Abstract
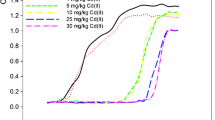
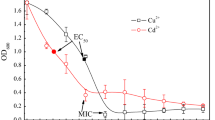
Bacteria have the ability to bind heavy metals on their cell wall. Biosorption is a passive and energy-independent mechanism to adsorb heavy metals. The efficiency of heavy metal biosorption can vary depending on several factors such as the growth phase of bacteria, solution pH, and existence of competitive heavy metals. In this study, Exiguobacterium sp. isolated from farmland soil near a mine site were used, and optimal conditions for Cd biosorption in solution were investigated. As bacterial growth progressed, Cd biosorption increased, which is attributed to changes in the structure and composition of the cell wall during bacterial growth. The biosorption process was rapid and was completed within 30 min. Cadmium biosorption was highest at pH 7 due to the dissociation of hydrogen ions and the increase of negative charges with increasing pH. In the mixed metal solution of Cd, Pb, and Zn, the amount of biosorption was in the order of Pb>Cd>Zn while in a single metal solution, the order was Cd≥Pb>Zn. The maximum adsorption capacity for Cd by the isolated bacteria was 15.6 mg/g biomass, which was calculated from the Langmuir isotherm model. Different adsorption efficiencies under various environmental conditions indicate that, to control metal mobility, the conditions for biosorption should be optimized before applying bacteria. The results showed that the isolated bacteria can be used to immobilize metals in metal-contaminated wastewater.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu Z (2001) Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of cadmium(II) biosorption by C. vulgaris in a batch system: effect of temperature. Sep Purif Technol 21:285–294
Aksu Z (2002) Determination of the equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of the batch biosorption of nickel(II) ions onto Chlorella vulgaris. Process Biochem 38:89–99
Alam MZ, Ahmad S (2013) Multi-metal biosorption and bioaccumulation by Exiguobacterium sp. ZM-2. Annals of Microbiology 63:1137–1146
Arora M, Kiran B, Rani S, Rani A, Kaur B, Mittal N (2008) Heavy metal accumulation in vegetables irrigated with water from different sources. Food Chem 111:811–815
Batool R, Qurrat-ul-ain K, Naeem A (2014) Comparative study of Cr(VI) removal by Exiguobacterium sp. in free and immobilized forms Bioremediation Journal 18:317-327
Brady JM, Tobin JM (1995) Binding of hard and soft metal ions to Rhizopus arrhizus biomass. Enzyme Microb Technol 17:791–796
Butler JAV, Ockrent C (1930) Studies in electrocapillarity. III. J Phys Chem 34:2841–2859
Cervantes C, Gutierrez-Corona F (1994) Copper resistance mechanisms in bacteria and fungi. FEMS Microbiol Rev 14:121–137
Chang J, Law R, Chang C (1997) Biosorption of lead, copper and cadmium by biomass of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PU21. Water Res 31:1651–1658
Chong KH, Volesky B (2004) Biosorption of heavy metals by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effects of nutrient conditions. Biotechnol Bioeng 47:451–460
Chaturvedi P, Shivaji S (2006) Exiguobacterium indicum sp. nov., a psychrophilic bacterium from the Hamta glacier of the Himalayan mountain ranges of India. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2765–2770
Chuan MC, Shu GY, Liu JC (1996) Solubility of heavy metals in a contaminated soil: effects of redox potential and pH. Water Air Soil Pollut 90:543–556
Collins MD, Lund BM, Farrow JAE, Schleifer KH (1983) Chemotaxonomic study of an alkalophilic bacterium, Exiguobacterium aurantiacum gen. nov., sp. nov. J Gen Microbiol 129:2037–2042
Dang VBH, Doan HD, Dang-Vu T, Lohi A (2009) Equilibrium and kinetics of biosorption of cadmium(II) and copper(II) ions by wheat straw. Bioresour Technol 100:211–219
Daughney C, Fowle DA, Fortin D (2001) The effect of growth phase on proton and metal adsorption by Bacillus subtilis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65:1025–1035
Engl A, Kunz B (1995) Biosorption of heavy metals by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effects of nutrient conditions. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 63:257–261
