Abstract
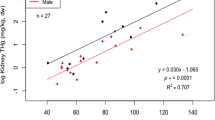
Total mercury concentrations were determined in the kidney (K), liver (L), and pectoral muscle (M) of 19 individuals representing wild carnivorous mammals from NW Poland: 10 red foxes Vulpes vulpes (Linnaeus, 1758), 3 raccoon dogs Nyctereutes procyonoides Gray, 1834, 2 badgers Meles meles Linnaeus, 1758, 3 pine martens Martes martes Linnaeus, 1758, and 1 polecat Mustela putorius Linnaeus, 1758. The sample of red fox included 3 immature specimens found on Mielin Island; the island supports a black cormorant colony, and the foxes found there had fed mostly on cormorant nestlings as well as on fish and their remains. In addition to the Mielin Island foxes, the group of foxes included 3 other immature and 4 adult individuals. The highest mean of mercury concentrations were revealed in the Mielin red fox juveniles: 5.11, 4.52, and 1.56 mg/kg d.w. being recorded in K, L, and M. No significant differences in mercury concentrations in the respective tissues were found between the remaining immature and adult red foxes; their mercury concentrations were several times lower than those of the Mielin individuals. In all the animals except the Mielin foxes, mercury concentrations in K, L, and M did not exceed 1.3, 1.0 and 0.5 mg/kg d.w., respectively, the highest values being in badgers (which feed mostly on soil invertebrates), followed by pine martens and then the canids (red fox and raccoon dog). Studies on common and widely distributed terrestrial animals, particularly red fox and badger, may provide numerous valuable comparative data on mercury contamination of different areas of the northern hemisphere.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alleva E., Francia N., Pandolfi M., De Marinis A. M., Chiarotti F. and Santucci D. 2006. Organochlorine and heavy-metal contaminants in wild mammals and birds of Urbino-Pesaro province, Italy: an analytic overview for potential bioindicators. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 51: 123–134. DOI:10.1007/s00244-005-0218-1
Baghli A., Engel E. and Verhagen R. 2002. Feeding habits and trophic niche overlap of two sympatric Mustelidae, the polecat Mustela putorius and the beech marten Martes foina. Zeitschrift für Jagdwissenschaft 48: 217–225. DOI: 10.1007/BF02189692
Basu N., Scheuhammer A. M., Bursian S. J., Elliott J., Rouvinen-Watt K. and Chan H. M. 2007. Mink as a sentinel species in environmental health. Environmental Research 103: 130–144. DOI:10.1016/j.envres.2006.04.005
Björkman L., Lundekvam B. F., Laegreid T., Bertelsen B. I., Morild I., Lilleng P., Lind B., Palm B. and Vahter M. 2007. Mercury in human brain, blood, muscle and toenails in relation to exposure: an autopsy study. Environmental Health 6: 30.
Borg K., Wanntorp H., Erne K. and Hanko E. 1969. Alkyl mercury poisoning in terrestrial Swedish wildlife. Viltrevy 6: 301–379.
Brookens T. J., O’Hara T. M., Taylor R. J., Bratton G. R. and Harvey J. T. 2008. Total mercury body burden in Pacific harbor seal, Phoca vitulina richardii, pups from central California. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56: 27–41. DOI:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2007.08.010
Burger J. and Gochfeld M. 2008. Knowledge about fish consumption advisories: A risk communication failure within a university population. Science of the Total Environment 390: 346–354. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.10.016
Caldwell C. A., Arnold M. A. and Gould W. R. 1999. Mercury distribution in blood, tissues, and feathers of doublecrested cormorant nestlings from arid-lands reservoirs in south central New Mexico. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 36: 456–461. DOI:10.1007/PL00006618
Čelechovská O., Literák I., Ondruš S. and Pospíšil Z. 2006. Heavy metals in brown bears from the central European Carpathians. Acta Veterinaria Brno 75: 501–506. DOI:10.2754/avb200675040501
Champoux L., Rodrigue J., Braune B. and Leclair D. 1999. Contaminants in Northern Québec wildlife. [In: Synopsis of research conducted under the 1997–1998 Northern Contaminants Program. J. Jensen, ed]. Department of Indian Affairs and Northern Development, Ottawa: 109–116.
Chen C., Zhang P. and Chai Z. 2005. Subcellular localization of several heavy metals of Hg, Cd and Pb in human liver. Chinese Science Bulletin 50: 113–116.
Churcher C. S. 1960. Cranial variation in the north American red fox. Journal of Mammalogy 4: 349–360.
Clarkson T. W. 2002. The three faces of mercury. Environmental Health Perspectives 110: 11–23.
