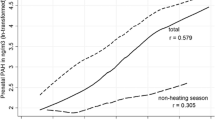
Abstract
Over the last years, concern for the possible influence of exposure to air pollutants in children during gestation or the first years of life has grown; exposure levels which may be reached nowadays in our dwellings and in our streets. In the present study evidence over the possible impact of ambient air pollution on the foetus and the infants (i.e.: less than 1 year) published during the last decade, 1994–2003, are revised. Studies on infant mortality and exposure to particles show an outstanding consistence in the magnitude of the effects, despite the different designs used. As a whole, data show that an increase in 10 μg/m3of particle concentration (measured as PM10) is associated with to about 5% increase in post-neonatal mortality for all causes and around 22% for post-neonatal mortality for respiratory diseases. Regarding damage in foetal health, although results are not always consistent, most studies show associations with exposure to air pollution during pregnancy. However, the precise mechanisms of action of air pollutants on adverse reproductive results are still unknown, so is the period of exposure most relevant during pregnancy and the specific pollutant which may represent a higher risk. Follow-up studies evaluating personal exposure to different air pollutants are required, allowing for the adequate evaluation of the impact of each pollutant in different periods of pregnancy, as well as providing hypotheses on their possible mechanisms of action.
Similar content being viewed by others
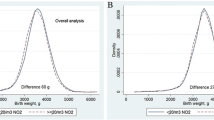
Abbreviations
- BW:
-
birth weight
- CI:
-
confidence interval
- CO:
-
carbon monoxide
- IQR:
-
interquartile range
- IUGR:
-
intrauterine growth retardation
- LBW:
-
low birth weight
- NOx :
-
nitrogen oxides
- O3 :
-
ozone
- PAH:
-
polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
- PCB:
-
polichlorinated biphenyls
- PM10 :
-
particles ≤ 10 μm diameter
- PM2.5 :
-
particles ≤ 2.5 μm diameter
- TSP:
-
total suspended particles
- SGA:
-
small for gestational age
- SIDS:
-
sudden infant death syndrome
- SMR:
-
standardized mortality ratio
- SO2 :
-
sulphur dioxide
- WP:
-
weeks of pregnancy
References
M Maisonet TJ Bush A Correa JJ Jaakkola (2001) ArticleTitleRelation between ambient air pollution and low birth weight in the northeastern United States Environ Health Perspect 109 IssueIDSuppl 3 351–356 Occurrence Handle11427384 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkvFent7s%3D
JF Rogers SJ Thompson CL Addy RE McKeown DJ Cowen P Decouflé (2000) ArticleTitleAssociation of very low birth weight with exposures to environmental sulfur dioxide and total suspended particles Am J Epidemiol 151 602–613 Occurrence Handle10733042 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7psFWrsg%3D%3D
J Dejmek I Solansky I Benes J Lenicek RJ Sram (2000) ArticleTitleThe impact of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and fine particles on pregnancy outcome Environ Health Perspect 108 1159–1164 Occurrence Handle11133396 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkslOnsg%3D%3D
QQ Bui MB Tran WL West (1986) ArticleTitleA comparative study of the reproductive effects of methadone and benzo[a]pyrene in the pregnant and pseudopregnant rat Toxicology 42 195–204 Occurrence Handle3798468 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXhsFWhtbY%3D
N Ribas-Fito M Sala C Mazón et al. (2002) ArticleTitleAssociation of hexachlorobenzene and other organochlorine compounds with anthropometric measures and thyroid hormone status at birth Pediatr Res 52 163–167 Occurrence Handle12149491 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmsFWnurk%3D
FP Perera SM Illman PL Kinney et al. (2002) ArticleTitleThe challenge of preventing environmentally related disease in young children: community-based research in New York City Environ Health Perspect 110 197–204 Occurrence Handle11836150 Occurrence Handle10.1289/ehp.02110197
T Woodruff J Grillo KC Schoendorf (1997) ArticleTitleThe relationship between selected causes of post-neonatal infant mortality and particulate air pollution in the United States Environ Health Perspect 105 608–612 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2svjsVKjuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9288495
L Pereira DP Loomis GMS Conceiao et al. (1998) ArticleTitleAssociation between air pollution and intrauterine mortality in Sao Paulo, Brazil Environ Health Perspect 106 325–329 Occurrence Handle9618348 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c3otlyltw%3D%3D
B Ritz F Yu S Fruin G Chapa GM Shaw JA Harris (2002) ArticleTitleAmbient air pollution and risk of birth defects in Southern California Am J Epidemiol 155 17–25 Occurrence Handle11772780
