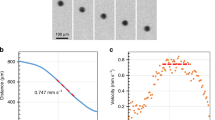
Abstract
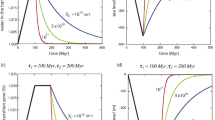
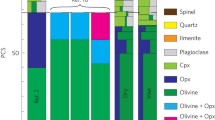
We present experiments showing that the lower oceanic crust should melt efficiently and quickly when heated by hot ascending magmas. Average plagioclase–olivine and plagioclase–augite pairs from the lower crust at the Southwest Indian Ridge have melt–mineral saturation boundaries at 1,190 and 1,154°C, respectively, and melt rapidly (>0.01 mm/h) at 50°C or more above these temperatures. Melting experiments performed on olivine–plagioclase and augite–plagioclase mineral pairs from actual oceanic lower crustal rock samples and under conditions applicable to a MOR setting (1,220–1,330°C, 1 atm, quartz–fayalite–magnetite oxygen buffer, 0.25–24 h) indicate that the resulting disequilibrium melts are linear mixes of the mineral compositions. The rates of melting are slower than the rate of heat-diffusion into a sample and are approximated as:
Our results indicate that great care must be taken in backward models using basalt chemistry alone to explore mantle-melting processes, assuming only crystallization and fractionation during ascent, as partial melts may mix with intruded hot magma.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta-Vigil A, London D, Dewers TA, Morgan GB VI (2002) Dissolution of corundum and andalusite in H2O-saturated haplogranitic melts at 800°C and 200 MPa: constraints on diffusivities and the generation of peraluminous melts. J Petrol 43:1885–1908
Acosta-Vigil A, London D, Morgan GB, Dewers TA (2006) Dissolution of quartz, albite, and orthoclase in H2O-saturated haplogranitic melt at 800 degrees C and 200 Mpa: diffusive transport properties of granitic melts at crustal anatectic conditions. J Petrol 47(2):231–254
Armstrong JT (1995) CITZAF: a package of correction programs for the quantitative electron microbeam X-ray analyses of thick polished materials, thin films, and particles. Microbeam Anal 4:177–200
Bédard JH (1988) Magma chamber dynamics and recycling of crustal cumulates by the mantle: evidence from the Bay of Islands Ophiolite (abs). Eos 69:1476
Bédard JH (1991) Cumulate recycling and crustal evolution on the Bay of Islands ophiolite. J Geol 99:225–249
Bédard JH (1993) The oceanic crust as a reactive filter: multiple syn-kinematic intrusion, hybridization and assimilation in an ophiolitic magma chamber. Geology 21:77–80
Bédard JH, Hébert R (1996) The lower crust of the Bay of Islands ophiolite, Canada: petrology, mineralogy and the importance of syntexis in magmatic differentiation in ophiolites and at ocean ridges: J Geophys Res 101:25105–25124
Bédard JH, Hebert R, Berclaz A, Varfalvy V (2000) Syntexis and the genesis of lower oceanic crust. In: Dilek Y, Moores EM, Elthon D, Nicolas A (eds) Ophiolites and oceanic crust: new insights from field studies and the OceanDrilling program, Special Paper––Geological Society of America 349, pp 105–119
Biggar GM (1972) Diopside, lithium metasilicate and the 1968 temperature scale. Mineral Mag 38:768–770
Biggar GM, Humphries DJ (1981) The plagioclase, forsterite, diopside liquid equilibrium in the system CaO–Na2O–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2. Mineral Mag 44:309–314
Blackman DK, Ildefonse B, John BE, Ohara Y, Miller DJ, MacLeod CJ, and the Expedition 304/305 Scientists (2006) In: Proceedings of IODP, 304/305: College Station, TX (Integrated Ocean Drilling Program Management International, Inc.). doi:10.2204/iodp.proc.304305.2006