Corsolini S., Focardi S., Leonzio C., Lovari S., Monaci F. and Romeo G. 1999. Heavy metals and chlorinated hydrocarbon concentrations in the red fox in relation to some biological parameters. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 54: 87–100. DOI:10.1023/A:1005974014029
Cristol D., Brasso R. L., Condon A. M., Fovargue R. E., Friedman S. L., Hallinger K. K., Manroe A. P. and White A. E. 2008. The movement of aquatic mercury through terrestrial food webs. Science 320, 335. DOI: 10.1126/science.320.5874.389b
Dehn L. A., Follmann E. H., Thomas D. L., Sheffield G. G., Rosa C., Duffy L. K., O’Hara T. M. 2006. Trophic relationships in an Arctic food web and implications for trace metal transfer. Science of the Total Environment. 362: 103–123. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.11.012
DesGranges J.-L., Rodrigue J., Tardif B. and Laperle M. 1998. Mercury accumulation and biomagnification in ospreys (Pandion haliaetus) in the James Bay and Hudson Bay regions of Québec. Archives Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 35: 330–341. DOI:10.1007/s002449900384
Dietz R., Pacyna J. and Thomas D. J. 1998. Heavy metals. [In: AMPAP Assessment Report: Arctic pollution issues. S. J. Wilson, J. L. Murray and H. P. Huntington, eds]. Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme, Oslo, Norway: 373–524.
DiFrancesco D. T. and Shinn R. C. 2002. New Jersey Mercury Task Force Report. Vol. II. Exposure and Impacts. New Jersey US, Department of Environmental Protection’s (http://www.nj.gov.dep/dsr/mercury_task_ force.htm).
Driscoll C. T., Han Y.-J., Chen C. Y., Evers D. C., Lambert K. F., Holsen T. M., Kamman N. C. and Munson R. K. 2007. Mercury contamination in forest and freshwater ecosystems in the northwestern United States. BioScience 57: 17–28. DOI:10.1641/B570106
Eisler R. 1987. Mercury hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebrates: a synoptic review. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Biological Report 85 (1.10): 63.
Farrar W. P., Edwards J. F. and Willard M. D. 1994. Pathology in a dog associated with elevated tissue mercury concentrations. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation 6: 511–514.
Fay F. H. and Stephenson R. O. 1989. Annual, seasonal, and habitat-related variation in feeding habits of arctic fox (Pandion haliaetus) on St Lawrence Island, Bering Sea. Canadian Journal of Zoology 67: 1986–1994. DOI:10.1139/z89-283
Foley R. E., Jackling S. J., Sloan R. J. and Brown M. K. 1988. Organochlorine and mercury residues in wild mink and otter: comparison with fish. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 7: 363–374. DOI: 10.1897/1552-8618(1988)7[363:OAMRIW]2.0.CO;2
Gamberg M. and Braune B. M. 1999. Contaminant residue levels in arctic wolves (Canis lupus) from the Yukon Territory, Canada. Science of the Total Environment 243/244: 329–338. DOI:10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00408-8
Gamberg M., Braune B., Davey E., Elkin B., Hoekstra P. F., Kennedy D., Macdonald C., Muir D., Nirwal A., Wayland M. and Zeeb B. 2005. Spatial and temporal trends of contaminants in terrestrial biota from the Canadian Arctic. Science of the Total Environment. 351–352: 148–164. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.10.032
Gołdyn B., Hromada M., Surmacki A. and Tryjanowski P. 2003. Habitat use and diet of the red fox Vulpes vulpes in an agricultural landscape in Poland. Zeitschrift für Jagdwissenschaft 49: 191–200. DOI:10.1007/BF02189737
Gutleb A. C., Kranz A., Nechay G. and Toman A. 1998. Heavy metal concentrations in livers and kidneys of the otter (Lutra lutra) from central Europe. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 60: 273–279. DOI:10.1007/s001289900621
Halbrook R. S., Jenkins J. H., Bush P. B. and Seabolt N. D. 1994. Sublethal concentrations of mercury in river otters: monitoring environmental contamination. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 27: 306–310. DOI:10.1007/BF00213164
Hansen J. C., Reske-Nielsen E., Thorlacius-Ussing O., Rungby J. and Danscher G. 1989. Distribution of dietary mercury in a dog. Quantitation and localization of total mercury in organs and central nervous system. Science of the Total Environment 78: 23–43.
Harding L. E. 2004. Environmental contaminants in wild martens (Martes amaricana) and wolverines (Gulo luscus). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 73: 98–105. DOI: 10.1007/s00128-004-0399-8
Harding L. E., Harris M. L. and Elliott J. E. 1998. Heavy and trace metals in wild mink (Mustela vision) and river otter (Lontra canadensis) captured on rivers receiving metals discharges. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 61: 600–607. DOI: 10.1007/s001289900803
Heinz G. H. 1996. Mercury poisoning in wildlife. [In: Non-infectious diseases of wildlife. A. Faibrother, L. N. Locke and G. L. Hoff, eds]. The Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa: 118–127.
