Abstract
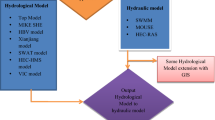
Flood is the most common natural disaster upsetting the highest population of the world. In recent times, severe floods in urban areas are occurring more frequently owing to uncontrolled urbanization and climate change and it will continue to grow in upcoming years. Prevention of such events is not possible but with advancement of technology, flood-vulnerable areas can be identified through 2-D modeling of critical rainfall events. The difficulty associated with urban floods is unpredictable flow conditions in urban environment due to rapid alterations in topography and unavailability of extensive raw dataset. Thus, modeling of urban floods becomes a complex process. A vast number of numerical models have evolved over the past few years which are capable of flood mapping; most of them are commercial, rigorous and need extensive dataset to generate precise results. This paper presents a simple sophisticated approach to analyze extreme rainfall events based on past critical events and synthetic hyetographs developed from IDF curves for a part of Hyderabad, India. HEC-RAS, a freely available 2-D hydraulic model with integration to GIS is used to generate depth of flood inundation over underlying terrain and risk maps of flood inundation are developed for different rainfall scenarios. The model results identify 17% of total area is liable to floods out of which 9% area indicates high risk, 52% area shows medium risk and remaining 35% area falls under low risk of flooding.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agilan V, Umamahesh NV (2017) What are the best covariates for developing non-stationary rainfall intensity–duration–frequency relationship? Adv Water Resour 101:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.12.016
Ahmed Z, Rao DRM, Reddy K (2013) Urban flooding-case study of Hyderabad. Glob J Eng Des Technol 2(4):63–66. ISSN: 2319-7293. https://www.longdom.org/articles/urban-flooding–case-study-of-hyderabad.pdf
Awakimjan I (2015) Urban flood modelling recommendations for Ciudad Del Plata. Bachelor Thesis, University of Twente, Netherland
Bansal N, Muhua M, Gairola A (2015) Causes and impact of urban flooding in Dehradun. Int J Curr Res 7(02):12615-12627 ISSN: 0975-833X. https://www.journalcra.com/article/causes-and-impact-urban-flooding-dehradun
Campana NA, Tucci CE (2001) Predicting floods from urban development scenarios: case study of the Dilúvio Basin, Porto Alegre, Brazil. Urban Water 3(1):113–124
Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters UNISDR (2015) The human cost of weather related disasters 1995–2015. https://www.unisdr.org/we/inform/publications/46796. Accessed Dec 2018
Chow VT, Maidment DR, Mays LW (1988) Applied hydrology. McGraw-Hill, New York. ISBN: 0070108102 9780070108103 0071001743 9780071001748
Climate Council (2017) Cranking up the intensity: climate change and extreme weather events. The Climate Council of Australia Limited. ISBN: 978-1-925573-15-2 (web). https://www.climatecouncil.org.au/uploads/1b331044fb03fd0997c4a4946705606b.pdf. Accessed Jan 2018
Goodell C, Warren C (2006) Flood inundation mapping using HEC-RAS. Obras y Proyectos, Nº. 2:18–23. ISSN-e: 0718-2813, ISSN: 0718-2805
Gupta AK, Nair S (2011) Urban floods in Bangalore and Chennai: risk management challenges and lessons for sustainable urban ecology. Curr Sci (Bangalore) 100(11):1638–1645
Halwatura D, Najim MMM (2013) Application of the HEC-HMS model for runoff simulation in a tropical catchment. Environ Model Softw 46:155–162
HEC-RAS (2016) River Analysis System: Hydraulic reference manual. USACE version: 5.0. US Army Corps of Engineers, CPD-68
Hirt C (2014) Digital terrain models. Encycl Geodesy. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-02370-0_31-1
Liu Z, Merwade V, Jafarzadegan K (2018) Investigating the role of model structure and surface roughness in generating flood inundation extents using 1D and 2D hydraulic models. J Flood Risk Manag. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfr3.12347
Mitchell VG, Duncan H, Inman M, Rahilly M, Stewart J, Vieritz A, Holt P, Grant A, Fletcher TD, Coleman J, Maheepala S, Sharma A, Deletic A, Breen P (2007) State of the art review of integrated urban water models. In: NOVATECH 2007 - 6th international conference on sustainable techniques and strategies in urban water management, 25–28 June 2007, Lyon, France. http://hdl.handle.net/102.100.100/125083?index=1
Mukherjee S, Aadhar S, Stone D, Mishra V (2018) Increase in extreme precipitation events under anthropogenic warming in India. Weather Climate Extremes 20:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wace.2018.03.005
NDMA (National Disaster Management Authority) GOI (2010) “Guidelines on urban flooding in India.” Government of India. https://ndma.gov.in/images/guidelines/management_urban_flooding.pdf
Prasad RK (2014) Urban floods—a review. Int J Innov Res Sci Eng Technol 5(6):2319–8753. http://www.ijirset.com/upload/2016/nerist/4%20RKP%20urban%20floods.pdf (ISSN (Online))
Quiroga VM, Kure S, Udo K, Mano A (2016) Application of 2D numerical simulation for the analysis of the February 2014 Bolivian Amazonia flood: application of the new HEC-RAS version 5. RIBAGUA Revista Iberoamericana del Agua 3:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riba.2015.12.001
Rafiq F, Ahmed S, Ahmad S, Khan AA (2016) Urban floods in India. Int J Sci Eng Res 7(1):721–734
Ramos HM, Perez-Sanchez M, Franco AB, Lopez-Jimenez PA (2017) Urban floods adaptation and sustainable drainage measures. Fluids. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids2040061
Rangari VA, Patel AK, Umamahesh NV (2015) Review of urban stormwater models. In: HYDRO 2015, 20th international conference on hydraulics, IIT Roorkee, India. Environmental Modelling & Software, vol 16, p 37
Schmitt TG, Thomas M, Ettrich N (2004) Analysis and modeling of flooding in urban drainage systems. J Hydrol 299:3–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.08.012
RAS Solution (2015) http://hecrasmodel.blogspot.com/2015/01/hec-ras-model-with-2d-mesh-only.html. Accessed Jan 2018
SOPUF Ministry of Urban Development, GOI (2017) Urban flooding standard operating procedure. Government of India. https://amrut.gov.in/writereaddata/SOP_Urbanflooding_5May2017.pdf. Accessed Dec 2018
Suriya S, Mudgal B (2012) Impact of urbanization on flooding: the Thirusoolam sub watershed—a case study. J Hydrol 412–413:210–219
Tingsanchali T (2011) Urban flood disaster management. Procedia Eng 32:25–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2012.01.1233
Turkingtona T, Breinlb K, Ettemaa J, Alkemaa D, Jettena V (2016) A new flood type classification method for use in climate change impact. Weather Climate Extremes 14:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wace.2016.10.001
Zoppou C (2001) Review of urban storm water models. Environ Model Softw 16:195–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1364-8152(00)00084-0
Acknowledgements
This research is funded by Information Technology Research Academy (ITRA), Media Lab Asia under sanctioned project entitled “Integrated Urban Flood Management in India: Technology Driven Solution”. We thank Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation (GHMC) and M/S Voyant’s Solutions Private Limited, Hyderabad, for sharing technical data. We also thank National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) for high-resolution dataset to take the study forward. The Landsat satellite images are downloaded from the United States Geological Survey. We also thank HEC-RAS technical team for their valuable suggestions and technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rangari, V.A., Umamahesh, N.V. & Bhatt, C.M. Assessment of inundation risk in urban floods using HEC RAS 2D. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 5, 1839–1851 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-019-00641-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-019-00641-8