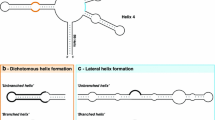
Summary
Computer-based structural analysis of the ribosomal DNA intergenic spacer (IGS) from the mosquito Aedes albopictus revealed a potential to form strong and extensive secondary structures throughout a 4.7-kilobase (kb) region. The predicted stability of secondary structures was particularly high within a 3.15-kb region containing 17 tandem 201 base-pair subrepeats. Similarly strong secondary structure potential was also found when IGS subrepeats were analyzed from 17 phylogenetically diverse eukaryotes, including vertebrates, invertebrates, and plants. Conservation of higher-order structure potential in the IGS region of ribosomal DNA may reflect evolutionary and functional constraints on chromatin organization, transcriptional regulation of the ribosomal RNA genes, and/or transcript processing and stability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bach R, Allet B, Crippa M (1981) Sequence organization of the spacer in the ribosomal genes of Xenopus clivii and Xenopus borealis. Nucleic Acids Res 9:5311–5330
Bachvarov D, Normandeau M, Moss T (1991) Heterogeneity in the Xenopus ribosomal transcription factor xUBF has a molecular basis distinct from that in mammals. FEBS Lett 288: 55–59
Baldridge GD, Fallon AM (1992) Primary structure of the ribosomal DNA intergenic spacer from the mosquito Aedes albopictus. DNA & Cell Biol 11:51–59
Barker RF, Harberd NP, Jarvis MG, Flavell RB (1988) Structure and evolution of the intergenic region in a ribosomal DNA repeat unit of wheat. J Mol Biol 201:1–17
Beach RF, Mills D, Collins FH (1989) Structure of ribosomal DNA in Anopheles albimanus (Diptera: Culicidae). Ann Ent Soc Amer 82:641–648
Bell SP, Jantzen H-M, Tijan R (1990) Assembly of alternative multiprotein complexes directs rRNA promoter selectivity. Genes & Develop 4:943–954
Bianchi ME, Beltrame M, Paonessa G (1989) Specific recognition of cruciform DNA by nuclear protein HMGl. Science 243:1056–1059
Clark CG (1987) On the evolution of ribosomal RNA. J Mol Evol 25:343–350
Clouet D'Orval B, D'Aubenton Carfa Y, Sirand-Pugnet P, Gallego M, Brody E, Marie J (1991) RNA secondary structure repression of a muscle-specific exon in Hela cell nuclear extracts. Science 252:1823–1828
Cross NCP, Dover GA (1987) Tsetse fly rDNA: an analysis of structure and sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 15:15–30
Delcasso-Tremousaygue D, Grellet F, Panabieres F, Ananiev ED, Delseny RM (1988) Structural and transcriptional characterization of the external spacer of a ribosomal RNA nuclear gene from a higher plant. Eur J Biochem 172:767–776
Dimitrov SI, Stefanovsky VY, Karagyozov L, Angelov D, Pashev IG (1990) The enhancers and promoters of the Xenopus laevis ribosomal spacer are associated with histones upon active transcription of the ribosomal genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 18:6393–6397
Dover GA (1982) Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature 299:111–117
Dover GA, Flavell RB (1984) Molecular coevolution: DNA divergence and the maintenance of function. Cell 38:622–623
Gale K, Crampton J (1989) The ribosomal genes of the mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Eur J Biochem 185:311–317
Gerbi SA (1985) Evolution of ribosomal DNA. In: MacIntyre RJ (ed) Molecular evolutionary genetics. Plenum Press, New York pp 419–517
Gerbi SA, Jeppesen C, Stebbins-Boaz B, Ares Jr. M (1987) Evolution of eukaryotic rRNA: constraints imposed by RNA interactions. CSH Symp Quant Biol 11:709–719
Grummt I, Roth E, Paule M (1982) Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature 296:173–174
Hancock JM, Dover GA (1990) ‘Compensatory slippage’ in the evolution of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 18:5949–5954
Hemleben V, Ganal M, Gerstner J, Scheibd K, Torres R (1987) Organization and length heterogeneity of plant ribosomal RNA genes. In: Kahl G (ed) Architecture of eukaryotic genes. VCH, Weinheim, Germany, pp 371–384
Hisatake K, Nishimura T, Maeda Y, Hanada K, Song C-H, Muramatsu M (1991) Cloning and structural analysis of cDNA and the gene for mouse transcription factor UBF. Nucleic Acids Res 19:4631–4637
Ishikawa Y, Safrany G, Hisatake K, Tanaka N, Maeda Y, Kato H, Kominami R, Muramatsu M (1991) Structure of the core promoter of human and mouse ribosomal RNA gene. J Mol Biol 218:55–67
Jaeger JA, Turner DH, Zuker M (1989) Improved predictions of secondary structures for RNA. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 86:7706–7710
Jaeger JA, Turner DH, Zuker M (1990) Predicting optimal and suboptimal secondary structure for RNA. In: Doolittle RF (ed) Molecular evolution: computer analysis of protein and nucleic acid sequences. Meth in Enzymol 183:281–306
Jantzen H-M, Admon A, Bell SP, Tijan R (1990) Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature 344:830–836
Karpen GH, Schaefer JE, Laird CD (1988) A Drosophila rRNA gene located in euchromatin is active in transcription and nucleolus formation. Genes & Develop 2:1745–1763
Koller HT, Frondort KA, Maschner PD, Vaughn JC (1987) In vivo transcription from multiple spacer rRNA gene promoters during early development and evolution of the intergenic spacer in the brine shrimp Artemia. Nucleic Acids Res 15:5391–5410
Kubo M, Higo Y, Imanaka TJ (1990) Biological threshold values of procaryotic gene expression which is controlled by the DNA inverted repeat sequence and the mRNA secondary structure. J Ferment & Bioeng 69:305–307
Kuehn M, Arnheim N (1983) Nucleotide sequence of the genetically labile repeated elements 5' to the origin of mouse rRNA transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 11:211–224
Libri D, Piseri A, Fiszman MY (1991) Tissue-specific splicing in vivo of the β-tropomyosin gene: dependence on an RNA secondary structure. Science 252:1842–1845
Linares AR, Hancock JM, Dover GA (1991) Secondary structure constraints on the evolution of Drosophila 28S ribosomal RNA expansion segments. J Mol Biol 219:381–390
Mandal R (1984) The organization and transcription of eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Prog Nucleic Acids Res & Mol Biol 31:115–160
McLain DK, Collins FH (1989) Structure of rDNA in the mosquito Anopheles gambiae and rDNA sequence variation within and between species of the A. gambiae complex. Heredity 62:233–242
McMullen MD, Hunter B, Phillips RL, Rubenstein I (1986) The structure of the maize ribosomal DNA spacer region. Nucleic Acids Res 14:4953–4968
McStay B, Reeder RH (1990) An RNA polymerase I termination site can stimulate the adjacent ribosomal gene promoter by two distinct mechanisms in Xenopus laevis. Genes & Develop 4:1240–1251
Miller OL, Beatty BR (1969) Visualization of nucleolar genes. Science 164:955–957
Moss T, Bosely PG, Birnsteil ML (1980) More ribosomal spacer sequences from Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res 8:467–485
Muller MT, Pfund WP, Mehta VB, Trask DK (1985) Eukaryotic type I topoisomerase is enriched in the nucleolus and catalytically active on ribosomal DNA. EMBO J 4:1237–1243
Mullner EW, Kuhn LC (1988) A stem-loop in the 3′ untranslated region mediates iron-dependent regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA stability in the cytoplasm. Cell 53:815–825
Murtif VL, Rae PMM (1985) In vivo transcription of rDNA spacers in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res 13:3221–3239
Palacek E (1991) Local supercoil-stabilized DNA structures. Crit Rev Biochem & Mol Biol 26:151–226
Park YJ, Fallon AM (1990) Mosquito ribosomal RNA genes: characterization of gene structure and evidence for changes in copy number during development. Insect Biochem 20:1–11