Hoekstra P. F., Braune B. M., Elkin B., Armstrong F. A. J. and Muir D. C. G. 2003. Concentrations of selected essential and non-essential elements in arctic fox (Alopex lagopus) and wolverines (Gulo gulo) from the Canadian Arctic. Science of the Total Environment 309: 81–92. DOI:10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00684-8
Horai S., Minagawa M., Ozaki H., Watanabe I., Takeda Y., Yamada K., Ando T., Akiba S., Abe S. and Kuno K. 2006. Accumulation of Hg and other heavy metals in the Javan mongoose (Herpestes javanicus) captured on Amamioshima Islans in Japan. Chemosphere 65: 657–665. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.01.078 http://www.stat.gov.pl/szczec/69_360_PLK_HTML.htm
Hylander L. D. and Goodsite M. E. 2006. Environmental costs of mercury pollution. Science of the Total Environment 368: 352–370. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.11.029
Jędrzejewska B. and Jędrzejewski W. 1998. Predation in vertebrate communities. Springer Verlag, Heidelberg, Berlin: 1–450.
Kauhala K., Laukkanen P. and von Rége I. 1998. Summer food composition and food niche overlap of the raccoon dog, red fox and badger in Finland. Ecography 21: 457–463.
Lanszki J., Zalewski A. and Horváth G. 2007. Comparison of red fox Vulpes vulpes and pine marten Martes martes food habits in a deciduous forest in Hungary. Wildlife Biology 13: 258–271. DOI: 10.2981/0909-6396(2007)13[258:CORFVV]2.0.CO;2
López-Alonso M., Miranda M., García-Partida P., Cantero F., Hernández J. and Benedito J. L. 2007. Use of dogs as indicators of metal exposure in rural and urban habitats in NW Spain. Science of the Total Environment 372: 668–675. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.10.003
Mason C. F. and Weber D. 1990. Organochlorine residues and heavy metals in kidneys of polecat (Mustela putorius) from Switzerland. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 45: 689–696. DOI: 10.1007/BF01700987
Mergler D., Anderson H. A., Chan L. H. M., Mahaffey K. R., Murry M., Sakamoto M. and Stern A. H. 2007. Methylmercury exposure and health effects in humans: a worldwide concern. Ambio 36: 3–11. DOI: 10.1579/0044-7447(2007)36[3:MEAHEI]2.0.CO;2
Millán J., Mateo R., Taggart M. A., López-Bao J. V., Viota M., Monsalve L., Camareo P. R., Blázquez E. and Jiménez B. 2008. Levels of heavy metals and metalloids in critically endangered Iberian lynx and other wild carnivores from Southern Spain. Science of the Total Environment 399: 193–201. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.03.038
Munthe J., Hellsten S. and Zetterberg T. 2007. Mobilization of mercury and methylmercury from forest soils after a severe storm-fell event. Ambio 36: 111–113. DOI: 10.1579/0044-7447(2007)36[111:MOMAMF]2.0.CO;2
Nilsson A. and Huntington H. 2002. Arctic Pollution 2002. AMAP, Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme, Box 8100 Dep. N-0032, Oslo, Norway: 111.
O’Brien D. J., Kaneene J. B. and Poppenga R. H. 1993. The use of mammals as sentinels for human exposure to toxic contaminants in the environment. Environmental Health Perspectives 99: 351–368.
Orłowski G. and Nowak L. 2006. Factors influencing mammal roadkills in the agricultural landscape of southwestern Poland. Polish Journal of Ecology 54: 283–294.
Pacyna E. G., Pacyna J. M., Fudala J., Strzelecka-Jastrzab E., Hlawiczka S. and Panasiuk D. 2006. Mercury emissions to the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources in Europe in 2000 and their scenarios until 2020. Science of the Total Environment 370: 147–156. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.06.023
Piskorová L., Vasilková Z. and Krupicer I. 2003. Heavy metals residues in tissues of wild boar (Sus scrofa) and red fox (Vulpes vulpes) in the Central Zemplin region of the Slovak Republic. Czech Journal of Animal Science 48: 134–138.
Poole K. G., Elkin B. T. and Bethke R. W. 1995. Environmental contaminants in wild mink in the Northwest Territories, Canada. Science of the Total Environment 160/161: 473–486.DOI:10.1016/0048-9697(95)04381-A
Prestrud P., Norheim G., Sivertsen T. and Daae H. L. 1994. Levels of toxic and essential elements in arctic fox in Svalbard. Polar Biology 14: 155–159. DOI:10.1007/BF00240520
Roustan Y. and Bocquet M. 2006. Inverse modeling for mercury over Europe. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics 6: 3085–3098.
