Summary
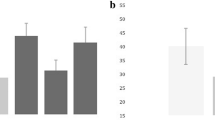
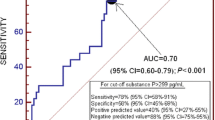
In previous studies, Katayama and our group have documented a massive increase in excitatory amino acid release following traumatic brain injury, in both rat fluid percussion, and humans [2,5]. To test the hypothesis that the magnitude of this “Excitotoxic Surge” plays a significant role in determining 6-month patient outcome. We have studied 83 consecutive severely head injured patients at the Medical College of Virginia for inclusion into this study. A microdialysis probe was placed within the cortex to continuously measure dialysate excitatory amino acids (Glutamate and Aspartate), along with several other analytes for approximately 5 days after injury. ICP, CPP, and MABP measurements were also time linked with each analyte measurement to create a neurochemical, clinical, and physiological “profile” for each patient. Outcome was determined by follow up using the Glasgow 6-Month outcome scale. A very strong correlation existed between the release of the EAA’s glutamate and aspartate after TBI (p < 0.0001). Patients with significantly elevated mean glutamate values for the entire monitoring period were most likely to exhibit elevated levels of ICP. The magnitude of glutamate released significantly correlates with 6-month patient outcome (p = 0.0234). When patients were subdivided by the CT diagnosis of lesion type, we found that those patients with contusions displayed the highest overall of EAA’s.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bullock R, Fujisawa H (1992) The role of glutamate antagonists for the treatment of CNS injury. J Neurotrauma 9: 5443–5546
Bullock R, Zauner A, Tsuji O, Woodward EE, Young HF, Marmarou AT (1994) Excitatory amino acid release after severe human head trauma: effect of intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure changes. In: Nagal H et al (eds) Intracranial pressure IX. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 264–267
Faden AI, Demediuk P, Panter SS, Vink R (1989) The role of excitatory amino acids and NMDA receptors in traumatic brain injury. Science 244: 798–800
Hillered L, Persson L, Carlson H, Ungerstedt U, Ronne-Engstrom E, Nilsson P (1979) Studies on excitatory amino acid receptor-linked brain disorders in rat and man using in vivo microdialysis. Clin Neuropharmacol 15: 95A-696A
Katayama Y, Becker DP, Tamura T, Hovda DA (1990) Massive increases in extracellular potassium and the indiscriminate release of glutamate following concussive brain injury. J Neurosurg 73: 889–990
Lindroth P, Mopper K (1979) High performance liquid chromatographic determination of sub-picomole amounts of amino acids by pre-column fluorescence derivatization with opthaldialdehyde. Anal Chem 51: 1667–1674
Nilsson P, Hillered L, Ponten U, Ungerstedt U (1990) Changes in cortical extracellular levels of energy-related metabolites and amino acids following concussive brain injury in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10: 631–637
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1998 Springer-Verlag Wien
About this paper
Cite this paper
Koura, S.S., Doppenberg, E.M.R., Marmarou, A., Choi, S., Young, H.F., Bullock, R. (1998). Relationship between Excitatory Amino Acid Release and Outcome after Severe Human Head Injury. In: Marmarou, A., et al. Intracranial Pressure and Neuromonitoring in Brain Injury. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplements, vol 71. Springer, Vienna. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6475-4_70
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6475-4_70
Publisher Name: Springer, Vienna
Print ISBN: 978-3-7091-7331-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-7091-6475-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive