Abstract
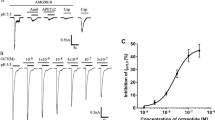
We showed that somatostatin (SST) exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects through somatostatin receptor subtypes 4 and 1 (sst4/sst1). Since cortistatin (CST) is a structurally similar peptide, we aimed at comparing the sst1- and sst4-binding and activating abilities, as well as the effects of SST-14 and CST-14 on inflammatory and nociceptive processes. CST-14 concentration-dependently displaced radiolabeled SST-14 binding, induced similar sst1 and sst4-activation with a less potency, and exerted significantly greater inhibitory effect on endotoxin-stimulated interleukin (IL)-1β production of murine peritoneal macrophages. Capsaicin-induced calcitonin gene-related peptide release from peripheral sensory nerve terminals of isolated rat tracheae was significantly decreased by 2 μM CST and 100 nM SST, but concentration-response correlation was not found. Mustard oil-evoked acute neurogenic plasma protein extravasation in the rat hindpaw skin, carrageenan-induced mouse paw edema, mechanical hyperalgesia, and IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α production, as well as mild heat injury-evoked thermal hyperalgesia were similarly attenuated by both peptides. In the latter case, i.pl. and i.p. injections exerted equal inhibitory actions. CST-14 and SST-14 similarly diminish both acute neurogenic and cellular inflammatory processes, as well as mechanical and heat hyperalgesia, in which their inhibitory effect on sensory nerve endings is likely to be involved. However, CST-14 exerts remarkably greater inhibition on cytokine production.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks WA, Schally AV, Barrera CM, Fasold MB, Durham DA, Csernus V, Groot K, Kastin A (1990) Permeability of the murine blood–brain barrier to some octapeptide analogs of somatostatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6762–6766
Bojnik E, Magyar A, Tóth G, Bajusz S, Borsodi A, Benyhe S (2009) Binding studies of novel, non-mammalian enkephalins, structures predicted from frog and lungfish brain cDNA sequences. Neuroscience 158(2):867–874
Bölcskei K, Horvath D, Szolcsanyi J, Petho G (2007) Heat injury-induced drop of the noxious heat threshold measured with an increasing-temperature water bath: a novel rat thermal hyperalgesia model. Eur J Pharmacol 564:80–87
Broglio F, Koetsveld Pv P, Benso A, Gottero C, Prodam F, Papotti M, Muccioli G, Gauna C, Hofland L, Deghenghi R, Arvat E, Van Der Lely AJ, Ghigo E (2002) Ghrelin secretion is inhibited by either somatostatin or cortistatin in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87(10):4829–4832
Capuano A, Currò D, Navarra P, Tringali G (2011) Cortistatin modulates calcitonin gene-related peptide release from neuronal tissues of rat. Comparison with somatostatin. Peptides 32(1):138–143
Carlton SM, Du J, Zhou S, Coggeshall RE (2001a) Tonic control of peripheral cutaneous nociceptors by somatostatin receptors. J Neurosci 21(11):4042–4049
Carlton SM, Du J, Davidson E, Zhou S, Coggeshall RE (2001b) Somatostatin receptors on peripheral primary afferent terminals: inhibition of sensitized nociceptors. Pain 90(3):233–244
Criado JR, Li H, Jiang X, Spina M, Huitrón-Reséndiz S, Liapakis G, Calbet M, Siehler S, Henriksen SJ, Koob G, Hoyer D, Sutcliffe JG, Goodman M, de Lecea L (1999) Structural and compositional determinants of cortistatin activity. J Neurosci Res 56(6):611–619
Dalm VA, van Hagen PM, van Koetsveld PM, Langerak AW, van der Lely AJ, Lamberts SW, Hofland LJ (2003a) Cortistatin rather than somatostatin as a potential endogenous ligand for somatostatin receptors in the human immune system. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88(1):270–276
Dalm VA, van Hagen PM, van Koetsveld PM, Achilefu S, Houtsmuller AB, Pols DH, van der Lely AJ, Lamberts SW, Hofland LJ (2003b) Expression of somatostatin, cortistatin, and somatostatin receptors in human monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285(2):E344–E353
Dalm VA, Hofland LJ, Ferone D, Croxen R, Lamberts SW, van Hagen PM (2003c) The role of somatostatin and somatostatin analogs in the pathophysiology of the human immune system. J Endocrinol Invest 26(8 Suppl):94–102
Delgado M, Ganea D (2008) Anti-inflammatory neuropeptides: a new class of endogenous immunoregulatory agents. Brain Behav Immun 22(8):1146–1151
Dong X, Han S, Zylka MJ, Simon MI, Anderson DJ (2001) A diverse family of GPCRs expressed in specific subsets of nociceptive sensory neurons. Cell 106(5):619–632
Elekes K, Helyes Z, Kereskai L, Sandor K, Pinter E, Pozsgai G, Tekus V, Benvolgyi A, Nemeth J, Szuts T, Keri G, Szolcsenyi J (2008) Inhibitory effects of synthetic somatostatin receptor subtype 4 agonists on acute and chronic airway inflammation and hyperreactivity in the mouse. Eur J Pharmacol 578(2–3):313–322
Engström M, Tomperi J, El-Darwish K, Åhman M, Savola JM, Wurster S (2005) Superagonism at the human somatostatin receptor subtype 4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:332–338
Engström M, Savola JM, Wurster S (2006) Differential efficacies of somatostatin receptor agonists for G-protein activation and desensitization of somatostatin receptor subtype 4-mediated responses. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316:1262–1268
Ferone D, Boschetti M, Resmini E, Giusti M, Albanese V, Goglia U, Albertelli M, Vera L, Bianchi F, Minuto F (2006) Neuroendocrine-immune interactions: the role of cortistatin/somatostatin system. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1069:129–144
Gamse R, Leeman SE, Holzer P, Lembeck F (1981) Differential effects of capsaicin on the content of somatostatin, substance P, and neurotensin in the nervous system of the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 317(2):140–148
Gilligan JP, Lovato SJ, Erion MD, Jeng AY (1994) Modulation of carrageenan-induced hind paw edema by substance P. Inflammation 18:285–292
Gonzalez-Rey E, Delgado M (2008) Emergence of cortistatin as a new immunomodulatory factor with therapeutic potential in immune disorders. Mol Cell Endocrinol 286(1–2):135–140
Gonzalez-Rey E, Chorny A, Robledo G, Delgado M (2006a) Cortistatin, a new antiinflammatory peptide with therapeutic effect on lethal endotoxemia. J Exp Med 203(3):563–571
Gonzalez-Rey E, Varela N, Sheibanie AF, Chorny A, Ganea D, Delgado M (2006b) Cortistatin, an antiinflammatory peptide with therapeutic action in inflammatory bowel disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(11):4228–4233
Gonzalez-Rey E, Chorny A, Del Moral RG, Varela N, Delgado M (2007) Therapeutic effect of cortistatin on experimental arthritis by downregulating inflammatory and Th1 responses. Ann Rheum Dis 66(5):582–588
Helyes Z, Nemeth J, Pinter E, Szolcsanyi J (1997) Inhibition by nociceptin of neurogenic inflammation and the release of SP and CGRP from sensory nerve terminals. Br J Pharmacol 121:613–615
Helyes Z, Than M, Oroszi G, Pinter E, Nemeth J, Keri G et al (2000) Anti-nociceptive effect induced by somatostatin released from sensory nerve terminals and by synthetic somatostatin analogues in the rat. Neurosci Lett 278:185–188
Helyes Z, Pinter E, Nemeth J, Keri G, Than M, Oroszi G et al (2001) Anti-inflammatory effect of synthetic somatostatin analogues in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 134:1571–1579
Helyes Z, Szabo A, Nemeth J, Jakab B, Pinter E, Banvolgyi A et al (2004) Antiinflammatory and analgesic effects of somatostatin released from capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve terminals in a Freund’s adjuvant-induced chronic arthritis model in the rat. Arthritis Rheum 50:1677–1685
Helyes Z, Pinter E, Nemeth J, Sandor K, Elekes K, Szabo A, Pozsgai G, Keszthelyi D, Kereskai L, Engström M, Wurster S, Szolcsanyi J (2006) Effects of the somatostatin receptor subtype 4 selective agonist J-2156 on sensory neuropeptide release and inflammatory reactions in rodents. Br J Pharmacol 149(4):405–415
Hoyer D, Bell GI, Berelowitz M, Epelbaum J, Feniuk W, Humphrey PP et al (1995) Classification and nomenclature of somatostatin receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 16:86–88
Kang JS, Jeon YJ, Kim HM, Han SH, Yang K-H (2002) Inhibition of inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression by silymarin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:138–144
Karalis K, Mastorakos G, Chrousos GP, Tolis G (1994) Somatostatin analogues suppress the inflammatory reaction in vivo. J Clin Invest 93:2000–2006
Lecea L, del Rio JA, Criado JR, Alcántara S, Morales M, Danielson PE, Henriksen SJ, Soriano E, Sutcliffe JG (1997) Cortistatin is expressed in a distinct subset of cortical interneurons. J Neurosci 17(15):5868–5880
Lembeck F, Donnerer J, Bartho L (1982) Inhibition of neurogenic vasodilation and plasma extravasation by substance P antagonists, somatostatin and [D-Met2, Pro5]enkephalinamide. Eur J Pharmacol 85:171–176
Méndez-Díaz M, Guevara-Martínez M, Alquicira CR, Guzmán Vásquez K, Prospéro-García O (2004) Cortistatin, a modulatory peptide of sleep and memory, induces analgesia in rats. Neurosci Lett 354(3):242–244
Nemeth J, Helyes Z, Gorcs T, Gardi J, Pinter E, Szolcsanyi J (1996) Development of somatostatin radioimmunoassay for the measurement of plasma and tissue contents of hormone. Acta Physiol Hung 84:313–315
Nemeth J, Gorcs T, Helyes Z, Oroszi G, Kocsy T, Pinter E et al (1998) Development of a new sensitive CGRP radioimmunoassay for neuropharmacological research. Neurobiology (Budapest) 6:473–475
Patel YC (1999) Somatostatin and its receptor family. Front Neuroendocrinol 20(3):157–198
Patel YC, Greenwood MT, Panetta R, Demchyshyn L, Niznik H, Srikant CB (1995) The somatostatin receptor family. Life Sci 57:1249–1265
Pinter E, Helyes Z, Nemeth J, Porszasz R, Petho G, Than M et al (2002) Pharmacological characterisation of the somatostatin analogue TT-232: effects on neurogenic and non-neurogenic inflammation and neuropathic hyperalgesia. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 366:142–150
Pinter E, Helyes Z, Szolcsanyi J (2006) Inhibitory effect of somatostatin on inflammation and nociception. Pharmacol Ther 112(2):440–456
Ramírez JL, Mouchantaf R, Kumar U, Otero Corchon V, Rubinstein M, Low MJ, Patel YC (2002) Brain somatostatin receptors are up-regulated in somatostatin-deficient mice. Mol Endocrinol 16(8):1951–1963
Reisine T, Bell GI (1995) Molecular properties of somatostatin receptors. Neuroscience 67:777–790
Robas N, Mead E, Fidock M (2003) MrgX2 is a high potency cortistatin receptor expressed in dorsal root ganglion. J Biol Chem 278(45):44400–44404
Rubio A, Avila J, de Lecea L (2007) Cortistatin as a therapeutic target in inflammation. Expert Opin Ther Targets 11(1):1–9
Schindler M, Humphrey PP, Emson PC (1996) Somatostatin receptors in the central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 50(1):9–47
Siehler S, Seuwen K, Hoyer D (1998) [125I]Tyr10-cortistatin14 labels all five somatostatin receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 357(5):483–489
Siehler S, Nunn C, Hannon J, Feuerbach D, Hoyer D (2008) Pharmacological profile of somatostatin and cortistatin receptors. Mol Cell Endocrinol 286(1–2):26–34
Spier AD, de Lecea L (2000) Cortistatin: a member of the somatostatin neuropeptide family with distinct physiological functions. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 33(2–3):228–241
Szolcsanyi J (2004) Forty years in capsaicin research for sensory pharmacology and physiology. Neuropeptides 38:377–384
Szolcsanyi J, Helyes Z, Oroszi G, Nemeth J, Pinter E (1998a) Release of somatostatin and its role in the mediation of the antiinflammatory effect induced by antidromic stimulation of sensory fibres of rat sciatic nerve. Br J Pharmacol 123:936–942
Szolcsanyi J, Pinter E, Helyes Z, Oroszi G, Nemeth J (1998b) Systemic anti-inflammatory effect induced by counter-irritation through a local release of somatostatin from nociceptors. Br J Pharmacol 125:916–922
ten Bokum AM, Hofland LJ, Van Hagen PM (2000) Somatostatin and somatostatin receptors in the immune system: a review. Eur Cytokine Netw 11:161–176
Tostivint H, Joly L, Lihrmann I, Parmentier C, Lebon A, Morisson M, Calas A, Ekker M, Vaudry H (2006) Comparative genomics provides evidence for close evolutionary relationships between the urotensin II and somatostatin gene families. PNAS 103:2237–2242
Vinegar R, Truax JF, Selph JL, Johnston PR, Venable AL, McKenzie KK (1987) Pathway to carrageenan-induced inflammation in the hind limb of the rat. Fed Proc 46:118–126
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by OTKA K73044, K78059, and K81984; ETT 03-380/2009 and ETT 04-364/2009; the “Science, Please! Research Teams on Innovation” program (SROP-4.2.2/08/1/2008-0011); and the Developing Competitiveness of Universities in the South Transdanubian Region (SROP-4.2.1.B-10/2/KONV-2010-0002). The Ph.D. fellowship of Adrienn Markovics was supported by Sanofi-Aventis/Chinoin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markovics, A., Szőke, É., Sándor, K. et al. Comparison of the Anti-inflammatory and Anti-nociceptive Effects of Cortistatin-14 and Somatostatin-14 in Distinct In Vitro and In Vivo Model Systems. J Mol Neurosci 46, 40–50 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9577-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9577-4