Esposito A, Pagnanelli F, Vegliò F (2002) pH-related equilibria models for biosorption in single metal systems. Chemical Engineering Science 57:307–313
Fan J, Okyay TO, Rodrigues DF (2014) The synergism of temperature, pH and growth phases on heavy metal biosorption by two environmental isolates. J Hazard Mater 279:236–243
Fein JB, Daughney CJ, Yee N, Davis TA (1997) A chemical equilibrium model for metal adsorption onto bacterial surfaces. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61:3319–3328
Fourest E, Canal C, Roux J (1994) Improvement of heavy metal biosorption by mycelial dead biomasses (Rhizopus arrhizus, Mucor miehei and Penicillium chrysogenum): pH control and cationic activation. FEMS Microbiol Rev 14:325–332
Fu F, Wang Q (2011) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manage 92:407–418
Gabr RM, Hassan SHA, Shoreit AAM (2008) Biosorption of lead and nickel by living and non-living cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ASU 6a. Int Biodeter Biodegr 62:195–203
Gadd GM (1992) Biosorption. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 55:302–304
Gadd GM (2010) Metals, minerals and microbes: geomicrobiology and bioremediation. Microbiology 156:609–643
Gardea-Torresdey JL, Gonzalez JH, Tiemann KJ, Rodriguez O, Gamez G (1998) Phytofiltration of hazardous cadmium, chromium, lead and zinc ions by biomass of Medicago sativa (Alfalfa). J Hazard Mater 57:29–39
Green-Ruiz C, Rodriguez-Tirado V, Gomez-Gil B (2008) Cadmium and zinc removal from aqueous solutions by Bacillus jeotgali: pH, salinity and temperature effects. Bioresour Technol 99:3864–3870
Holan ZR, Volesky B, Prasetyo I (1993) Biosorption of cadmium by biomass of marine algae. Biotechnol Bioeng 41:819–825
Jo-Shu C, Juan H (1994) Biosorption of mercury by the inactivated cells of pseudomonas aeruginosa PU21 (Rip64). Biotechnol Bioeng 44:999–1006
Kaduková J, Virčíková E (2005) Comparison of differences between copper bioaccumulation and biosorption. Environ Int 31:227–232
Kefala MI, Zouboulis AI, Matis KA (1999) Biosorption of cadmium ions by Actinomycetes and separation by flotation. Environ Pollut 104:283–293
Kim DS (2003) The removal by crab shell of mixed heavy metal ions in aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 87:355–357
Kim I, Lee M, Jung S, Song JJ, Oh T, Yoon J (2005) Exiguobacterium aestuarii sp. nov. and Exiguobacterium marinum sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat of the Yellow Sea in Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:885–889
Kratochvil D, Volesky B (1998) Advances in the biosorption of heavy metals. Trends Biotechnol 16:291–300
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. The Journal of the American Chemical Society 40:1361–1403
Li G, Zhang D, Li Q, Chen G (2014) Effects of pH on isotherm modeling and cation competition for Cd(II) and Cu(II) biosorption on Myriophyllum spicatum from aqueous solutions. Environmental Earth Sciences 72:4237–4247
Lovley DR, Coates JD (1997) Bioremediation of metal contamination. Curr Opin Biotechnol 8:285–289
Li WW, Yu HQ (2014) Insight into the roles of microbial extracellular polymer substances in metal biosorption. Bioresour Technol 160:15–23
Markai S, Andrès Y, Montavon G, Grambow B (2003) Study of the interaction between europium (III) and Bacillus subtilis: fixation sites, biosorption modeling and reversibility. J Colloid Interface Sci 262:351–361
Mashitah MD, Yus Azila Y, Bhatia S (2008) Biosorption of cadmium (II) ions by immobilized cells of Pycnoporus sanguineus from aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 99:4742–4748
Nagashetti V, Mahadevaraju GK, Muralidhar TS, Javed A, Trivedi D, Bhusal P (2013) Biosorption of heavy metals from soil by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int J innovative Technol Exploring Eng 2:22–24
Namasivayam C, Ranganathan K (1995) Removal of Cd(II) from wastewater by adsorption on “waste” Fe(III)/Cr(III) hydroxide. Water Res 29:1737–1744
Nieboer E, McBryde WAE (1973) Free-energy relationships in coordination chemistry. III. A comprehensive index to complex stability Canadian Journal of Chemistry 51:2512–2524
Nies DH (1992) Resistance to cadmium, cobalt, zinc, and nickel in microbes. Plasmid 27:17–28
