Abstract
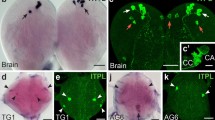
Trissin has recently been identified as a conserved insect neuropeptide, but its cellular expression and function is unknown. We detected the presence of this neuropeptide in the silkworm Bombyx mori using in silico search and molecular cloning. In situ hybridisation was used to examine trissin expression in the entire central nervous system (CNS) and gut of larvae, pupae and adults. Surprisingly, its expression is restricted to only two pairs of small protocerebral interneurons and four to five large neurons in the frontal ganglion (FG). These neurons were further characterised by subsequent multiple staining with selected antibodies against insect neuropeptides. The brain interneurons innervate edges of the mushroom bodies and co-express trissin with myoinhibitory peptides (MIP) and CRF-like diuretic hormones (CRF-DH). In the FG, one pair of neurons co-express trissin with calcitonin-like diuretic hormone (CT-DH), short neuropeptide F (sNPF) and MIP. These neurons innervate the brain tritocerebrum and musculature of the anterior midgut. The other pair of trissin neurons in the FG co-express sNPF and project axons to the tritocerebrum and midgut. We also used the baculovirus expression system to identify the promoter regulatory region of the trissin gene for targeted expression of various molecular markers in these neurons. Dominant expression of trissin in the FG indicates its possible role in the regulation of foregut–midgut contractions and food intake.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audsley N, Duve H, Thorpe A, Weaver RJ (2000) Morphological and physiological comparisons of two types of allatostatin in the brain and retrocerebral complex of the tomato moth, Lacanobia oleracea, (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Comp Neurol 424:37–46
Ayali A (2004) The insect frontal ganglion and stomatogastric pattern generator networks. Neurosignals 13:20–36
Blackburn MB, Wagner RM, Kochansky JP, Harrison DJ, Thomas-Laemont P, Raina AK (1995) The identification of two myoinhibitory peptides, with sequence similarities to the galanins, isolated from the ventral nerve cord of Manduca sexta. Regul Pept 57:213–219
Cavanaugh DJ, Geratowski JD, Wooltorton JR, Spaethling JM, Hector CE, Zheng X, Johnson EC, Eberwine JH, Sehgal A (2014) Identification of a circadian output circuit for rest:activity rhythms in Drosophila. Cell 157(3):689–701
Copenhaver PF, Truman JW (1986) Metamorphosis of the cerebral neuroendocrine system in the moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Neurol 249:186–204
Daubnerová I, Roller L, Žitňan D (2009) Transgenesis approaches for functional analysis of peptidergic cells in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Gen Comp Endocrinol 162:36–42
Davis NT, Velleman SG, Kingan TG, Keshishian H (1989) Identification and distribution of a proctolin-like neuropeptide in the nervous system of the gypsy moth, Lymantria dispar, and in other Lepidoptera. J Comp Neurol 283(1):71–85
Davis NT, Veenstra JA, Feyereisen R, Hildebrand JG (1997) Allatostatin-like immunoreactive neurons of the Tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta, and isolation and identification of a new peptide related to cockroach allatostatins. J Comp Neurol 385:265–284
Davis NT, Blackburn MB, Golubeva EG, Hildebrand JG (2003) Localization of myoinhibitory peptide immunoreactivity in Manduca sexta and Bombyx mori, with indications that the peptide has a role in molting and ecdysis. J Exp Biol 206:1449–1460
Dus M, Lai JS, Gunapala KM, Min S, Tayler TD, Hergarden AC, Geraud E, Joseph CM, Suh GS (2015) Nutrient sensor in the brain directs the action of the brain-gut axis in drosophila. Neuron 87:1–13
Duve H, Thorpe A (1994) Distribution and functional significance of Leu-callatostatins in the blowfly Calliphora vomitoria. Cell Tissue Res 276:367–379
Duve H, Thorpe A (2003) Neuropeptide co-localisation in the lepidopteran frontal ganglion studied by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Cell Tissue Res 311(1):79–89
Duve H, Johnsen AH, Maestro JL, Scott AG, Crook N, Winstanley D, Thorpe A (1997) Identification, tissue localisation and physiological effect in vitro of a neuroendocrine peptide identical to a dipteran Leu-callatostatin in the codling moth Cydia pomonella (Tortricidae: Lepidoptera). Cell Tissue Res 289:73–83
Duve H, East PD, Thorpe A (1999) Regulation of lepidopteran foregut movement by allatostatins and allatotropin from the frontal ganglion. J Comp Neurol 413(3):405–416
