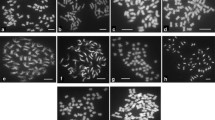
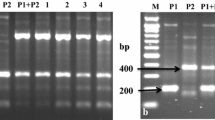
Abstract
Somatic hybridization is a biotechnological tool, which allows the transfer of multiple resistance genes from sexually incompatible Solanum species into cultivated potato. Here we report the effect of the recipient commercial tetraploid potato cultivar on the genetic make-up of the somatic hybrids (SHs) with an accession of the incongruent diploid species Solanum bulbocastanum Dun. The SHs were produced by mesophyll protoplast electrofusion. The analysis of ploidy by flow cytometry was first used to select hexaploid putative SH shoots but SSR and AFLP markers, DAPI staining and later flow cytometry evaluation of ploidy reveals symmetric and asymmetric SH plants regeneration in proportions that depend on the potato cultivar. The growth and fertility of the SHs support the effect of recipient cultivar. Out of five different fusion combinations, the highest number of SHs and tuberosum morphology was recorded for the combinations: blb41 (+) ‘Delikat’ 235 SHs (104 symmetric and 131 asymmetric) and blb41 (+) ‘Rasant’ 33 SH plants (22 symmetric, 11 asymmetric). There were fertile SHs of these combinations and BC1 and BC2 progenies were obtained. Less successful were the combinations: blb41 (+) ‘Quarta’ 64 SHs (57 symmetric and 7 asymmetric), blb41 (+) ‘Baltica’ 25 SHs (16 symmetric and 9 asymmetric), which were infertile and blb41 (+) ‘Agave’ with only one highly asymmetric non-viable SH plant. The production of a large number of SHs with diverse commercial cultivars is a prerequisite for further selection of useful pre-breeding material. The causes of nuclear constitution asymmetry and somatic incompatibility of the two species are also discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonova OY, Kostina LI, Gavrilenko T, Schüler K, Thieme R (2001) Proof of long-term stored potato germplasm by use of molecular markers http://www.genres.de/infos/igrreihe.htm. Accessed 2 Dec 2014
Antonova OY, Kostina LI, Gavrilenko T, Schüler K, Thieme R (2003) Proof of long-term stored potato germplasm by use of molecular markers. In: Knüpffer H, Ochsmann J (eds.) Rudolf Mansfeld and plant genetic resources. Schriften zu Genetischen Ressourcen IGR-ZADI, Bonn 22:192–197
Austin S, Pohlman JD, Brown CR, Mojtahed H, Santo GS, Douches DS, Helgeson JP (1993) Interspecific somatic hybridization between Solanum tuberosum L. and S. bulbocastanum Dun. as a means of transferring nematode resistance. Am Potato J 70:485–495
Bałtowicz D, Szczerbakowa A, Wielgat B (2005) RAPD analysis of the interspecific somatic hybrids Solanum bulbocastanum (+) S. tuberosum. Cell Mol Biol Lett 10:151–162
Bradshaw JE, Bryan GJ, Ramsay G (2006) Genetic resources (including wild and cultivated Solanum species) and progress in their utilisation in potato breeding. Potato Res 49:49–65
Doležel J, Greilhuber J, Suda J (2007) Estimation of nuclear DNA content in plants using flow cytometry. Nat Protoc 2(9):2233–2244
Feingold S, Lloyd J, Norero J, Bonierbale N, Lorenzen M (2005) Mapping and characterization of new EST-derived microsatellites for potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Theor Appl Genet 111:456–466
Gavrilenko TA, Antonova OY, Kostina LI (2007) Study of genetic diversity in potato cultivars using PCR analysis of organelle DNA. Russ J Genet 43(11):1301–1305 © Pleiades Publishing Inc
Greplová M, Polzerová H, Vlastníková H (2008) Electrofusion of protoplasts from Solanum tuberosum, S. bulbocastanum and S. pinnatisectum. Acta Physiol Plant 30:787–796