Nies DH (2003) Efflux-mediated heavy metal resistance in prokaryotes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:313–339
Pagnanelli F, Esposito A, Toro L, Vegliò F (2003) Metal speciation and pH effect on Pb, Cu, Zn and Cd biosorption onto Sphaerotilus natans: Langmuir-type empirical model. Water Res 37:627–633
Puranik PR, Paknikar KM (1999) Influence of co-cations on biosorption of lead and zinc—a comparative evaluation in binary and multimetal systems. Bioresour Technol 70:269–276
Rangsayatorn N, Upatham ES, Kruatrachue M, Pokethitiyook P, Lanza GR (2002) Phytoremediation potential of Spirulina (Arthrospira) platensis: biosorption and toxicity studies of cadmium. Environ Pollut 119:45–53
Salleh MM, Illias R, Hassan O, Kamaruddin K, Shahab N (2006) Cloning and expression of pullulanase a gene from locally isolated bacillus. Report of the Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Johor
Sanità di Toppi L, Gabbrielli R (1999) Response to cadmium in higher plants. Environ Exp Bot 41:105–130
Scott J, Palmer S (1988) Cadmium bio-sorption by bacterial exopolysaccharide. Biotechnol Lett 10:21–24
Selatnia A, Boukazoula A, Kechid N, Bakhti MZ, Chergui A, Kerchich Y (2004) Biosorption of lead (II) from aqueous solution by a bacterial dead Streptomyces rimosus biomass. Biochem Eng J 19:127–135
Sheng PX, Ting Y, Chen JP, Hong L (2004) Sorption of lead, copper, cadmium, zinc, and nickel by marine algal biomass: characterization of biosorptive capacity and investigation of mechanisms. J Colloid Interface Sci 275:131–141
Smolyakov SS, Ryzhikh AP, Romanov RE (2010) The fate of Cu, Zn, and Cd in the initial stage of water system contamination: the effect of phytoplankton activity. J Hazard Mater 184:819–825
Sud D, Mahajan G, Kaur MP (2008) Agricultural waste material as potential adsorbent for sequestering heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions—a review. Bioresour Technol 99:6017–6027
Tobin JM, White E, Gadd GM (1994) Metal accumulation by fungi: applications in environmental biotechnology. J Ind Microbiol 13:126–130
Vijayaraghavan K, Yun YS (2008) Bacterial biosorbents and biosorption. Biotechnol Adv 26:266–291
Volesky B (1990) Biosorption and biosorbents. In: Volesky B (ed) Biosorption of heavy metals. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 3–5
Vullo DL, Ceretti HM, Daniel MA, Ramírez SAM, Zalts A (2008) Cadmium, zinc and copper biosorption mediated by Pseudomonas veronii 2E. Bioresour Technol 99:5574–5581
Yan G, Viraraghavan T (2003) Heavy-metal removal from aqueous solution by fungus Mucor rouxii. Water Res 37:4486–4496
Yang J, Volesky B (1999) Modeling uranium-proton ion exchange in biosorption. Environ Sci Technol 33:4079–4085
Yee N, Benning LG, Phoenix VR, Ferris FG (2004) Characterization of metal-cyanobacteria sorption reactions: a combined macroscopic and infrared spectroscopic investigation. Environ Sci Technol 38:775–782
Yetis U, Dolek A, Dilek FB, Ozcengiz G (2000) The removal of Pb(II) by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Water Res 34:4090–4100
Yu H, Wang J, Fang W, Yuan J, Yang Z (2006) Cadmium accumulation in different rice cultivars and screening for pollution-safe cultivars of rice. Science of the Total Environment 370:302–309
Yu J, Tong M, Sun X, Li B (2007) Cystine-modified biomass for Cd(II) and Pb(II) biosorption. J Hazard Mater 143:277–284
Zouboulis AI, Loukidou MX, Matis KA (2004) Biosorption of toxic metals from aqueous solutions by bacteria strains isolated from metal-polluted soils. Process Biochem 39:909–916
Zouboulis AI, Matis KA (1995) Removal of cadmium from dilute solutions by flotation. Water Sci Technol 31:315–326
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Basic Research Project (No. 3414) of the Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources (KIGAM) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.H., Chon, HT. Characterization of cadmium biosorption by Exiguobacterium sp. isolated from farmland soil near Cu-Pb-Zn mine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 11814–11822 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6335-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6335-8