Bloomer SH, Natland JH, Fisher RL (1989) Mineral relationships in gabbroic rocks from fracture zones of Indian Ocean ridges: evidence for extensive fractionation, parental diversity and boundary-layer recrystallization. In: Saunders AD, Norry MJ (eds) Magmatism in the ocean basins, vol 42. Geol Soc Spec Publ, London, pp 107–124
Bloomer SH, Meyer PS, Dick HJB, Ozawa K, Natland JH (1991) Texture and mineralogic variations in gabbroic rocks from Hole 735B. In: Proceeding of the Ocean Drilling Program. Scientif Results 118:21–39
Bryan WB, Finger LW, Chayes F (1969) Estimating proportions in petrographic mixing equations by least-squares approximation. Science 163:926–927
Bottinga Y, Weill DF (1972) The viscosity of magmatic silicate liquids: a model for calculation. Am J Sci 272:438–475
Boudier F, Nicholas A, Ildefonse B (1996) Magma chambers in the Oman ophiolite: fed from the top and the bottom. Earth Planet Sci Lett 144:239–250
Bowen NL (1928) The evolution of the igneous rocks. Princeton University Press (Reprinted by Dover Press 1956)
Chen YJ, Lin J (2004) High sensitivity of ocean ridge thermal structure to changes in magma supply: the Galapagos spreading center. Earth Planet Sci Lett 221:263–273
Coogan LA, Saunders AD, Kempton PD, Norry MJ (2000) Evidence from oceanic gabbros for porous melt migration within a crystal mush beneath the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 1. doi:10.1029/2000GC000072
Coogan LA, MacLeod CJ, Dick HJB, Edwards SJ, Kvassnes A, Natland JH, Robinson PT, Thompson G, O’Hara MJ (2001) Whole-rock geochemistry of gabbros from the Southwest Indian Ridge: constraints on geochemical fractionations between the upper and lower oceanic crust and magma chamber processes at (very) slow-spreading ridges. Chem Geol 178:1–22
DePaolo DJ (1981) Trace element and isotopic effects on combined wallrock assimilation and fractional crystallization. Earth Planet Sci Lett 53:189–202
Detrick RS, Buhl P, Vera E, Mutter J, Orcutt J, Madsen J, Brocher T (1987) Multi-channel seismic imaging of a crustal magma chamber along the East Pacific Rise. Nature 326:35–41
Dewey JF, Kidd WSF (1977) Geometry of plate accretion. Geol Soc Am Bull 88:960–968
Dick HJB, Bullen T (1984) Chromian spinel as a petrogenetic indicator in abyssal and Alpine-type peridotites and spatially associated lavas. Contr Mineral Petrol 86:54–76
Dick HJB, Ozawa K, Meyer PS, Niu Y, Robinson PT, Constantin M, Hebert R, Maeda J, Natland JH, Hirth G, Mackie S (2002) Primary silicate mineral chemistry of a 1.5-km section of very slow spreading lower ocean crust: ODP Hole 735B, Southwest Indian Ridge. In: Natland JH, Dick HJB, Miler DJ, Von Herzen R (eds) Proceedings of the ocean drilling program, scientific results 176, ocean drilling program, College Station, TX, pp 1–60 (CD-ROM)
Dunn RA, Toomey DR, Solomon SC (2000) Three-dimensional seismic structure and physical properties of the crust and shallow mantle beneath the East Pacific Rise at 9°30′N. J Geophys Res 105:23537–23555
Ehlers EG (1972) The interpretation of phase diagrams. Freeman & Co
Elthon D (1987) Mineral chemistry of gabbroic rocks from the Mid-Cayman Rise spreading center. J Geophys Res 92:658–682
Elthon D, Stewart M, Ross K (1992) Compositional trends of minerals in oceanic cumulates. J Geophys Res 97(B11):15,189–15,199
Fram MS, Longhi J (1992) Phase equilibria of dikes associated with Proterozoic anorthosite complexes. Am Mineral 77:605–616
Gaetani GA, Watson EB (2000) Open system behavior of olivine-hosted melt inclusions. Earth Planet Sci Lett 183:27–41