Duve H, Audsley N, Weaver RJ, Thorpe A (2000) Triple colocalisation of two types of allatostatin and an allatotropin in the frontal ganglion of the lepidopteran Lacanobia oleracea (Noctuidae): innervation and action on the foregut. Cell Tissue Res 300(1):153–163
Dyrløv JB, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S (2004) Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 340:783–795
Emery SB, Ma MC, Wong WKR, Tips A, De Loof A (1994) Immunocytochemical localization of a diuretic peptide Manduca diuresin (Mas DPII) in the brain and suboesophageal ganglion of the tobacco hawkmoth Manduca sexta (Lepidoptera: Sphingidae). Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 27:137–152
Gonzalez R, Orchard I (2009) Physiological activity of neuropeptide F on the hindgut of the blood-feeding hemipteran, Rhodnius prolixus. J Insect Sci 9:57
Grimmelikhuijzen CJP, Spencer AN (1984) FMRFamide immunoreactivity in the nervous system of the medusa Polyorchis penicillatus. J Comp Neurol 230:361–371
Hewes RS, Taghert PH (2001) Neuropeptides and neuropeptide receptors in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Genome Res 11:1126–1142
Hummon AB, Richmond TA, Verleyen P, Baggerman G, Huybrechts J, Ewing MA, Vierstraete E, Rodriguez-Zas SL, Schoofs L, Robinson GE, Sweedler JV (2006) From the genome to the proteome: uncovering peptides in the Apis brain. Science 314:647–649
Ida T, Takahashi T, Tominaga H, Sato T, Kume K, Yoshizawa-Kumagaye K, Nishio H, Kato J, Murakami N, Miyazato M, Kangawa K, Kojima M (2011) Identification of the endogenous cysteine-rich peptide trissin, a ligand for an orphan G protein-coupled receptor in Drosophila. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 414(1):44–48
Jiang H, Ikhagva A, Daubnerová I, Chae H, Šimo L, Jung S-H, Yoon Y-K, Seong J-Y, Žitňan D, Park Y, Kim Y-J (2013) Natalisin, a new tachykinin-like signaling system, regulates sexual activity and fecundity in insects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(37):3526–3534
Kim YJ, Žitňan D, Cho KH, Schooley DA, Mizoguchi A, Adams ME (2006) Central peptidergic ensembles associated with organization of an innate behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:14211–14216
Lee K-M, Daubnerová I, Isaac RE, Zhang C, Choi S, Chung J, Kim Y-J (2015) A neuronal pathway that controls sperm ejection and storage in female Drosophila. Curr Biol 25:790–797
Li B, Predel R, Neupert S, Hauser F, Tanaka Y, Cazzamali G, Williamson M, Arakane Y, Verleyen P, Schoofs L, Schachtner J, Grimmelikhuijzen CJ, Park Y (2008) Genomics, transcriptomics, and peptidomics of neuropeptides and protein hormones in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum. Genome Res 18:113–122
Li C, Song X, Chen X, Liu X, Sang M, Wu W, Yun X, Hu X, Li B (2014) Identification and comparative analysis of G protein-coupled receptors in Pediculus humanus humanus. Genomics 104(1):58–67
Matsumoto S, Brown MR, Crim JW, Vigna SR, Lea AO (1989) Isolation and primary structure of neuropeptides from the mosquito, Aedes aegypti, immunoreactive to FMRFamide antiserum. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 19:277–283
Miles CI, Booker R (1994) The role of the frontal ganglion in foregut movements of the moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol 174:755–767
Mita K, Morimyo M, Okano K, Koike Y, Nohata J, Kawasaki H, Kadono-Okuda K, Yamamoto K, Suzuki MG, Shimada T, Goldsmith MR, Maeda S (2003) The construction of an EST database for Bombyx mori and its application. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:14121–14126
Nässel DR, Homberg U (2006) Neuropeptides in interneurons of the insect brain. Cell Tissue Res 326:1–24
Nässel DR, Winther AM (2010) Drosophila neuropeptides in regulation of physiology and behavior. Prog Neurobiol 92(1):42–104
Oh Y, Yoon SE, Zhang Q, Chae HS, Daubnerová I, Shafer OT, Choe J, Kim YJ (2014) A homeostatic sleep-stabilizing pathway in drosophila composed of the sex peptide receptor and its ligand, the myoinhibitory peptide. PLoS Biol 12(10):e1001974
Park D, Veenstra JA, Park JH, Taghert PH (2008) Mapping peptidergic cells in Drosophila: where DIMM fits in. PLoS ONE 3:e1896
Roller L, Yamanaka N, Watanabe K, Daubnerova I, Zitnan D, Kataoka H, Tanaka Y (2008) The unique evolution of neuropeptide genes in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 38:1147–1157
Sadd BM, Barribeau SM, Bloch G et al. (2015) The genomes of two key bumblebee species with primitive eusocial organization. Genome Biol 16(1): Article 76
