Abstract
Key message
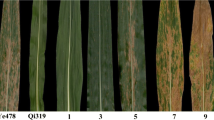
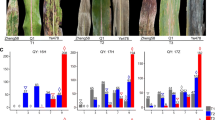
In this study we mapped the QTL Qgls8 for gray leaf spot (GLS) resistance in maize to a ~130 kb region on chromosome 8 including five predicted genes.
Abstract
In previous work, using near isogenic line (NIL) populations in which segments of the teosinte (Zea mays ssp. parviglumis) genome had been introgressed into the background of the maize line B73, we had identified a QTL on chromosome 8, here called Qgls8, for gray leaf spot (GLS) resistance. We identified alternate teosinte alleles at this QTL, one conferring increased GLS resistance and one increased susceptibility relative to the B73 allele. Using segregating populations derived from NIL parents carrying these contrasting alleles, we were able to delimit the QTL region to a ~130 kb (based on the B73 genome) which encompassed five predicted genes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asea G, Vivek BS, Lipps PE, Pratt RC (2012) Genetic gain and cost efficiency of marker-assisted selection of maize for improved resistance to multiple foliar pathogens. Mol Breed 29:515–527
Balint-Kurti PJ, Wisser R, Zwonitzer JC (2008) Use of an advanced intercross line population for precise mapping of quantitative trait loci for gray leaf spot resistance in maize. Crop Sci 48:1696–1704
Beckman PM, Payne GA (1982) External growth, penetration, and development of Cercospora zeae-maydis in corn leaves. Phytopathology 72:810–815
Benson JM, Poland JA, Benson BM, Stromberg EL, Nelson RJ (2015) Resistance to gray leaf spot of maize: genetic architecture and mechanisms elucidated through nested association mapping and near-isogenic line analysis. PLoS Genet 11:e1005045
Berger DK, Carstens M, Korsman JN, Middleton F, Kloppers FJ, Tongoona P, Myburg AA (2014) Mapping QTL conferring resistance in maize to gray leaf spot disease caused by Cercospora zeina. BMC Genet 15:60
Bubeck DM, Goodman MM, Beavis WD, Grant D (1993) Quantitative trait loci controlling resistance to gray leaf spot. Crop Sci 33:838–847
Chung CL, Jamann T, Longfellow J, Nelson R (2010) Characterization and fine-mapping of a resistance locus for northern leaf blight in maize bin 8.06. Theor Appl Genet 121:205–227
Chung CL, Poland J, Kump K, Benson J, Longfellow J, Walsh E, Balint-Kurti P, Nelson R (2011) Targeted discovery of quantitative trait loci for resistance to northern leaf blight and other diseases of maize. Theor Appl Genet 123:307–326
Clements MJ, Dudley JW, White DG (2000) Quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to gray leaf spot of corn. Phytopathology 90:1018–1025
Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Groenewald M, Caldwell P, Braun U, Harrington TC (2006) Species of Cercospora associated with grey leaf spot of maize. Stud Mycol 55:189–197
Danson J, Lagat M, Kimani M, Kuria A (2008) Quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for resistance to gray leaf spot and common rust diseases of maize. Afr J Biotechnol 7:3247–3254
Davis GL, McMullen MD, Baysdorfer C, Musket T, Grant D, Staebell M, Xu G, Polacco M, Koster L, Melia-Hancock S, Houchins K, Chao S, Coe EH Jr (1999) A maize map standard with sequenced core markers, grass genome reference points and 932 expressed sequence tagged sites (ESTs) in a 1736-locus map. Genetics 152:1137–1172
Dhami NB, Kim SK, Paudel A, Shrestha J, Rija TR (2015) A review on threat of gray leaf spot disease of maize in Asia. J Maize Res Dev 1:71–85
Doebley JF, Iltis HH (1980) Taxonomy of Zea (gramineae).Ι. A subgeneric classification with key to taxa. Am J Bot 67: 982–993
Gordon SG, Bartsch M, Matthies I, Gevers HO, Lipps PE, Pratt RC (2004) Linkage of molecular markers to Cercospora zeae-maydis resistance in maize. Crop Sci 44:628–636
He C, Holme J, Anthony J (2014) SNP genotyping: the KASP assay. Methods Mol Biol 1145:75–86
Hirsch CN, Hirsch CD, Brohammer AB, Bowman MJ, Soifer I, Barad O, Shem-Tov D, Baruch K, Lu F, Hernandez AG, Fields CJ, Wright CL, Koehler K, Springer NM, Buckler E, Buell CR, de Leon N, Kaeppler SM, Childs KL, Mikel MA (2016) Draft assembly of elite inbred line PH207 provides insights into genomic and transcriptome diversity in maize. Plant Cell 28:2700–2714