Sepúlveda M. S., Poppenga R. H., Arregis J. J. and Quinn L. B. 1998. Concentrations of mercury and selenium in tissues of double-crested cormorants (Phalacrocorax auritus) from southern Florida. Colonial Waterbirds 21: 35–42.
Sheffy T. B. and Amant J. R. S. 1982. Mercury burdens in furbearers in Wisconsin. The Journal of Wildlife Management 46: 1117–1120.
Shore R. F., Casulli A., Bologov V., Wienburg C. L., Afsar A., Toyne P. and Dell’Omo G. 2001. Organochlorine pesticide, polychlorinated biphenyl and heavy metal concentrations in wolves (Canis lupus L. 1758) from north-west Russia. Science of the Total Environment 280: 45–54. DOI: 10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00802-6
Sidorovich V. E., Sidorovich A. and Izotova I. V. 2006. Variations in the diet and population density of the red fox Vulpes vulpes in the mixed woodlands on northern Belarus. Mammalian Biology 71: 74–89. DOI: 10.1016/j.mambio.2005.12.001
Sonne C., Dietz R., Leifsson P. S., Asmund G., Born E. W. and Kirkegaard M. 2007. Are liver and renal lesions in East Greenland polar bears (Ursus maritimus) associated with high mercury levels? Environmental Health. 6: 11 (http://www.ehjournal.net/content/6/1/11). DOI:10.1186/1476-069X-6-11
Spalding M. G., Frederick P. C. McGill H. C., Bouton S. N. and McDowell L. R. 2000. Methylmercury accumulation in tissues and its effects on growth and appetite in captive great egrets. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 36: 411–422.
Storelli M. M., Zizzo N. and Marcotrigiano G. O. 1999. Heavy metals and methylmercury in tissues of risso’s dolphin (Grampus griseus) and cuvier’s beaked whale (Ziphius cavirostris) stranded in Italy (South Adriatic Sea). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 63: 703–710. DOI: 10.1007/s001289901037
Strom S. M. 2008. Total mercury and methylmercury residues in river otters (Lutra canadensis) from Wisconsin. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 54: 546–554. DOI:10.1007/s00244-007-9053-x
Sutor A. 2008. Dispersal of the alien raccoon dog Nyctereutes proconoides in southern Brandenburg, Germany. European Journal of Wildlife Research 54: 321–326. DOI:10.1007/s10344-007-0153-8
UNEP 2002. Chemicals. Global Mercury assessment. Report no. 54790-01. Geneva, Switzerland: 1–258. http://www.chem.unep.ch.
[US EPA] US Environmental Protection Agency 1997a. Mercury Study Report to Congress. Vol. VI: An Ecological Assessment for Anthropogenic Mercury Emissions in the United States. EPA-452/R-97-008.
[US EPA] US Environmental Protection Agency 1997b. Mercury Study Report to Congress. Vol. VII. Characterization of Human Health and Wildlife Risks from Mercury Exposure in the United States. Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards and Office of Research and Development. Report no. EP-452/R-97-009.
Vilella F. J. 1998. Biology of the mangoose (Herpestes javanicus) in a rain forest of Puerto Rico. Biotropica 30: 120–125. DOI: 10.1111/j.1744-7429.1998.tb00374.x
Wiener J. G., Krabbenhoft D. P., Heinz G. H. and Scheuhammer A. M. 2003. Ecotoxicology of Mercury. [In: Handbook of Ecotoxicology. D. J. Hoffman, B. A. Rattner, G. A. Burton and J. Cairns, eds]. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton: 409–463.
Wolfe M. F., Schwarzbach S. and Sulaiman R. A. 1998. Effects of mercury on wildlife: a comprehensive review. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 17: 146–160. DOI:10.1897/1551-5028(1998)017<0146:EOMOWA>2.3.CO;
Yates D. E., Mayack D. T., Munney K., Evers D. C., Major A., Kaur T. and Taylor R. J. 2005. Mercury levels in mink (Mustella vison) and river otter (Lontra canadensis) from northeastern North America. Ecotoxicology 14: 263–274. DOI: 10.1007/s10646-004-6273-y
Zillioux E. J., Porcella D. B. and Benoit J. M. 1993. Mercury cycling and effects in freshwater wetland ecosystems. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 12: 2245–2264. DOI: 10.1897/1552-8618(1993)12[2245:MCAEIF]2.0.CO;2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate editor was Andrzej Zalewski.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalisińska, E., Lisowski, P., Salicki, W. et al. Mercury in wild terrestrial carnivorous mammals from north-western Poland and unusual fish diet of red fox. Acta Theriol 54, 345–356 (2009). https://doi.org/10.4098/j.at.0001-7051.032.2008
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4098/j.at.0001-7051.032.2008