Abstract
Ammonia concentrations of 4 g N/l or more inhibited thermophilic digestion of cattle manure. A stable digestion of cattle manure could be maintained with ammonia concentrations up to 6 g N/l after 6 months of operation. However, the methane yield was reduced and the concentration of volatile fatty acids increased from 1 to 3 g/l as acetate, compared to controls with an ammonia concentration of 2.5 g N/l. The temporary strong inhibition following an one-step increase in ammonia concentration was reduced by applying a gradual increase. The specific methanogenic activity of ammonia-inhibited reactors (6 g N/l) with acetate or hydrogen as substrate was reduced by 73 and 52%, respectively. Tests of ammonia toxicity on the acetate- and hydrogen-utilizing populations showed a higher sensitivity of the aceticlastic compared to the hydrogenotrophic methanogens; the specific growth rate for the aceticlastic methanogens was halved at ammonia concentrations of 3.5 g N/l, compared to 7 g N/l for the hydrogenotrophic methanogens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (1985) Standard methods for the examination of waste and wastewater, 16th edn. MAH Franson (ed) APHA AWWA WPCF, Washington, D.C.
Angelidaki I, Ahring BK (1991) Ammonia inhibition during anaerobic thermophilic degradation of animal waste. In: Verachtert H, Verstraete W (eds) Proceedings of the International Symposium on Environmental Biotechnology, Royal Flemish Society of Engineers, vol 2, 22–25 April, Ostend, Belgium. pp 389–392
Angelidaki I, Petersen SP, Ahring BK (1992) Effects of lipids on thermophilic anaerobic digestion and reduction of lipid inhibition upon addition of bentonite. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 33:469–472
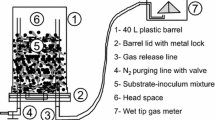
Angelidaki I, Ellegaard L, Ahring BK (1992) Compact automated displacement gas metering system for measurement of low gas rates from laboratory fermentors. Biotechnol Bioeng 39:351–353
Bhattacharya SK, Parkin GF (1989) The effect of ammonia on methane fermentation processes. J Water Pollut Control Fed 61:55–59
Braun R, Huber P, Meyrath J (1981) Ammonia toxicity in liquid piggery manure digestion. Biotechnol Lett 3:159–164
De Baere LA, Devocht M, Assche P van, Verstrate W (1984) Influence of high NaCl and NH4Cl salt levels on methanogenic associations. Water Res 18:543–548
Hashimoto G (1986) Ammonia inhibition of methanogenesis from cattle wastes. Agric Wastes 17:241–261
Koster IW, Lettinga G (1984) The influence of ammonia-nitrogen on the specific activity of pelletized methanogenic sludge. Agric Wastes 9:205–216
McCarty PL (1964) Anaerobic waste treatment fundamentals III. Public Works 95:91–94
McCarty PL, McKinney RE (1961) Salt toxicity in anaerobic digestion. J Water Pollut Control Fed 33:399–415
Poggi-Varaldo HM, Tingley J, Oleszkiewicz JA (1991) Inhibition of growth and acetate uptake by ammonia in batch anaerobic digestion. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 52:135–143
Robbins JE, Gerhard SA, Kappel TJ (1989) Effects of ammonia in anaerobic digestion and an example of digestor performance from cattle manure protein mixtures. Biol Wastes 27:1–14
Sprott GD, Patel GB (1986) Ammonia toxicity in pure cultures of methanogenic bacteria. System Appl Microbiol 7:358–363
Van Velsen AFM (1979) Adaptation of methanogenic sludge to high ammonia-nitrogen concentrations. Water Res 13:995–999
Wiegant WM, Zeeman G (1986) The mechanism of ammonia inhibition in the thermophilic digestion of livestock wastes. Thermophilic digestion for waste and wastewater treatment. Ph. D Thesis, Agricultural University, Wageningen, pp 57–67
Zeeman G, Wiegant WM, Koster-Treffers ME, Lettinga G (1985) The influence of the total ammonia concentration on thermophilic digestion of cow manure. Agric Wastes 14:19–35
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: B. K. Ahring
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angelidaki, I., Ahring, B.K. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of livestock waste: the effect of ammonia. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 560–564 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00242955
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00242955