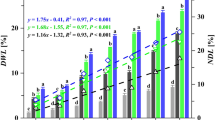
Summary
Of eight white-rot fungi examined, seven fungi grew on nitrogen-limited poplar wood meal medium and degraded 14C-lignin in wood meal to 14CO2. Increased oxygen enhanced both the rate and extent of degradation. However, whereas Pleurotus ostreatus, Pycnoporus cinnabarinus 115 and Pycnoporus cinnabarinus A-360 degraded 12–17% of 14C-(U)-lignin of poplar wood to 14CO2 also in an air atmosphere, Sporotrichum pulverulentum, Phlebia radiata 79 and Phanerochaete sordida 37 degraded only 1–5% under these conditions. Addition of cellulose and glucose to the poplar wood medium stimulated degradation of 14C-(RING)-lignin of poplar wood by Phlebia radiata 79 but repressed degradation by Polyporus versicolor and Pleurotus ostreatus. Cellulose added to the wood meal medium had no effect on the degradation of lignin by Phanerochaete sordida 37 and Sporotrichum pulverulentum but glucose slightly repressed lignin degradation by these fungi. Those white-rot fungi which were considered as preferentially lignin attacking fungi could degrade 14C-(RING)-lignin of poplar wood efficiently under 100% oxygen. They did not require an extra energy source in addition to wood meal polysaccharides for rapid ring cleavage and they degraded up to 50–60% of the 14C-lignin to 14CO2 in 6–7 weeks at a maximum rate of 3–4% per day.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ander P, Eriksson K-E (1975) Influence of carbohydrates on lignin degradation by the white-rot fungus Sporotrichum pulverulentum. Svensk Papperstidn 78:643–652
Ander P, Eriksson K-E (1977) Selective degradation of wood components by white-rot fungi. Physiol Plant 41:239–248
Ander P, Hatakka A, Eriksson KE (1980) Degradation of lignin and lignin-related substances by Sporotrichum pulverulentum (Phanerochaete chrysosporium). In: Kirk TK, Higuchi T, Chang H-M (eds) Lignin biodegradation: Microbiology, chemistry and potential applications, vol II. CRC Press, Boca Raton Florida, pp 1–15
Bar-Lev SS, Kirk TK (1981) Effects of molecular oxygen on lignin degradation by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 99:373–378
Buswell JA, Ander P, Eriksson K-E (1981) A study of ammonia-assimilating enzymes and lignin degradation in Sporotrichum pulverulentum grown under conditions of high and low nitrogen. Proc International Symposium on Wood and Pulping Chemistry (The Ekman Days) Stockholm, Sweden, June 9–12, 1981, vol III: 88–92
Cowling EB (1961) Comparative biochemistry of decay of sweetgum sapwood by white-rot and brown-rot fungi. USDA Techn Bull No. 1258, pp 1–79
Crawford DL, Crawford RL (1976) Microbial degradation of lignocellulose: the lignin component. Appl Environ Microbiol 31:714–717
Crawford RL (1981) Lignin biodegradation and transformation. Wiley-Interscience, New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto
Crawford RL, Robinson LE, Cheh AM (1980) 14C-labeled lignins as substrates for the study of lignin biodegradation and transformation. In: Kirk TK, Higuchi T, Chang H-M (eds) Lignin biodegradation: Microbiology, chemistry and potential applications, vol I. CRC Press, Boca Raton Florida, pp 61–76
Eriksson K-E (1978) Enzyme mechanisms involved in cellulose hydrolysis by the rot fungus Sporotrichum pulverulentum. Biotechnol Bioeng 20:317–332
Eriksson K-E (1981) Fungal degradation of wood components. Pure Appl Chem 53:33–43
Eriksson K-E, Grünewald A, Vallander L (1980) Studies of growth conditions in wood for three white-rot fungi and their cellulaseless mutants. Biotechnol Bioeng 22:363–376
Fenn P, Choi S, Kirk TK (1981) Ligninolytic activity of Phanerochaete chrysosporium: physiology of suppression by NH +4 and L-glutamate. Arch Microbiol 130:66–71
Fenn P, Kirk TK (1981) Relationship of nitrogen to the onset and suppression of ligninolytic activity and secondary metabolism in Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Microbiol 130:59–65
Freer SN, Detroy RW (1982) Biological delignification of 14C-labeled lignocelluloses by basidiomycetous fungi: degradation and solubilization of the lignin and cellulose components. Mycologia 74:943–952
Haider K, Trojanowski J (1980) A comparison of the degradation of 14C-labeled DHP and corn stalk lignins by micro- and macrofungi and bacteria. In: Kirk TK, Higuchi T, Chang H-M (eds) Lignin biodegradation: Microbiology, chemistry and potential applications, vol I. CRC Press, Boca Raton Florida, pp 111–134
Hiroi T, Eriksson K-E (1976) Microbiological degradation of lignin, part 1. Influence of cellulose on the degradation of lignins by the white-rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Svensk Papperstidn 79:157–161
Kaneshiro T (1977) Lignocellulosic agricultural wastes degraded by Pleurotus ostreatus. Dev Ind Microbiol 18:591–597
Kirk TK (1975) Lignin-degrading enzyme system. Biotechnol Bioeng Symp No. 5:139–150
Kirk TK, Connors WJ, Zeikus JG (1976) Requirement for a growth substrate during lignin decomposition by two wood-rotting fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 32:192–194
Kirk TK, Moore WE (1972) Removing lignin from wood with white-rot fungi and digestibility of resulting wood Wood and Fiber 4:72–79
Kirk TK, Schultz E, Connors WJ, Lorenz LF, Zeikus JG (1978) Influence of culture parameters on lignin metabolism by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Microbiol 117:277–285
Leatham G, Kirk TK (1983) Regulation of ligninolytic activity by nutrient nitrogen in white-rot basidiomycetes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 16:65–67
Odier E, Janin G, Monties B (1981) Poplar lignin decomposition by gram-negative aerobic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 41:337–341
Reid ID (1979) The influence of nutrient balance on lignin degradation by the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Can J Bot 57:2050–2058
Reid ID, Seifert KA (1980) Lignin degradation by Phanerochaete chrysosporium in hyperbaric oxygen. Can J Microbiol 26:1168–1171
Roch P (1982) Biodegradation de la lignine et metabolisme secondaire chez des champignons Basidiomycetes de pourriture blanche. Proc Journées Internationales d'Etudes du Groupe Polyphenols, 29. 9.–1. 10. 1982, Toulouse, France (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
These results were reported in part at the Journées Internationales d'Etudes du Groupe Polyphenols, 29. 9.–1. 10. 1982, Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hatakka, A.I., Uusi-Rauva, A.K. Degradation of 14C-labelled poplar wood lignin by selected white-rot fungi. European J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 17, 235–242 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00510422
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00510422