B Ritz F Yu G Chapa S Fruin (2000) ArticleTitleEffect of air pollution on preterm birth among children born in Southern California between 1989 and 1993 Epidemiology 11 502–511 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00001648-200009000-00004 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2FntlSgtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10955401
Maroziene L, Grazuleviciene R. Maternal exposure to low-level air pollution and pregnancy outcomes: a population-based study. Environ Health 2002; 1: 6
FP Perera V Rauh WY Tsai et al. (2003) ArticleTitleEffects of transplacental exposure to environmental pollutants on birth outcomes in a multiethnic population Environ Health Perspect 111 201–206 Occurrence Handle12573906 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXhsFyguro%3D Occurrence Handle10.1289/ehp.5742
M Bobak DA Leon (1992) ArticleTitleAir pollution and infant mortality in the Czech Republic, 1986–88 Lancet 340 IssueID8826 1010–1014 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0140-6736(92)93017-H Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3s%2Fitlegsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle1357409
R Der-Simonian N Laird (1986) ArticleTitleMeta-analysis in clinical trials Control Clinical Trials 7 177–188 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2s7gsVamtA%3D%3D
FR Witter (1993) ArticleTitlePerinatal mortality and intrauterine growth retardation Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 5 56–59 Occurrence Handle8425036 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3s7ksVKlsg%3D%3D
SJ Chen BR Vohr W Oh (1993) ArticleTitleEffects of birth order, gender, and intrauterine growth retardation on the outcome of very low birth weight in twins J Pediatr 123 132–136 Occurrence Handle8320607 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3szgvVGkug%3D%3D
B Luke C Williams J Minogue L Keith (1993) ArticleTitleThe changing pattern of infant mortality in the US: the role of prenatal factors and their obstetrical implications Int J Gynaecol Obstet 40 199–212 Occurrence Handle8096471 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3s3hsF2isw%3D%3D
A Spinillo E Capuzzo TO Egbe E Fazzi L Colonna S Nicola (1995) ArticleTitlePregnancies complicated by idiopathic intrauterine growth retardation. Severity of growth failure, neonatal morbidity and two-year infant neurodevelopmental outcome J Reprod Med 40 209–215 Occurrence Handle7539849 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2M3psV2gsg%3D%3D
KS Joseph MS Kramer (1996) ArticleTitleReview of the evidence on fetal and early childhood antecedents of adult chronic disease Epidemiol Rev 18 158–174 Occurrence Handle9021310 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s7ntlCjtg%3D%3D
EH Ha YC Hong BE Lee BH Woo J Schwartz DC Christiani (2001) ArticleTitleIs air pollution a risk factor for low birth weight in Seoul? Epidemiology 12 643–648 Occurrence Handle11679791 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MrntF2nsw%3D%3D
CC Arnold MS Kramer CA Hobbs FH McLean RH Usher (1991) ArticleTitleVery low birth weight: a problematic cohort for epidemiologic studies of very small or immature neonates Am J Epidemiol 134 604–613 Occurrence Handle1951265 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK38%2FlvV2gsA%3D%3D
MS Kramer (1987) ArticleTitleDeterminants of low birth weight: methodological assessment and meta-analysis Bull World Health Organ 65 663–737 Occurrence Handle3322602 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c7gvFyjtQ%3D%3D
SV Glinianaia J Rankin R Bell T Pless-Mulloli D Howel (2004) ArticleTitleParticulate air pollution an fetal health A systematic review of the epidemiologic evidence. Epidemiology 15 36–45
M Bobak (2000) ArticleTitleOutdoor air pollution, low birth weight, and prematurity Environ Health Perspect 108 173–176 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7itlyltA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10656859
R Bhopal P Phillimore S Moffatt C Foy (1994) ArticleTitleIs living near a coking works harmful to health? A study of industrial air pollution J Epidemiol Community Health 48 IssueID237 247
O Landgren (1996) ArticleTitleEnvironmental pollution and delivery outcome in southern Sweden: a study with central registries Acta Paediatr 85 1361–1364 Occurrence Handle8955467 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s7htlKisg%3D%3D
J Dejmek SG Selevan I Benes I Solansky RJ Sram (1999) ArticleTitleFetal growth and maternal exposure to particulate matter during pregnancy Environ Health Perspect 107 475–480 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3nt1GgtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10339448