Harms CT (1983) Somatic incompatibility in the development of higher plant somatic hybrids. Quart Rev Biol 58:325–353
Haverkort AJ, Struik PC, Visser RGF, Jacobsen E (2009) Applied biotechnology to combat late blight in potato caused by Phytophthora infestans. Potato Res 52:249–264
Hawkes JG (1990) The potato: evolution, biodiversity and genetic resources. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, DC, pp 1–259
Helgeson JP, Pohlman JD, Austin S, Haberlach GT, Wielgus SM, Ronis D, Zambolim L, Tooley P, McGrath JM, James RV, Stevenson WR (1998) Somatic hybrids between Solanum bulbocastanum and potato: a new source of resistance to late blight. Theor Appl Genet 96:738–742
Henry Y, Vain IP, De Buyser J (1994) Genetic analysis of in vitro plant tissue culture responses and regeneration capacities. Euphytica 79:45–58
Hermsen JGT, Ramanna MS (1973) Double-bridge hybrids of Solanum bulbocastanum and cultivars of Solanum tuberosum. Euphytica 22:457–466
http://wheat.pw.usda.gov/ggpages/keygeneAFLPs.html Accessed Mar 2015
Iovene M, Savarese S, Cardi T, Frusciante L, Scotti N, Simon PW, Carputo D (2007) Nuclear and cytoplasmatic 425 genome composition of Solanum bulbocastanum (+) S. tuberosum somatic hybrids. Genome 50:443–450
Iovene M, Aversano R, Savarese S, Caruso I, DiMatteo A, Cardi T, Frusciante L, Carputo D (2012) Interspecific somatic hybrids between Solanum bulbocastanum and S. tuberosum and their haploidization for potato breeding. Biol Plant 56(1):1–8
Johnston SA, den Nijs TPM, Peloquin SJ, Hanneman RE Jr (1980) The significance of genic balance to endosperm development in interspecific crosses. Theor Appl Genet 57:5–9
Kawchuk LM, Lynch DR, Thomas J, Penner B, Sillito D, Kulcsar F (1996) Characterization of Solanum tuberosum simple sequence repeats and application to potato cultivar identification. Am Potato J 73:325–335
Kemble RJ, Shepard JF (1984) Cytoplasmic DNA variation in a potato protoclonal population. Theor Appl Genet 69:211–216
Khrustaleva LI, Kik C (2000) Introgression of Allium fistulosum into A. cepa mediated by A. roylei. Theor Appl Genet 100:17–26
Lössl A, Adler N, Horn R, Frei U, Wenzel G (1999) Chondriome-type characterization of potato: mt α, β, γ, δ, ε and novel plastid-mitochondrial configurations in somatic hybrids. Theor Appl Genet 98:1–10
Masuelli RW, Tanimoto EY, Brown CR, Comai L (1995) Irregular meiosis in a somatic hybrid between S. bulbocastanum and S. tuberosum detected by species-specific PCR markers and cytological analysis. Theor Appl Genet 91:401–408
Milbourne D, Meyer RC, Collins AJ, Ramsay LD, Gebhardt C, Waugh R (1998) Isolation, characterization and mapping of simple sequence repeat loci in potato. Mol Gen Genet 259:233–245
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Oberwalder B, Schilde-Rentschler L, Ruoss B, Wittemann S, Ninnemann H (1998) Asymmetric protoplast fusions between wild species and breeding lines of potato: effect of recipients and genome stability. Theor Appl Genet 97:1347–1354
Orczyk W, Przetakiewicz J, Nadolska-Orczyk A (2003) Somatic hybrids of Solanum tuberosum: application to genetics and breeding. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 74:1–13
Patel D, Power JB, Anthony P, Badakshi F, Heslop-Harrison JSP, Davey MR (2011) Somatic hybrid plants of Nicotiana × sanderae (+) N. debneyi with fungal resistance to Perenospora tabacina. Ann Bot 108(5):809–819
Provan J, Powell W, Waugh R (1996) Microsatellite analysis of relationships within cultivated potato (Solanum tuberosum). Theor Appl Genet 92:1078–1084