Hurni S, Scheuermann D, Krattinger SG, Kessel B, Wicker T, Herren G, Fitze MN, Breen J, Presterl T, Ouzunova M, Keller B (2015) The maize disease resistance gene Htn1 against northern corn leaf blight encodes a wall-associated receptor-like kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:8780–8785
Iltis HH, Doebley JF (1980) Taxonomy of Zea (gramineae). II. Subspecific categories in the Zea mays complex and a generic synopsis. Am J Bot 67: 994–1004
Juliatti FC, Pedrosa MG, Silva HD, da Silva JVC (2009) Genetic mapping for resistance to gray leaf spot in maize. Euphytica 169:227–238
Kinyua ZM, Smith JJ, Kibata GN, Simons SA, Langat BC (2010) Status of grey leaf spot disease in Kenyan maize production ecosystems. Afr Crop Sci J 18:183–194
Korsman J, Meisel B, Kloppers FJ, Crampton BG, Berger DK (2012) Quantitative phenotyping of grey leaf spot disease in maize using real-time PCR. Eur J Plant Pathol 133:461–471
Krattinger SG, Lagudah ES, Spielmeyer W, Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, McFadden H, Bossolini E, Selter LL, Keller B (2009) A putative ABC transporter confers durable resistance to multiple fungal pathogens in wheat. Science 323:1360–1363
Latterell FM, Rossi AE (1983) Gray leaf spot of corn: a disease on the move. Plant Dis 67:842–847
Lehmensiek A, Esterhuizen AM, van Staden D, Nelson SW, Retief AE (2001) Genetic mapping of gray leaf spot (GLS) resistance genes in maize. Theor Appl Genet 103:797–803
Lennon J, Krakowsky M, Goodman M, Flint-Garcia S, Balint-Kurti PJ (2016) Identification of alleles conferring resistance to gray leaf spot in maize derived from its wild progenitor species teosinte. Crop Sci 56:209–218
Lipps PE (1998) Gray leaf spot: a global threat to corn production. APSnet Features. doi:10.1094/APSnetFeature-1998-0598
Liu KJ, Xu XD (2013) First report of gray leaf spot of maize caused by Cercospora zeina in China. Plant Dis 97:1656
Liu Z, Cook J, Melia-Hancock S, Guill K, Bottoms C, Garcia A, Ott O, Nelson R, Recker J, Balint-Kurti P, Larsson S, Lepak N, Buckler E, Trimble L, Tracy W, McMullen MD, Flint-Garcia SA (2016) Expanding maize genetic resources with predomestication alleles: maize–teosinte introgression populations. Plant Genome 9:1
Manandhar G, Ferrara GO, Tiwari TP, Baidya S, Bajracharya ASR, Khadge BR, Narro L (2011) Response of maize genotypes to gray leaf spot disease (Cercospora zeae-maydis) in the hills of Nepal. Agron J N 2:93–101
Matsuoka Y, Vigouroux Y, Goodman MM, Sanchez GJ, Buckler E, Doebley J (2002) A single domestication for maize shown by multilocus microsatellite genotyping. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:6080–6084
McMullen MD, Kresovich S, Villeda HS, Bradbury P, Li H, Sun Q, Flint-Garcia S, Thornsberry J, Acharya C, Bottoms C, Brown P, Browne C, Eller M, Guill K, Harjes C, Kroon D, Lepak N, Mitchell SE, Peterson B, Pressoir G, Romero S, Oropeza Rosas M, Salvo S, Yates H, Hanson M, Jones E, Smith S, Glaubitz JC, Goodman M, Ware D, Holland JB, Buckler ES (2009) Genetic properties of the maize nested association mapping population. Science 325:737–740
Meisel B, Korsman J, Kloppers FJ, Berger DK (2009) Cercospora zeina is the causal agent of grey leaf spot disease of maize in southern Africa. Eur J Plant Pathol 124:577–583
Nega A, Lemessa F, Berecha G (2016) Distribution and importance of maize grey leaf spot Cercospora zeae-maydis (Tehon and Daniels) in south and southwest Ethiopia. J Plant Pathol Microbiol 7:362. doi:10.4172/2157-7471.1000362
Newman MA, Sundelin T, Nielsen JT, Erbs G (2013) MAMP (microbe-associated molecular pattern) triggered immunity in plants. Front Plant Sci 4:139
Okori P, Rubaihayo PR, Adipala E, Dixelius C (2004) Interactive effects of host, pathogen and mineral nutrition on grey leaf spot epidemics in Uganda. Eur J Plant Pathol 110:119–128
