Abstract
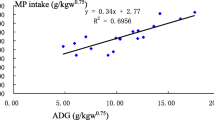
A study was conducted to compare the nutrient utilization, growth, and rumen enzyme profile of mithun (Bos frontalis) and Tho-tho cattle (Bos indicus) reared in the same feeding and managemental conditions. For the purpose, male mithun (n = 8) and male Tho-tho cattle (n = 8) of 1.5 years age, selected from the farm of National Research Centre on Mithun, Nagaland, India, were fed on mixed-tree-leaves-based ration as per the requirement of NRC (2001) for cattle for 12 months. Average daily gain (ADG), average dry matter intake (DMI), and feed conversion ratio (FCR) for all animals were recorded. A metabolic trial was conducted at 6 months of the experiment to assess the digestibility coefficient of different nutrients and nutritive value of ration. At 12 months of the experiment, rumen liquor was collected from all animals and analyzed for rumen enzyme profiles, viz., carboxymethylcellulase, xylanase, α-amylase, β-glucosidase, α-glucosidase, urease, and protease. It was found that ADG (507.8 g vs 392.8 g), DM intake (6.59 vs 5.85 kg/day) and DMI/W0.75 (98.75 g vs 91.00 g/day), crude protein intake (780 vs 700 g/day), and total digestible nutrient intake (3.65 vs 3.32 kg/day) were higher (p < 0.05) in mithun than cattle. The nitrogen balance was higher and FCR was better (p < 0.05) in mithun compared with cattle. The digestibility coefficient of different nutrients was similar (p > 0.05) between the species. The microbial enzyme profiles of mithun and cattle were not different (p > 0.05). The better growth performance of mithun than cattle as found in the present study clearly indicates that the mithun has higher genetic potential for growth than Tho-tho cattle of north-eastern hilly region of India.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC 1990. Official Methods of Analysis, 15th edition, Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, DC
Das, K.C., Malik, S. and Subudhi, P.K., 2006. Chemical Composition of tree leaves and shrubs used as fodder in Mizoram. Indian Journal of Animal Science, 76, 163-164
Das, K.C., Prakash, B., Dutta, P. and Rajkhowa, C., 2010. Performance of male and female mithun (Bos frontalis) reared in captivity and fed mixed tree leaves and straw based ration. Animal Nutrition and Feed Technology, 10, 75-80
Ichinohe, T., Orden, E. A., Delbarrio, A. N., Lapitan, R. M., Fujihara, T., Cruz, L. C. and Kanai, Y., 2004. Comparison of voluntary feed intake, rumen passage and degradation kinetics between crossbred Brahmam cattle (Bos indicus) and swamp buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) fed a fattening diet based on corn silage. Animal Science Journal. 75, 533-540
Kamra, D.N. and Agarwal, N., 2003. Techniques in Rumen Microbiology, published by Director, IVRI, Izatnagar, Bareilly, UP, India
Kennedy, P.M., 1990. Digestion and passage of tropical forages in swamp buffaloes and cattle. In: Domestic Buffalo Production in Asia, International Atomic Energy Agency Document, Vienna, 21–40.
Kennedy, P.M., McSweeney, C.S., Ffoulkes, D., John, A., Schlink, A.C., LeFeuvre, R.P. and Kerr, J. D., 1992. Intake and digestion in swamp buffaloes and cattle. 1. The digestion of rice straw (Oryza sativa). Journal of Agricultural Science, 119, 227–242
Kumar, R. and Vaithiyanathan, S., 1990. Occurrence, nutritional significance and effect on animal productivity of tannin in tree leaves. Animal Feed Science and Technology. 30, 21–38
Lapitan, R.M., Del Barrio, A.N., Katsube, O., Ban-tokuda, T., Orden, E. A., Robles, A.Y., Kanai, L.C., Cruz, Y. and Fujihara, T., 2008. Comparison of fattening performance in Brahman grade cattle (Bos indicus) and crossbred water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) fed on high roughage diet. Animal Science Journal, 79, 76–82
Mondal, S.K., Pal, D.T., Singh, G. and Bujarbaruah, K.M., 2001. Physio-chemical properties of mithun milk. Indian Journal of Animal Science, 71, 1066
Nha, P.T., Thu, N.V. and Preston, T.R., 2008. Effects of different levels and sources of crude protein supplementation on feed intake, digestibility and nitrogen retention in swamp buffaloes compared to local cattle. Livestock Research for Rural Development, 20(supplement)
NRC, 2001. Nutrient Requirements of Dairy cattle, 7th rev. edn. National Academy of Science, Washington, DC
Pal, D.T., Bujarbaruah, K.M., Mondal, S.K. and Dutta, M., 2001. Nutritional Evaluation of crop residues, natural grass, cultivated fodder, tree leaves and concentrate feed. In: Annual Report, 2000–2001, National Research Centre on Mithun (ICAR), Jharnapani, Medziphema, Nagaland, India, 40–41
Paul, S.S., Mandal, A.B., Kannan, A., Mandal, G. P. and Pathak, N. N., 2003. Comparative dry matter intake and nutrient utilization efficiency in lactating cattle and buffaloes. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 83, 258-267
Porter, L.J., Hrstich, L.N. and Chan, B.G., 1986. The conversion of procyanidins and prodelphinidins to cyanidin and delphinidin. Phytochemistry, 25, 223–230
Prakash, B., Mondal, M., Rajkhowa, S. and Rajkhowa, C., 2005. Nutritional evaluation of tree lopping based ration in Mithun. Indian Journal of Animal Nutrition, 22, 166-169
Prakash, B., Dhali, A., Das, K.C., Rathore, S.S., Hazarika, H. and Rajkhowa, C., 2008. Nutrient composition and In Situ degradability of forest foliages consumed by Mithun (Bos frontalis). Animal Nutrition and Feed Technology, 8, 175-183
Prakash, B., Dhali, A., Rathore, S.S., Das, K.C., Walling, I., Vupru, K., Mech, A., Baruah, K.K and Rajkhowa, C., 2009. Chemical composition and nutritional evaluation of various foliages consumed by mithun (Bos frontalis). Animal Feed Science and Technology, 150, 223–229.
Puppo, S., Bartocci, S., Terramoccia, S., Grandoni, F. and Amici, A., 2002. Rumen microbial counts and in vivo digestibility in buffaloes and cattle given different diets. Animal Science, 75, 323-329
Reid, R. L., Jung, G.A., Cox-Ganser, J.M., Rybeck, B.F. and Townsend, E.C., 1990. Comparative utilization of warm- and cool-season forages by cattle, sheep and goats. Journal of Animal Science, 68, 2986-2994
Snedecor, G. W. and Cochran, W.G., 1980. Statistical Method, 9th edition, The Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa.
Trach, N. X. and Thom, M. T., 2004. Responses of growing beef cattle to a feeding regime combining road side grazing and rice straw feeding supplemented with urea and brewers' grains following an oil drench. Livestock Research for Rural Development, 16(7)
Wanapat, M., Ngarmasang, A., Kokhuntot, S., Wachirapakom, C. and Rowlinson, P., 2000. A comparative study on the ruminal microbial population of cattle and swamp buffalo raised under traditional village conditions in the northeast of Thailand. Asian–Australasian Journal of Animal Science, 13, 918–921
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, K.C., Haque, N., Baruah, K.K. et al. Comparative nutrient utilization, growth, and rumen enzyme profile of mithun (Bos frontalis) and Tho-tho cattle (Bos indicus) fed on tree-leaves-based ration. Trop Anim Health Prod 43, 209–214 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-010-9676-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-010-9676-1