R Development Core Team. Version 2.11.1 (2010)
Rakosy-Tican E, Aurori CM, Dijkstra C, Thieme R, Aurori A, Davey MR (2007) The usefulness of the gfp reporter gene for monitoring Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of potato dihaploid and tetraploid genotypes. Plant Cell Rep 26(5):661–671
Reddivari L, Vanamala J, Safe SH, Miller JC Jr (2010) The bioactive compounds α-chaconine and gallic acid in potato extracts decrease survival and induce apoptosis in LNCaP and PC3 prostate cancer cells. Nutr Cancer 62(5):601–610
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Szczerbakowa A, Boltowicz D, Wielgat B (2003) Interspecific somatic hybrids Solanum bulbocastanum (+) S. tuberosum H-8105. Acta Physiol Plant 25:365–373
Thieme R (1991) Embryo- und Samenkultur bei der Kartoffel. Vortr Pflanzenzüchtg 21:125–129
Thieme R, Darsow U, Gavrilenko T, Dorokhov D, Tiemann H (1997) Production of somatic hybrids between S. tuberosum L. and late blight resistant Mexican wild potato species. Euphytica 97:189–200
Thieme R, Rakosy-Tican E, Gavrilenko T, Antonova O, Heimbach U, Schubert J, Nachtigall M, Thieme T (2005) Utilization of the resistance to pathogens and pests in wild species of Solanum for breeding potatoes. 16th triennial confernece of the EAPR, 17–22.7.2005, Bilbao, Spain, pp. 246–250
Thieme R, Rakosy-Tican E, Gavrilenko T, Antonova O, Schubert J, Nachtigall M, Heimbach U, Thieme T (2008) Novel somatic hybrids and their fertile BC1 progenies of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) (+) S. tarnii, extremely resistant to potato virus Y and resistant to late blight. Theor Appl Genet 116:691–700
Thieme R, Rakosy-Tican R, Nachtigall M, Schubert J, Hammann T, Antonova O, Gavrilenko T, Heimbach U, Thieme T (2010) Characterization of multiple resistance traits of somatic hybrids between Solanum cardiophyllum Lindl. and two commercial potato cultivars. Plant Cell Rep 29:1187–1201
Veilleux RE, Shen LY, Paz MM (1995) Analysis of the genetic composition of anther-derived potato by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA and simple sequence repeats. Genome 38:1153–1162
Vreugdenhil D (ed) (2007) Potato Biology and Biotechnology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
www.lsw.uni-heidelberg.de/users/christlieb/teaching/…./R-refman.pdf. Accessed Sep 2013
Acknowledgments
E R-T acknowledges the financial support of a grant of the Romanian Authority for Scientific Research, CNCS-UEFISCDI project number PNII-ID-PCE-2011-3-0586. Márta Molnár-Láng and Éva Szakács are kindly acknowledged for their help with GISH and late flow cytometry analyses. The authors wish to thank technical staff for excellent assistance. We gratefully thank T. Dixon for his helpful revision of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
fig. S1
GISH analysis of the BC1 potato ‘Delikat’ (+) S. bulbocastanum (blb41) 94/5/5 after hybridization with potato DNA: in green = FITC stained potato chromosomes (22 pairs), in blue = counterstained DAPI blb41 chromosomes (5 pairs), total chromosome number = 54; bar = 2 µm (PDF 103 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rakosy-Tican, E., Thieme, R., Nachtigall, M. et al. The recipient potato cultivar influences the genetic makeup of the somatic hybrids between five potato cultivars and one cloned accession of sexually incompatible species Solanum bulbocastanum Dun.. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 122, 395–407 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0777-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0777-4