RF Lamont (2003) ArticleTitleThe role of infection in preterm labour and birth Hosp Med 64 644–647 Occurrence Handle14671873
WW Andrews JC Hauth RL Goldenberg (2000) ArticleTitleInfection and preterm birth Am J Perinatol 17 357–365 Occurrence Handle12141522 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38zptlaisw%3D%3D
X Xu H Ding X Wang (1995) ArticleTitleAcute effects of total suspended particles and sulfur dioxides on preterm delivery: a community-based cohort study Arch Environ Health 50 407–415 Occurrence Handle8572718 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XosFaisg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1080/00039896.1995.9935976
A Peters A Döring HE Wichmann W Koenig (1997) ArticleTitleIncreased plasma viscosity during an air pollution episode: a link to mortality? The Lancet 349 1582–1587 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2szhslGntA%3D%3D
X Wang H Ding L Ryan X Xu (1997) ArticleTitleAssociation between air pollution and low birth weight: a community-based study Environ Health Perspect 105 514–520 Occurrence Handle9222137 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2szmsFaltQ%3D%3D
M Bobak DA Leon (1999) ArticleTitlePregnancy outcomes and outdoor air pollution: an ecological study in districts of the Czech Republic 1986–1988 Occup Environ Med 56 539–543 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXltlOit7k%3D Occurrence Handle10492651
KA Wood RJ Youle (1995) ArticleTitleThe role of free radicals and p53 in neuron apoptosis in vivo J Neurosci 15 IssueID8 5851–5857 Occurrence Handle7643225 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnsVOrtL0%3D
M Wilhelm B Ritz (2003) ArticleTitleResidential proximity to traffic and adverse birth outcomes in Los Angeles county, California, 1994–1996 Environ Health Perspect 111 207–216 Occurrence Handle12573907 Occurrence Handle10.1289/ehp.5688
S Tabacova DD Baird L Balabaeva (1998) ArticleTitleExposure to oxidized nitrogen: lipid peroxidation and neonatal health risk Arch Environ Health 53 214–221 Occurrence Handle9814718 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXktVSrtLc%3D Occurrence Handle10.1080/00039899809605698
JJ Duvekot EC Cheriex FA Pieters LL Peeters (1995) ArticleTitleSeverely impaired fetal growth is preceded by maternal hemodynamic maladaptation in very early pregnancy Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 74 693–697 Occurrence Handle7572102 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK28%2Fis1SgsA%3D%3D
TJ Dummer HO Dickinson L Parker (2003) ArticleTitleAdverse pregnancy outcomes around incinerators and crematoriums in Cumbria, north west England, 1956–1993 J Epidemiol Community Health 57 456–461 Occurrence Handle12775795 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3s3lt1WmsQ%3D%3D
M Mathieu-Nolf (2002) ArticleTitlePoisons in the air: a cause of chronic disease in children J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 40 483–491 Occurrence Handle12217001 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XnsVSnt7k%3D
M Bobak DA Leon (1999) ArticleTitleThe effect of air pollution on infant mortality appears specific for respiratory causes in the post-neonatal period Epidemiology 10 666–670 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00001648-199911000-00001 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2FgsVCgtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10535778
H Dolk B Thakrar P Walls et al. (1999) ArticleTitleMortality among residents near cokeworks in Great Britain Occup Environ Med 56 34–40 Occurrence Handle10.1136/oem.56.1.34 Occurrence Handle10341744 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3ntlaqsg%3D%3D
D Loomis M Castillejos DR Gold W McDonnell VH Borja-Aburto (1999) ArticleTitleAir pollution and infant mortality in Mexico City Epidemiology 10 118–123 Occurrence Handle10069245 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7ms1Oktw%3D%3D
NA Janssen G Hoek B Brunekreef H Harssema I Mensink A Zuidhof (1998) ArticleTitlePersonal sampling of particles in adults: relation among personal, indoor, and outdoor air concentrations Am J Epidemiol 147 537–547 Occurrence Handle9521180 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7otVCktw%3D%3D
S Zeger D Thomas F Dominici JM Samet J Schwartz DW Dockery AJ Cohen (2000) ArticleTitleExposure measurement error in time-series studies of air pollution: concepts and consequences Environ Health Perspect 108 419–426 Occurrence Handle10811568 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXktlGhsbw%3D
