Abstract
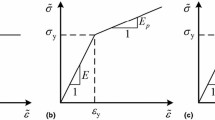
A simple model is described with which the entire force versus penetration behavior of indentation with a sphere, during loading and unloading, may be simulated from knowledge of the four test material parameters, Young’s modulus, Poisson’s ratio, flow stress at the onset of full plastic flow and strain hardening index, and the elastic properties of the indenter. The underlying mechanisms are discussed and the predictions of the model are compared with data produced by an ultra low load, penetration measuring instrument.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. J. Bell A. Bendeli J. S. Field M. V. Swain and E. G. Thwaite Metrologia 28, 463 (1991/1992).
R. Hill E.H. Lee and S.J. Tupper Proc. R. Soc. A 188, 273 (1947).
L. E. Samuels in Microindentation in Metals, Microindentation Techniques in Materials Science and Engineering, edited by P. J. Blau and B.R. Lawn (ASTM Special Technical Publication, 1985), p. 889.
M. C. Shaw and G.J. DeSalvo Trans. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng., Series B 92, 480 (1970).
T. O. Mulhearn J. Mech. and Phys. of Solids 7, 85 (1959).
H. A. Francis Trans, of the ASME, July 272 (1976).
P. S. Follansbee and G. B. Sinclair Int. J. Solids and Structures 20, 172 (1981).
K. L. Johnson Contact Mechanics (Cambridge University Press, 1985).
I. N. Sneddon Int. J. Eng. Sci. 3, 47 (1965).
D. Tabor Hardness of Solids (Oxford University Press, 1951).
L. E. Goodman and L. M. Keer Int. J. Solids and Structures I 407, 117 (1965).
A. E. H. Love A Treatise on the Mathematical Theory of Elasticity, 4th ed. (Cambridge University Press).
M. J. Puttock and E.G. Thwaite Elastic Compression of Spheres and Cylinders at Point and Line Contact, National Standards Laboratory Technical Paper No. 25 (Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization, Australia, 1969).
A.I. Nadai Theory of Flow and Fracture of Solids (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1963), Vol. 2, p. 221.
E. Meyer Z. Ver Deutch Ing. 52, 645 (1908).
M.V. Sinnott The Solid State for Engineers (John Wiley and Sons Inc., New York, 1961).
The Properties of Diamond, edited by J. E. Field (Academic Press, London, 1979).
A. G. Guy and J. J. Hren Elements of Physical Metallurgy, 3rd ed. (Addison-Wesley Pub. Co., Reading, MA, 1974), p. 138.
B.W. Mott Microhardness Indentation Hardness Testing (Butterworths, London, 1956).
W. R. LaFontaine B. Yost and Che-Yu Li, J. Mater. Res. 5, 776 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Field, J.S., Swain, M.V. A simple predictive model for spherical indentation. Journal of Materials Research 8, 297–306 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1993.0297
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1993.0297