Abstract
Key message
This paper is the first to directly link two types of ion channel regulation pathway into an emerging and complex CBL–CIPK signal system in wooden plant.
Abstract
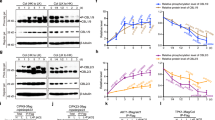
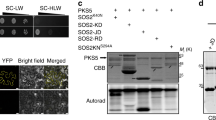
In Arabidopsis thaliana, the calcineurin b-like (CBL) 1 gene has been shown to be necessary in response to abiotic stresses. In this study, we identified CBL1 in the woody plant Populus euphratica, designated as PeCBL1. Heterologous expression of PeCBL1 could build the resistance of sensitive phenotypes to low K+ stress in the corresponding Arabidopsis cbl1/cbl9 mutant, and display a salt-sensitive phenotype compared with the mutant. Protein interaction analysis showed that PeCBL1 can interact with PeCIPK24, 25 and 26, and form different complexes of PeCBL–PeCIPK. To further investigate the mechanism of PeCBL1, we analyzed the fluxes of K+ and Na+ in roots of the wild-type Arabidopsis, cbl1/9 mutant, and PeCBL1 transgenic plants under low K+ stress and high Na+ stress. These analyses revealed that, compared to the cbl1/9 mutant, the PeCBL1 transgenic plant roots exhibited a higher capacity to absorb K+ after exposure to low K+ stress, and a lower capacity to discharge Na+ after exposure to salt stress. The results suggest that CBL1 interacts with CIPK24, CIPK25 and CIPK26 to regulate Na+/K+ homeostasis in Populus euphratica.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- AD:
-
Activation domain
- BD:
-
Binding domain
- BiFC:
-
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation
- CaM:
-
Calmodulin
- CaMV:
-
Cauliflower mosaic virus
- CBL:
-
Calcineurin B-like
- CDPK:
-
Calcium-dependent protein kinase
- CIPK:
-
CBL-interacting protein kinases
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- SOS:
-
Salt overly sensitive
- WT:
-
Wild type
- YFP:
-
Yellow fluorescent protein
References
Albrecht V, Ritz O, Linder S, Harter K, Kudla J (2001) The NAF domain defines a novel protein–protein interaction module conserved in Ca2+-regulated kinases. EMBO J 20:1051–1063
Albrecht V, Weinl S, Blazevic D, D’Angelo C, Batistic O, Kolukisaoglu Ü, Bock R, Schulz B, Harter K, Kudla J (2003) The calcium sensor CBL1 integrates plant response to abiotic stresses. Plant J36:457–470
Batistic O, Kudla J (2004) Integration and channeling of calcium signaling through the CBL calcium sensor/CIPK proteins kinase network. Planta 219:915–924
Batistič O, Sorek N, Schültke S, Yalovsky S, Kudlaa J (2008) Dual fatty acyl modification determines the localization and plasma membrane targeting of CBL/CIPK Ca2+ signaling complexes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20(5):1346–1362
Chang S, Puryear J, Cairney J (1993) A simple and efficient method for isolating RNA from pine trees. Plant Mol Biol Rep 11:113–116
Cheong YH, Kim KN, Pandey GK, Gupta R, Grant JJ, Luan S (2003) CBL1, a calcium sensor that differentially regulates salt, drought, and cold responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:1833–1845
Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Grant JJ, Batistic O, Li L, Kim BG, Lee SC, Kudla J, Luan S (2007) Two calcineurin B-like calcium sensors, interacting with protein kinase CIPK23, regulate leaf transpiration and root potassium uptake in Arabidopsis. Plant Jl 52:223–239
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Halfter U, Ishitani M, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis SOS2 protein kinase physically interacts with and is activated by the calcium-binding protein SOS3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3735–3740
Harper JF, Harmon A (2005) Plants, symbiosis and parasites: a calcium signaling connection. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 6:555–566
Hedrich R, Kudla J (2006) Calcium signaling network channel plant K+ uptake. Cell 125:1221–1223
Ho CH, Lin SH, Hu HC, Tsay YF (2009) CHL1 functions as a nitrate sensor in plants. Cell 138(6):1184–1194
Huang C, Ding S, Zhang H, Du H, An L (2011) CIPK7 is involved in cold response by interacting with CBL1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci 181(1):57–64