Olukolu BA, Wang GF, Vontimitta V, Venkata BP, Marla S, Ji J, Gachomo E, Chu K, Negeri A, Benson J, Nelson R, Bradbury P, Nielsen D, Holland JB, Balint-Kurti PJ, Johal G (2014) A genome-wide association study of the maize hypersensitive defense response identifies genes that cluster in related pathways. PLoS Genet 10:e1004562
Pozar G, Butruille D, Silva HD, McCuddin ZP, Penna JCV (2009) Mapping and validation of quantitative trait loci for resistance to Cercospora zeae-maydis infection in tropical maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 118:553–564
Rupe JC, Siegel MR, Hartman JR (1982) Influence of environment and plant maturity on gray leaf spot of corn caused by Cercospora zeae-maydis. Phytopathology 72:1587–1591
Saghai Maroof MA, Yue YG, Xiang ZX, Stromberg EL, Rufener GK (1996) Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling resistance to gray leaf spot disease in maize. Theor Appl Genet 93:539–546
Shi L, Li X, Hao Z, Xie C, Ji H, Lü X, Zhang S, Pan G (2007) Comparative QTL mapping of resistance to gray leaf spot in maize based on bioinformatics. Agr Sci China 6: 1411–1419
Silva da LCE, Wang S, Zeng ZB (2012) Composite interval mapping and multiple interval mapping: procedures and guidelines for using Windows QTL Cartographer. Methods Mol Biol 871:75–119
Simcox KD, Bennetzen JL (1993) The use of molecular markers to study Setosphaeria turcica resistance in maize. Phytopathology 83:1326–1330
Snape JW, Foulkes MJ, Simmonds J, Leverington M, Fish LJ, Wang Y, Ciavarrella M (2007) Dissecting gene × environmental effects on wheat yields via QTL and physiological analysis. Euphytica 154:401–408
Tehon LR, Daniels E (1925) Notes on the parasitic fungi of Illinois: II. Mycologia 17:240–249
Veiga AD, Von Pinho RG, Resende LV, Pinho ÉVDRV, Balestre M, Pereira LA (2012) Quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to gray leaf spot and grain yield in corn. Ciênc Agrotec 36: 31–38
Wallace JG, Larsson SJ, Buckler ES (2014) Entering the second century of maize quantitative genetics. Heredity 112:30–38
Ward JMJ, Stromberg EL, Nowell DC, Nutter FW Jr (1999) Gray leaf spot: a disease of global importance in maize production. Plant Dis 83:884–895
Xu L, Zhang Y, Shao S, Chen W, Tan J, Zhu M, Zhong T, Fan X, Xu M (2014) High-resolution mapping and characterization of qRgls2, a major quantitative trait locus involved in maize resistance to gray leaf spot. BMC Plant Biol 14:230
Yan W, Li Y, Song MX, Zhang KY, Sun MZ, Qu H, Li FH, Zhong XM, Zhu M, Du WL, Lü XL (2016) Meta-analysis and validation of QTL for resistance to gray leaf spot in maize. Acta Agron Sin 42:758–767
Zaitlin D, DeMars SJ, Gupta M (1992) Linkage of a second gene for NCLB resistance to molecular markers in maize. Maize Genet Coop Newsl 66: 69–70
Zhang Y, Xu L, Fan X, Tan J, Chen W, Xu M (2012) QTL mapping of resistance to gray leaf spot in maize. Theor Appl Genet 125:1797–1808
Zwonitzer JC, Coles ND, Krakowsky MD, Arellano C, Holland JB, McMullen MD, Pratt RC, Balint-Kurti PJ (2010) Mapping resistance quantitative trait loci for three foliar diseases in a maize recombinant inbred line population—evidence for multiple disease resistance? Phytopathology 100:72–79
Acknowledgements
QY is supported by NSF Grant #1127076, “Genetic and Histological Dissection of Phenotypic Variation in Quantitative Resistance to Maize Diseases”; XY is supported by a China Scholarship Council Fellowship. We are very grateful to Jose Santa-Cruz Hidalgo, Julie Taylor, and Monsanto Inc. for planting and managing our experiments in Andrews NC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving animal and human rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Mingliang Xu.
Xinye Zhang and Qin Yang have contributed equally to the work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Yang, Q., Rucker, E. et al. Fine mapping of a quantitative resistance gene for gray leaf spot of maize (Zea mays L.) derived from teosinte (Z. mays ssp. parviglumis). Theor Appl Genet 130, 1285–1295 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2888-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2888-2