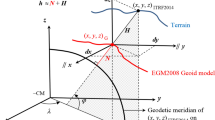
Abstract
A closed-form analytical method needing no approximation and deduced from a single quartic equation is offered to transform geocentric into geodetic coordinates. It is valid at any point inside and outside the Earth including the polar axis, the equatorial plane and the Earth’s center. Comparison with the method of extrema with constraints to obtain this quartic equation is made.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariel A, Ariel-Berger N (2006) Plotting the globe. Praeger, Wesport, Part 3
Borkowski KM (1987) Transformation of geocentric to geodetic coordinates without approximations. Astron Space Sci 139: 1–4
Borkowski KM (1989) Accurate algorithms to transform geocentric to geodetic coordinates. Bull Geod 63: 52–54
Cardanus H (1545) Artis magnae, sive de regulis algebraicis. Pavia, p 294
Descartes R (1637) Discours de la Méthode plus la Dioptrique, les Météores et la Géométrie. Ian Maire Leiden 3: 373
Featherstone WE, Claessens SJ (2008) Closed-form transformation between geodetic and ellipsoidal coordinates. Stud Geophys Geod 52: 12
Fok HS, Iz HB (2003) A comparative analysis of the performance of iterative and non-iterative solutions to the Cartesian to geodetic coordinate transformation. J Geospat Eng 5: 61–74
Fukushima T (1999) Fast transform from geocentric to geodetic coordinates. J Geod 73: 603–610
Fukushima T (2006) Transformation from Cartesian to geodetic coordinates accelerated by Halley’s method. J Geod 79((12): 689–693
Gonzalez-Vega L, Polo-Blanco I (2009) A symbolic analysis of Verm- eille and Borkowski polynomials for transforming 3D Cartesian to geodetic coordinates. J Geod 83: 1071–1081
IERS Conventions (1996) Technical note no. 21, pp 12–13
IERS Conventions (2003) Technical note no. 32, pp 30
Jones GC (2002) New solutions for the geodetic coordinate transformation. J Geod 76: 443
Merriman M (1892) The deduction of final formulas for the algebraic solution of quartic equation. Am J Math 14: 237–245
NIMA (2000) National Imagery and Mapping Agency (USA) Technical Report TR8350.2, 3
Taylor B (1715) Methodus incrementorum directa et inversa. Gul. Innys, London, pp 21–23
Vermeille H (2002) Direct transformation from geocentric coordinates to geodetic coordinates. J Geod 76: 451–454
Vermeille H (2004) Computing geodetic coordinates from geocentric coordinates. J Geod 78: 94–95
Zhang CD et al (2005) An alternative algorithm to transform Cartesian to geodetic coordinates. J Geod 79: 413–420
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vermeille, H. An analytical method to transform geocentric into geodetic coordinates. J Geod 85, 105–117 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-010-0419-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-010-0419-x