Kim BG, Waadt R, Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Dominguez-Solis JR, Schultke S, Lee SC, Kudla J, Luan S (2007) The calcium sensor CBL10 mediates salt tolerance by regulating ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 52:473–484
Kim MC, Chung WS, Yun D, Cho MJ (2009) Calcium and calmodulin-mediated regulation of gene expression in plants. Mol Plant 2:13–21
Kolukisaoglu Ü, Weinl S, Blazevic D, Batistic O, Kudla J (2004) Calcium sensors and their interacting protein kinases: genomics of the Arabidopsis and rice CBL–CIPK signaling networks. Plant Physiol 134:43–58
Li L, Kim BG, Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Luan S (2006) A Ca2+ signaling pathway regulated a K+ channel for low-K+ response in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12625–12630
Liu J, Ishitani M, Halfter U, Kim CS, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis thaliana SOS2 gene encodes a protein kinase that is required for salt tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3730–3734
Luan S (2009) The CBL–CIPK network in plant calcium signaling. Trends Plant Sci 14(1):37–42
Luan S, Kudla J, Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Yalovsky S, Gruissem W (2002) Calmodulins and calcineurin B-like proteins: calcium sensors for specific signal response coupling in plants. Plant Cell 14:389–400
Pandey GK, Cheong YH, Kim KN, Luan S (2004) The calcium sensor calcineurin B-like 9 modulates abscisic acid sensitivity and biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:1912–1924
Quan R, Lin H, Mendoza I, Zhang Y, Cao W, Yang Y, Shang M, Chen S, Pardo JM, Guo Y (2007) SCABP8/CBL10, a putative calcium sensor, interacts with the protein kinase SOS2 to protect Arabidopsis shoots from salt stress. Plant Cell 19:1415–1431
Sanders D, Pelloux J, Brownlee C, Harper JF (2002) Calcium at the crossroads of signaling. Plant Cell 14:401–417
Shi J, Kim KN, Ritz O, Albrecht V, Gupta R, Harter K, Luan S, Kudla J (1999) Novel protein kinases associated with calcineurin B-like calcium sensors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 11:2393–2405
Waadt R, Kudla J (2008) In planta visualization of protein interactions using bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC). CSH Protoc. doi:10.1101/pdb.prot4995
Weinl S, Kudla J (2009) The CBL–CIPK Ca2+-decoding signaling network: function and perspectives. New Phytol 184:517–528
White PJ, Broadley PJ (2003) Calcium in plant. Ann Bot 92:487–511
Xiong L, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK (2002) Cell signaling during cold, drought, and salt stress. Plant Cell 14:165–183
Xu J, Li HD, Chen LQ, Wang Y, Liu LL, He L, Wu WH (2006) A protein kinase, interacting with two calcineurin B-like proteins, regulates K+ transporter AKT1 in Arabidopsis. Cell 125(7):1347–1360
Yu Y, Yin W, Xia X, Zhang H (2007) Comparative genomic analysis of CIPK gene family in Arabidopsis and Populus. Plant Growth Regul 52:101–110
Zhang H, Yin W, Xia X (2008) Calcineurin B-Like family in Populus: comparative genome analysis and expression pattern under cold, drought and salt stress treatment. Plant Growth Regul 56:129–140
Zhang H, Yin W, Xia X (2010) Shaker-like potassium channels in Populus, regulated by the CBL–CIPK signal transduction pathway, increase tolerance to low-K+ stress. Plant Cell Rep 29:1007–1012
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Key Technologies R&D Program of China (2011BAD38B01, 2009CB119101), National Natural Science Foundation of China (30972339, and 31070597), the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2009CB119101), and the Scientific Research and Graduate Training Joint Programs from BMEC (Regulation of Tree WUE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by L. Jouanin.
H. Zhang and F. Lv contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Lv, F., Han, X. et al. The calcium sensor PeCBL1, interacting with PeCIPK24/25 and PeCIPK26, regulates Na+/K+ homeostasis in Populus euphratica . Plant Cell Rep 32, 611–621 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1394-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1394-5