RA, Jones M, Bitter GA (1987) Controlled expression and purification of human immune interferon from high-cell-density fermentations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in fed-batch. Biotechnol Bioeng 29:1113–1121
Gu MB, Jung KH, Park MH, Shin KS, Kim KH (1989) Production of HBsAg by growth rate control with recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae in fed-batch. Biotechnol Lett 11:1–4
Hsieh JH, Shih KY, Kung HF, Shiang M, Lee LY, Meng MH, Chang CC, Lin HM, Shih SC, Lee SY, Chow TY, Feng TY, Kuo TT, Choo KB (1988) Controlled fed-batch fermentation of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce hepatitis B surface antigen. Biotechnol Bioeng 32:334–340
Imanaka T, Aiba S (1981) A perspective on the application of genetic engineering: stability of recombinant plasmid. Ann NY Acad Sci 369:1–14
Kleinman MJ, Gingold EB, Stanbury PF (1986) The stability of the yeast plasmid pJDB248 depends on growth rate of the culture. Biotechnol Lett 8:225–230
Park MH, Kim SJ, Gu MB, Jung KH, Song HB, Park KN, Kim KH (1988) Studies on the yeast-derived hepatitis B vaccine. J Korean Soc Virol 18:11–19
Parker C, DiBiasio D (1987) Effect of growth rate and expression level on plasmid stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 29:215–221
Siegel R, Ryu DY (1985) Kinetic study of instability of recombinant plasmids pPlc25 TrpA1 in E. coli using two-stage continuos culture system. Biotechnol Bioeng 27:28–33
Valenzuela P, Medina A, Rutter WJ (1982) Synthesis and assembly of hepatitis B virus surface antigen particles in yeast. Nature 298:347–350
Wang H, Cooney CL, Wang DIC (1977) Computer-aided baker's yeast fermentations. Biotechnol Bioeng 19:69–86
Woehrer W, Roehr M (1981) Regulatory aspects of baker's yeast metabolism in aerobic fed-batch cultures. Biotechnol Bioeng 23:567–581
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: M. B. Gu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, M.B., Park, M.H. & Kim, DI. Growth rate control in fed-batch cultures of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae producing hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 35, 46–50 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180634
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180634