Abstract
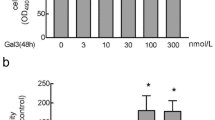
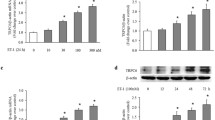
Inhibition of proteasome function has been shown to suppress several types of cells proliferation; this study investigates whether this also occurs in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) and its potential mechanisms. Serotonin induced 4.27-fold increase in DNA synthesis in PASMCs, and this effect was dose-dependently blocked by prior incubation of cells with MG132, a specific proteasome inhibitor. Inhibition of proteasome function did not modulate serotonin-triggered pro-proliferation signaling pathways, such as extracellular signal-regulated mitogen-activated protein kinase (ERK1/2 MAPK) and Ras homolog gene family member A (RhoA). Further study indicated that treatment of PASMCs with serotonin reduced p21WAF1 protein level but not its transcription; this was reversed by inhibiting ERK1/2 MAPK or RhoA cascade equally. In addition, MG132 increased the protein level of p21WAF1 in a dose-dependent manner in the presence of serotonin, 10 μM MG132 led to a 4.2-fold increase in p21WAF1 protein level, and this effect was not mediated by increasing p21WAF1 mRNA level. More importantly, cell lacking p21WAF1 by siRNA transfection abolished the inhibitive effect of MG132 on cells proliferation. Our study suggests that accumulation of p21WAF1 protein level caused by proteasome inhibition particularly mediated its inhibitive effect on PASMCs proliferation, and inhibition of proteasome function might have potential value in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awasthi N, Wagner BJ (2006) Suppression of human lens epithelial cell proliferation by proteasome inhibition, a potential defense against posterior capsular opacification. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:4482–4489
Barringhaus KG, Matsumura ME (2007) The proteasome inhibitor lactacystin attenuates growth and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells and limits the response to arterial injury. Exp Clin Cardiol 12:119–124
Brugarolas J, Bronson RT, Jacks T (1998) p21 is a critical CDK2 regulator essential for proliferation control in Rb-deficient cells. J Cell Biol 141:503–514
Ghofrani HA, Barst RJ, Benza RL, Champion HC, Fagan KA, Grimminger F, Humbert M, Simonneau G, Stewart DJ, Ventura C, Rubin LJ (2009) Future perspectives for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 54:S108–S117
Goldberg AL (2003) Protein degradation and protection against misfolded or damaged proteins. Nature 426:895–899
Hanze J, Weissmann N, Grimminger F, Seeger W, Rose F (2007) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of hypoxia-inducible factor driven vascular remodeling. Thromb Haemost 97:774–787
He G, Siddik ZH, Huang Z, Wang R, Koomen J, Kobayashi R, Khokhar AR, Kuang J (2005) Induction of p21 by p53 following DNA damage inhibits both Cdk4 and Cdk2 activities. Oncogene 24:2929–2943
Hwang CY, Lee C, Kwon KS (2009) Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2-dependent phosphorylation induces cytoplasmic localization and degradation of p21Cip1. Mol Cell Biol 29:3379–3389
Kaufman JL, Nooka A, Vrana M, Gleason C, Heffner LT, Lonial S (2010) Bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone as induction therapy for patients with symptomatic multiple myeloma: a retrospective study. Cancer 116:3143–3151
Kumeda SI, Deguchi A, Toi M, Omura S, Umezawa K (1999) Induction of G1 arrest and selective growth inhibition by lactacystin in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Anticancer Res 19:3961–3968
Lagna G, Ku MM, Nguyen PH, Neuman NA, Davis BN, Hata A (2007) Control of phenotypic plasticity of smooth muscle cells by bone morphogenetic protein signaling through the myocardin-related transcription factors. J Biol Chem 282:37244–37255
Li M, Liu Y, Dutt P, Fanburg BL, Toksoz D (2007) Inhibition of serotonin-induced mitogenesis, migration, and ERK MAPK nuclear translocation in vascular smooth muscle cells by atorvastatin. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 293:L463–L471
Li M, Li Z, Sun X (2008) Statins suppress MMP2 secretion via inactivation of RhoA/ROCK pathway in pulmonary vascular smooth muscles cells. Eur J Pharmacol 591:219–223
Li M, Sun X, Li Z, Liu Y (2009) Inhibition of cGMP phosphodiesterase 5 suppresses serotonin signalling in pulmonary artery smooth muscles cells. Pharmacol Res 59:312–318
Li M, Li Z, Sun X, Yang L, Fang P, Liu Y, Li W, Xu J, Lu J, Xie M, Zhang D (2010) Heme oxygenase-1/p21WAF1 mediates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma signaling inhibition of proliferation of rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. FEBS J 277:1543–1550
Moore BS, Eustaquio AS, McGlinchey RP (2008) Advances in and applications of proteasome inhibitors. Curr Opin Chem Biol 12:434–440
Oka M, Homma N, Taraseviciene-Stewart L, Morris KG, Kraskauskas D, Burns N, Voelkel NF, McMurtry IF (2007) Rho kinase-mediated vasoconstriction is important in severe occlusive pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats. Circ Res 100:923–929
Ravid T, Hochstrasser M (2008) Diversity of degradation signals in the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:679–690
Reed SI (2006) The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in cell cycle control. Results Probl Cell Differ 42:147–181
Rogers N, Paine S, Bedford L, Layfield R (2010) Review: the ubiquitin-proteasome system: contributions to cell death or survival in neurodegeneration. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 36:113–124
Ruggeri B, Miknyoczki S, Dorsey B, Hui AM (2009) The development and pharmacology of proteasome inhibitors for the management and treatment of cancer. Adv Pharmacol 57:91–135
Schwartz AL, Ciechanover A (2009) Targeting proteins for destruction by the ubiquitin system: implications for human pathobiology. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 49:73–96
Stenmark KR, Fagan KA, Frid MG (2006) Hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Circ Res 99:675–691
Sun XZ, Li ZF, Liu Y, Fang P, Li MX (2009) Inhibition of cGMP phosphodiesterase 5 suppresses matrix metalloproteinase-2 production in pulmonary artery smooth muscles cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 37:362–367
Wang X, Robbins J (2006) Heart failure and protein quality control. Circ Res 99:1315–1328
Willis MS, Townley-Tilson WH, Kang EY, Homeister JW, Patterson C (2010) Sent to destroy: the ubiquitin proteasome system regulates cell signaling and protein quality control in cardiovascular development and disease. Circ Res 106:463–478
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Chinese National Science Foundation (30871116) and the start-up package to Manxiang Li from the Second Affiliated Hospital of Medical College of Xi'an Jiaotong University, People’s Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Dong, X., Liu, Y. et al. Inhibition of ubiquitin proteasome function suppresses proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 384, 517–523 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-011-0678-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-011-0678-y