Gaetani GA, Grove TL, Bryan WB (1993) The influence of water on the petrogenesis of subduction-related igneous rocks. Nature 365(6444):332–334
Ghiorso GA, Sack RO (1995) Chemical mass transfer in magmatic processes IV: a revised and internally consistent thermodynamics model for the interpolation and extrapolation of liquid–solid equilibria in magmatic systems at elevated temperatures and pressures. Contrib Mineral Petrol 119:197–212
Grove TL (1981) Use of FePt alloys to eliminate the iron-loss problem in 1-atmosphere gas mixing experiments: theoretical and practical considerations. Contrib Mineral Petrol 78:289–304
Grove TL, Bence AE (1977) Experimental study of pyroxene–liquid interaction in quartz-normative basalt 15597. In: Proceedings of the eighth lunar science conference, pp 1549–1579
Grove TL, Juster TC (1989) Experimental investigations of low-Ca pyroxene and olivine-pyroxene-liquid equilibria at 1-atm. in natural basaltic and andesitic liquids. Contrib Mineral Petrol 103:287–305
Grove TL, Kinzler RJ, Bryan WF (1992) Fractionation of mid-ocean ridge basalts (MORB). In: Sinton J et al (eds) Mantle flow and melt generation at mid-ocean ridges. Geophysical Monograph, AGU, Washington DC, pp 281–310
Harding AJ, Orcutt JA, Kappus ME, Vera EE, Mutter JC, Buhl P, Detrick RS, Brocher TM (1989) Structure of young oceanic crust at 13°N on the East Pacific Rise from expanding spread profiles. J Geophys Res 94:B12163–B12196
Johannes W, Holtz F (1992) Melting of plagioclase in granite and related systems: composition of coexisting phases and kinetic observations. Trans R Soc Edinburgh Earth Sci 83:417–422
Johannes W, Koepke J, Behrens H (1994) Partial melting reactions of plagioclase and plagioclase-bearing systems. In: Parsons I (ed) Feldspars and their reactions. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Kelemen PB (1990) Reaction between ultramafic rock and fractionating basaltic magma 1: phase relations, the origin of calc–alkaline magma series and the formation of discordant dunite. J Petrol 31(1):51–98
Kelemen PB, Koga K, Shimizu N (1997) Geochemistry of gabbro sills in the crust–mantle transition zone of the Oman ophiolite: implications for the origin of the oceanic lower crust. Earth Planet Sci Lett 146:475–488
Kinzler RJ, Grove TL (1992) Primary magmas of midocean ridge basalts: 1. Experiments and methods. J Geophys Res 97:B6885–B6906
Klein EM, Langmuir CH (1989) Local versus global variations in ocean ridge basalt corporation: a reply. J Geophys Res 94(B4):4241–4252
Klein EM, Langmuir CH (1987) Global correlations of ocean ridge basalt chemistry with axial depth and crustal thickness. J Geophys Res 92(B8):8089–8115
Koepke J, Berndt J, Bussy F (2003) An experimental study on the shallow-level migmatization of ferrogabbros from the Fuerteventura Basal Complex, Canary Islands. Lithos 69:105–125
Koepke J, Feig ST, Snow J, Freise M (2004) Petrogenesis of oceanic plagiogranites by partial melting of gabbros: an experimental study. Contrib Mineral Petrol 146:414–432
Koepke J, Feig S, Snow JE (2005) Late stage magmatic evolution of oceanic gabbros as a result of hydrous partial melting: evidence from the Ocean Drilling Program (ODP) Leg 153 drilling at the Mid Atlantic Ridge. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 6:Q02001. doi:10.1029/2004GC000805
Korenaga J, Kelemen PB (1997) Origin of gabbro sills in the Moho transition zone of the Oman ophiolite: implications for magma transport in the oceanic lower crust. J Geophys Res 102(B12):27729–27749