Schoofs L, Clynen E, Cerstiaens A, Baggerman G, Wei Z, Vercammen T, Nachman R, De Loof A, Tanaka S (2001) Newly discovered functions for some myotropic neuropeptides in locusts. Peptides 22:219–227
Schooley DA, Horodyski FM, Coast GM et al. (2012) Hormones controlling homeostasis in insects. In: Gilbert, LI (ed) Insect Endocrinology. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 366–429
Shiomi K, Kajiura Z, Nakagaki M, Yamashita O (2003) Baculovirus-mediated efficient gene transfer into the central nervous system of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Insect Biotechnol Sericol 72:149–155
Stay B, Chan KK, Woodhead AP (1992) Allatostatin-immunoreactive neurons projecting to the corpora allata of adult Diploptera punctata. Cell Tissue Res 270:15–23
Tanaka Y, Suetsugu Y, Yamamoto K, Noda H, Shinoda T (2013) Transcriptome analysis of neuropeptides and G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) for neuropeptides in the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Peptides 53:125–133
Te Brugge VA, Miksys SM, Coast GM, Schooley DA, Orchard I (1999) The distribution of a CRF-like diuretic peptide in the blood-feeding bug Rhodnius prolixus. J Exp Biol 202:2017–2027
Te Brugge VA, Schooley DA, Orchard I (2008) Amino acid sequence and biological activity of a calcitonin-like diuretic hormone (DH31) from Rhodnius prolixus. J Exp Biol 211:382–390
Veenstra JA (2000) Mono- and dibasic proteolytic cleavage sites in insect neuroendocrine peptide precursors. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 43:49–63
Veenstra JA (2014) The contribution of the genomes of a termite and a locust to our understanding of insect neuropeptides and neurohormones. Front Physiol 5: Article 454
Veenstra JA (2015) The power of next-generation sequencing as illustrated by the neuropeptidome of the crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Gen Comp Endocrinol. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2015.06.013
Veenstra JA, Rombauts S, Grbić M (2012) In silico cloning of genes encoding neuropeptides, neurohormones and their putative G-protein coupled receptors in a spider mite. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 42(4):277–295
Yamanaka N, Yamamoto S, Žitňan D, Watanabe K, Kawada T, Satake H, Kaneko Y, Hiruma K, Tanaka Y, Shinoda T, Kataoka H (2008) Neuropeptide receptor transcriptome reveals unidentified neuroendocrine pathways. PLoS ONE 3:e3048
Yamanaka N, Hua Y-J, Roller L, Spalovská-Valachová I, Mizoguchi A, Kataoka H, Tanaka Y (2010) Bombyx prothoracicostatic peptides activate the sex peptide receptor to regulate ecdysteroid biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(5):2060–2065
Yamanaka N, Roller L, Žitňan D, Satake H, Mizoguchi A, Kataoka H, Tanaka Y (2011) Bombyx orcokinins are brain-gut peptides involved in the neuronal regulation of ecdysteroidogenesis. J Compara Neurol 519:238–246
Žitňan D, Endo Y, Sehnal F (1989) Stomatogastric nervous system of Galleria mellonella L. (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae): changes during metamorphosis with special reference to FMRFamide neurons. Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 18(4):227–237
Žitňan D, Šauman I, Sehnal F (1993) Peptidergic innervation and endocrine cells of insect midgut. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 22(1–2):113–132
Žitňan D, Kingan TG, Kramer SJ, Beckage NE (1995) Accumulation of neuropeptides in the cerebral neurosecretory system of Manduca sexta larvae parasitised by the braconid wasp Cotesia congregata. J Comp Neurol 356(1):83–100
Žitňan D, Hollar L, Spalovská I, Takáč P, Žitňanová I, Gill SS, Adams ME (2002) Molecular cloning and function of ecdysis-triggering hormones in the silkworm Bombyx mori. J Exp Biol 205:3459–3473
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Slovak grant agencies, Agentúra na podporu výskumu a vývoja (APVV-0827-11) a Vedecká grantová agentúra (VEGA 2/0162/13; VEGA 2/0121/13). We are grateful to C.J.P. Grimelikhuijzen, A. Mizoguchi, Y. Tanaka and J.A. Veenstra for providing valuable antisera.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roller, L., Čižmár, D., Gáliková, Z. et al. Molecular cloning, expression and identification of the promoter regulatory region for the neuropeptide trissin in the nervous system of the silkmoth Bombyx mori . Cell Tissue Res 364, 499–512 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2352-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2352-z