Perry KL, Palukaitis P (1990) Transcription of tomato ribosomal DNA and the organization of the intergenic spacer. Mol Gen Genetics 221:102–112
Pikaard CS, Pape LK, Henderson SL, Ryan K, Paalman MH, Lopata MA, Reeder RH, Sollner-Webb B (1990) Enhancers for RNA polymerase I in mouse ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol 10:4816–4825
Reeder RH (1989) Regulatory elements of the generic ribosomal gene. Curr Opinions Cell Biol 1:466–474
Rose KM, Szopa J, Han F, Cheng Y, Richter A, Scheer U (1988) Association of DNA topoisomerase I and RNA polymerase I: a possible role for topoisomerase I in ribosomal gene transcription. Chromosoma 96:411–416
Simeone A, deFalco A, Macino G, Boncinelli E (1982) Sequence organization of the ribosomal spacer of D. melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res 10:8263–8272
Singh J, Dixon GH (1990) High mobility group I proteins 1 and 2 function as general class II transcription factors. Biochemistry 29:6295–6302
Sollner-Webb B, Tower J (1986) Transcription of cloned ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem 55:801–830
Sollner-Webb B, Mougey EB (1990) News from the nucleolus. Trends Biochem Sci 16:58–62
Sollner-Webb B, Pape L, Ryan K, Mougey EB, Poretta R, Nikolov E, Paalman MH, Lazdins I, Martin C (1991) Expression of mouse and frog rRNA genes: transcription and processing. Mol Cell Biochem 104:149–154
Stern DB, Radwanski ER, Kindle KL (1991) A 3′ stem/loop structure of the Chlamydomonas chloroplast atpB gene regulates mRNA accumulation in vivo. Plant Cell 3:285–297
Taira T, Kato A, Tanifuji S (1988) Difference between two major size classes of carrot rDNA repeating units is due to reiteration of sequences of about 460 by in the large spacer. Mol Gen Genetics 213:170–174
Takaiwa F, Kikuchi S, Oono K (1990) The complete nucleotide sequence of the intergenic spacer between 255 and 17S rDNAs in rice. Plant Mol Biol 15:933–935
Tautz D, Tautz C, Webb D, Dover GA (1987) Evolutionary divergence of promoters and spacers in the rDNA family of four Drosophila species. J Mol Biol 195:525–542
Trendelenburg MF, Gurdon JB (1978) Transcription of cloned Xenopus ribosomal genes visualized after injection into oocyte nuclei. Nature 276:292–294
Tsao YP, Wu HY, Liu LF (1989) Transcription-driven supercoiling of DNA: direct biochemical evidence from in vitro studies. Cell 56:111–118
Udvardy A, Louis C, Han S, Schedl P (1984) Ribosomal RNA genes of Drosophila melanogaster have a novel chromatin structure. J Mol Biol 175:113–130
Waga S, Mizuno S, Yoshida M (1990) Chromosomal protein HMG1 removes the transcriptional block caused by the cruciform in supercoiled DNA. J Biol Chem 265:19424–19428
Ward GK, Shihab-el-Deen A, Zannis-Hadjopoulos M, Price GB (1991) DNA cruciforms and the nuclear supporting structure. Exp Cell Res 195:92–98
Yavachev, LP, Georgiev OI, Braga EA, Avdonina TA, Bogmolova AE, Zhurkin VB, Nosikov VV, Hadjiolov AA (1986) Nucleotide sequence analysis of the spacer regions flanking the rat rRNA transcription unit and identification of repetitive elements. Nucleic Acids Res 14:2799–2810
Young LS, Dunstan HM, Witte PR, Smith TP, Ottonello S, Sprague KU (1991) A class III transcription factor composed of RNA. Science 252:542–546
Zhang H, Wang JC, Liu LF (1988) Involvement of DNA topoisomerase I in transcription of human ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 85:1060–1064
Zuker M (1989) On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science 244:48–52
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: G.D. Baldridge
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baldridge, G.D., Dalton, M.W. & Fallon, A.M. Is higher-order structure conserved in eukaryotic ribosomal DNA intergenic spacers?. J Mol Evol 35, 514–523 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00160212
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00160212