Kvassnes AJS (2004) The evolution of oceanic gabbros: in situ and ancient examples. PhD, MIT––Woods Hole Joint Program in Oceanography
Lasaga AC (1998) Kinetic theory in the earth sciences. Princeton University Press, Princeton, 811 pp
Liang Y (2000) Dissolution in molten silicates: effects of solid solution. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64(9):1617–1627
Lissenberg CJ, Bédard JH, van Staal CR (2004) The structure and geochemistry of the gabbro zone of the Annieopsquotch ophiolite, Newfoundland: implications for lower crustal accretion at spreading ridges. Earth Planet Sci Lett 229(1–2):105–123
Maclennan J, Hulme T, Singh SC (2004) Thermal models of oceanic crustal accretion: linking geophysical, geological and petrological observations. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 5(2). doi:10.1029/2003/GC000605
Marvin UB, Walker D (1985) A transient heating event in the history of a highlands troctolite from Apolli 12 Soil 12033. Proceedings of the fifth lunar planet science conference (2). J Geophys Res 90:C421–C429
McKenzie D, Bickle MJ (1988) The volume and composition of melt generated by extension of the lithosphere. J Petrol 29:625–679
Meyer PS, Dick HJB, Thompson G (1989) Cumulate gabbros from the Southwest Indian Ridge, 54°S–7°16′E: implications for magmatic processes at a slowspreading ridge. Contrib Mineral Petrol 103(1989):44–63
Michael PJ, Cornell WC (1998) Influence of spreading rate and magma supply on crystallization and assimilation beneath mid-ocean ridges: evidence from chlorine and major element chemistry of mid-ocean ridge basalts. J Geophys Res 103(B8):18,325–18,356
Natland JH, Dick HJB (1996) Melt migration through high-level gabbroic cumulates of the East Pacific Rise at Hess Deep: the origin of magma lenses and the deep crustal structure of fast-spreading ridges. In: Mevel C, Gillis KM, Allan JF, Meyer PS (eds) Proceedings of the ocean drilling program, scientific results 147, ocean drilling program, College Station, TX, pp 21–58
Natland JH, Dick HJB (2002) Formation of the lower ocean crust and the crystallization of gabbroic cumulates at a very slowly spreading ridge. J Volc Geotherm Res 110:191–233
Nicolas A, Mainprice D (2005) Burst of high-temperature seawater injection throughout accreting oceanic crust: a case study in Oman ophiolite. Terra Nova 17(4):326–330
Nicolas A, Mainprice D, Boudier F (2003) High-temperature seawater circulation throughout crust of oceanic ridges: a model derived from the Oman ophiolites. J Geophys Res 108(B8):2371.doi:10.1029/2002JB002094
Pedersen RB (1986) The nature and significance of magma chamber margins in ophiolites: examples from the Norwegian Caledonides. Earth Planet Sci Lett 77:100–112
Philpotts AR, Asher PM (1993) Wallrock melting and reaction effects along the Higganum diabase dike in Connecticut: contamination of a continental flood basalt feeder. J Petrol 34:1029–1058
Philpotts AR, Dickinson LD (2000) The formation of plagioclase chains during convective transfer in basaltic magma. Nature 406(6791):59–61
Phipps Morgan J, Chen YJ (1993) Dependence of ridge-axis morphology on magma supply and spreading rate. Nature 364:706–708
Presnall DC, Dixon SA, Dixon JR, O’Donnell TH, Brenner NL, Schrock RL, Dycus DW (1978) Liquidus phase relations on the join diopside–forsterite–anorthite from 1 atm to 20 kbar: their bearing on the generation and crystallization of basaltic magma. Contrib Mineral Petrol 66:203–220
Quick JE, Denlinger RP (1993) Ductile deformation and the origin of layered gabbro in ophiolites. J Geophys Res 98:B14015–B14027