JA Sarnat J Schwartz PJ Catalano HH Suh (2001) ArticleTitleGaseous pollutants in particulate matter epidemiology: confounders or surrogates? Environ Health Perspect 109 1053–1061 Occurrence Handle11675271 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXotlGjurY%3D
EH Ha JT Lee H Kim et al. (2003) ArticleTitleInfant susceptibility of mortality to air pollution in Seoul, South Korea Pediatrics 111 284–290 Occurrence Handle12563052
DM Stieb S Judek RT Burnett (2002) ArticleTitleMeta-analysis of time-series studies of air pollution and mortality: effects of gases and particles and the influence of cause of death, age, and season J Air Waste Manag Assoc 52 470–484 Occurrence Handle12002192
CA Pope RT Burnett MJ Thun EE Calle D Krewski K Ito GD Thurston (2002) ArticleTitleLung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution JAMA 287 1132–1141 Occurrence Handle11879110 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XhslGgtbo%3D
JM Peters E Avol W Navidi et al. (1999) ArticleTitleA study of twelve Southern California communities with differing levels and types of air pollution I. Prevalence of respiratory morbidity Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159 760–767 Occurrence Handle10051248 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7mtVOrsw%3D%3D
WJ Gauderman GF Gilliland H Vora et al. (2002) ArticleTitleAssociation between air pollution and lung function growth in southern California children: results from a second cohort Am J Respir Crit Care Med 166 76–84 Occurrence Handle10.1164/rccm.2111021 Occurrence Handle12091175
M Brauer G Hoek P Van Vliet et al. (2002) ArticleTitleAir pollution from traffic and the development of respiratory infections and asthmatic and allergic symptoms in children Am J Respir Crit Care Med 166 1092–1098 Occurrence Handle12379553
SH Gavett N Haykal-Coates LB Copeland J Heinrich MI Gilmour (2003) ArticleTitleMetal Composition of ambient PM2.5 influences severity of allergic airways disease in mice Environ Health Perspect 111 1471–1477 Occurrence Handle12948886 Occurrence Handle10.1289/ehp.6300
B Ritz F Yu (1999) ArticleTitleThe effect of ambient carbon monoxide on low birth weight among children born in southern California between 1989 and 1993 Environ Health Perspect 107 17–25 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M%2FptFGjug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9872713
H Dolk S Pattenden S Vrijheid et al. (2000) ArticleTitlePerinatal and infant mortality and low birth weight among residents near cokeworks in Great Britain Arch Environ Health 55 26–30 Occurrence Handle10735516 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7pslGlsQ%3D%3D
EH Ha JT Lee H Kim et al. (2003) ArticleTitleInfant susceptibility of mortality to air pollution in Seoul, South Korea Pediatrics 111 284–290 Occurrence Handle12563052
M Bobak M Richards M Wadsworth (2001) ArticleTitleAir pollution and birth weight in Britain in 1946 Epidemiology 16 358–359
MC Lin HS Yu SS Tsai et al. (2001a) ArticleTitleAdverse pregnancy outcome in a petrochemical polluted area in Taiwan J Toxicol Environ Health 63 565–574 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXmsFyqsbg%3D
M Wilhelm B Ritz (2003) ArticleTitleResidential proximity to traffic and adverse birth outcomes in Los Angeles county, California, 1994–1996 Environ Health Perspect 111 201–216
CY Yang YT Tseng CC Chang (2003) ArticleTitleEffects of air pollution on birth weight among children born between 1995 and 1997 in Kaohsiung, Taiwan J Toxicol Environ Health 66 807–816 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXivFOgtLw%3D
MC Lin HF Chiu HS Yu et al. (2001b) ArticleTitleIncreased risk of preterm delivery in areas with air pollution from a petroleum refinery plant in Taiwan J Toxicol Environ Health 64 637–644 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXptFGis7Y%3D
SS Tsai HS Yu CC Liu CY Yang (2003) ArticleTitleIncreased incidence of preterm delivery in mothers residing in an industrialized area in Taiwan J Toxicol Environ Health 66 987–994 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjvV2kurw%3D
Woodruff TJ, Parker JD, Kyle AD, Schoendorf KC. Disparities in exposure to air pollution during pregnancy Environ Health Perspect 2003; 111: 942–946.
Yang CY, Chiu HF, Tsai SS, Chang CC, Chuang HY. Increased risk of preterm delivery in areas with cancer mortality problems from petrochemical complexes Environ Res 2002; 89: 195–200.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lacasaña, M., Esplugues, A. & Ballester, F. Exposure to ambient air pollution and prenatal and early childhood health effects. Eur J Epidemiol 20, 183–199 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-004-3005-9
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-004-3005-9