Ridley WI, Perfit MR, Smith MC, Fornari DJ (2006) Magmatic processes in developing oceanic crust revealed in a cumulate xenolith collected at the East Pacific Rise, 9°50′N. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 7:Q12O04
Rivalenti G (1980) Guide to the exscursion in the Balmuccia Zone, Sesia Valley, Ivrea–Verbano Complex. In: Proceedings of the second symposium Ivrea–Verbano, Memorie degli Instituti Geologia e Mineraligia dell’ Universita di Padova, 1979, vol 33, pp 3–9
Robie RA, Hemingway BS, Fisher JR (1978) Thermodynamic properties of minerals and related substances at 298.15K and 1 bar (105 pascals) pressure and higher temperatures. US Geological Survey Bulletin, vol 1452, 456p
Robins B, Tumyr O, Tysseland M, Garmann LB (1997) The Bjerkreim–Sokndal layered intrusion, Rogaland, SW Norway: evidence from marginal rocks for a jotunite parent magma. Lithos 39(3–4):121–133
Shaw CSJ (2004) Effects of composition and temperature on the dissolution rate of quartz in the CMAS system. Contrib Mineral Petrol 148:180–200
Shaw CSJ (2006) Interface vs. diffusion control and the effects of melt viscosity on the dissolution rate of quartz in melts of the CMAS and CAS systems. Contrib Mineral Petrol 151:665–680
Sinton JM, Detrick RS (1992) Mid-ocean ridge magma chambers. J Geophys Res 97:197–216
Sleep NH (1975) Formation of oceanic crust: some thermal constraints. J Geophys Res 80:B4037–B4042
Toplis MM (2004) Thermodynamic assessment of equilibrium in olivine saturated experiment. Lithos 73(Suppl):112
Tormey DR, Grove TL, Bryan WB (1987) Experimental petrology of normal MORB near the Kane Fracture Zone: 22°–25°N, mid-Atlantic ridge. Contrib Mineral Petrol 96:121–139
Tsuchiyama A (1985) Partial melting kinetics of plagioclase–diopside pairs. Contrib Mineral Petrol 91:12–23
Tsuchiyama A (1986) Melting and dissolution kinetics: application to partial melting and dissolution of xenoliths. J Geophys Res 91(B9):9395–9406
Ulmer P (1989) The dependence of the Fe2+–Mg cation partitioning between olivine and basaltic liquid on pressure, temperature and composition. Contrib Mineral Petrol 101:261–273
Van Orman JA, Grove TL (2000) Origin of lunar high-titanium ultramafic glass: constraints from phase relations and dissolution kinetics of clinopyroxene–ilmenite cumulates. Meteorit Planet Sci 35:783–794
Vera EE, Mutter JC, Buhl P, Orcutt JA, Harding AJ, Kappus ME et al (1990) The structure of 0- to 0.2 my old oceanic crust at 9°N on the East Pacific Rise from expanded spread profiles. J Geophys Res 95:B15529–B15556
Woods AW (1992) Melting and dissolving. J Fluid Mech 239:429–448
Zhang Y, Walker D Lesher CE (1989) Diffusive crystal dissolution. Contrib Mineral Petrol 102:492–513
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank H. Dick for providing starting material for our partial melting experiments, Nilanjan Chatterjee for assistance in the Electron Microprobe Lab at MIT, and Lindy Elkins and Steve Parman for help in the experimental laboratories. This manuscript was greatly improved by reviews by Cliff Shaw, Jean Bédard, and an anonymous reviewer, together with an informal review by Colin Devey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Hoefs.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kvassnes, A.J.S., Grove, T.L. How partial melts of mafic lower crust affect ascending magmas at oceanic ridges. Contrib Mineral Petrol 156, 49–71 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-007-0273-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-007-0273-x