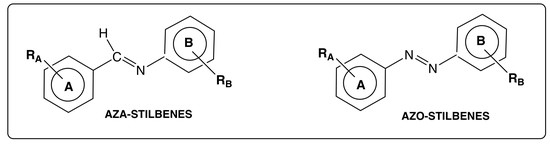
Aza- and Azo-Stilbenes: Bio-Isosteric Analogs of Resveratrol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structural and Synthetic Sights of AZA-ST and AZO-ST Compared with trans-RSV
2.1. Isosteric Features of C=N and N=N Bonds
2.2. Synthetic Pathways for Obtaining AZA-ST and AZO-ST
2.3. Symmetry or Dissymmetry of Double Bonds
3. Biological Activities of Aza-Stilbenes
3.1. Aza-Stilbenes Bearing A Hydroxyl Group in Ortho Position of Cycles A or/and B
3.2. Aza-Stilbenes Bearing A Catechol Group on Cycle A
4. Biological Activities of Azo-Stilbenes AZO-ST
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takaoka, M. Phenolic substances of white hellebore (Veratrum grandiflorum Loes. fil.). J. Faculty Sci. 1940, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arichi, H.; Kimura, Y.; Okuda, H.; Baba, M.; Kozowa, K.; Arichi, S. Effects of stilbene compounds of the roots of Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc. on lipid metabolism. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1982, 30, 1766–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burns, J.; Yokota, T.; Ashihara, H.; Lean, M.E.J.; Crozier, A. Plant foods and herbal sources of resveratrol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3337–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrian, M.; Jeandet, P. Effects of resveratrol on the ultrastructure of Botrytis cinerea conidia and biological significance in plant/pathogen interactions. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlus, A.D.; Sahli, R.; Bisson, J.; Rivière, C.; Delaunay, J.C.; Richard, T.; Gomes, E.; Bordenave, L.; Waffo-Teguo, P.; Mérillon, J.M. Stilbenoid profiless of canes from Vitis and Muscadinia species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutegrabet, L.; Fekete, A.; Hertkorn, N.; Papastamoulis, Y.; Waffo-Téguo, P.; Mérillon, J.M.; Jeandet, P.; Gougeon, R.D.; Schmitt-Koplin, P. Determination of stilbene derivatives in Burgundy red wines by ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülçin, I. Antioxidant properties of resveratrol: A structure-activity insight. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, O.S.; Bhat, A.A.; Krishnankutty, R.; Mohammad, R.M.; Uddin, S. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol in lymphoid malignancies. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, C.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Chang, L.K.; Chiu, Y.F.; Lin, T.P. Inhibitory effects of resveratrol on the Epstein-Barr virus lytic cycle. Molecules 2010, 15, 7115–7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tili, E.; Michaille, J.J.; Adair, B.; Alder, H.; Limagne, E.; Taccioli, C.; Ferracin, M.; Delmas, D.; Latruffe, N.; Croce, C.M. Resveratrol decreases the levels of miR-155 by upregulating miR-663, a microRNA targeting JunB and JunD. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, J.; Lançon, A.; Aires, V.; Limagne, E.; Tili, E.; Michaille, J.J.; Latruffe, N. Resveratrol initiates differentiation of mouse skeletal muscle-derived C2C12 myoblasts. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namsi, A.; Nury, T.; Hamdouni, H.; Yammine, A.; Vejux, A.; Vervandier-Fasseur, D.; Latruffe, N.; Masmoudi-Kouki, O.; Lizard, G. Induction of neuronal differentiation of murine N2a cells by two polyphenols present in the mediterranean diet mimicking neurotrophins activities: Resveratrol and apigenin. Diseases 2018, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.; Agrawal, M.; Doré, S. Neuroprotective properties and mechanisms of resveratrol in in vitro and in vivo experimental cerebral stroke models. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stef, G.; Csiszar, A.; Lerea, K.; Ungvari, Z.; Veress, G. Resveratrol inhibits aggregation of platelets from high-risk cardiac patients with aspirin resistance. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 48, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.G.; Rogina, B.; Lavu, S.; Howitz, K.; Helfand, S.L.; Tatar, M.; Sinclair, D. Sirtuin activators mimic caloric restriction and delay ageing in metazoans. Nature 2004, 430, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, M.A.; Morris, B.J. Resveratrol in prevention and treatment of common clinical conditions of aging. Clin. Interv. Aging 2008, 3, 331–339. [Google Scholar]
- Westphal, C.H.; Dipp, M.A.; Guarente, L. A therapeutic role for situins in diseases of aging? Trends Biochem. Res. 2007, 32, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonkowski, M.S.; Sinclair, D.A. Slowing ageing by design: The rise of NAD+ and sirtuin-activating compounds. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore Benito, A.; Valero Zanuy, M.Á.; Alarza Cano, M.; Ruiz Alonso, A.; Alda Bravo, I.; Rogero Blanco, E.; Maíz Jiménez, M.; León Sanz, M. Adherence to Mediterranean diet: A comparison of patients with head and neck cancer and healthy population. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2019, 66, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Peng, B.; Yan, W. Measurement and correlation of solubility of trans-resveratrol in 11 solvents at T = (278.2, 282.2, 298.2, 308.2 and 318.2) K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2008, 40, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, D.; Aires, V.; Limagne, E.; Dutartre, P.; Mazué, F.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Latruffe, N. Transport, stability and biological activity of resveratrol. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1215, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardile, V.; Chillemi, R.; Lombardo, L.; Sciuto, S.; Spatafora, C.; Tringali, C. Antiproliferative activity of methylated analogues of E- and Z-resveratrol. Z. Naturforsch. C 2007, 62, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Kim, C.T.; Jo, Y.H.; Kim, S.B.; Hwang, B.Y.; Lee, M.K. Synthesis and biological evaluation of resveratrol derivatives as melanogenesis inhibitors. Molecules 2015, 20, 16933–16945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nawaz, W.; Zhou, Z.; Deng, S.; Ma, X.; Ma, X.; Li, C.; Shu, X. Therapeutic versatility of resveratrol derivatives. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chalal, M.; Vervandier-Fasseur, D.; Meunier, P.; Cattey, H.; Hierso, J.C. Syntheses of polyfunctionalized resveratrol derivatives using Wittig and Heck protocols. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 3899–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalal, M.; Klinguer, A.; Echairi, A.; Meunier, P.; Vervandier-Fasseur, D.; Adrian, M. Antimicrobial activity of resveratrol analogues. Molecules 2014, 19, 7679–7688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalal, M.; Delmas, D.; Meunier, P.; Latruffe, N.; Vervandier-Fasseur, D. Inhibition of cancer derived cell lines proliferation by newly synthesized hydroxylated stilbenes and ferrocenyl-stilbene analogs. Comparison with resveratrol. Molecules 2014, 19, 7850–7868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latruffe, N.; Vervandier-Fasseur, D. Strategic syntheses of vine and wine resveratrol derivatives to explore their effects on cell functions and dysfunctions. Diseases 2018, 6, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belluti, F.; Fontana, G.; Dal Bo, L.; Carenini, N.; Giommarelli, C.; Zunino, F. Design, synthesis and anticancer activities of stilbene-coumarin hybrid compounds: Identification of novel proapopoptic agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 3543–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, C.; Desideri, N. New 4H-chromene-4-one and 2H-chromene derivatives as anti-picornavirus capsid-binders. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 6480–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.M.; Barreiro, E.J. Bio-isosterism: A useful strategy for molecular modification and drug design. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.J.; Ha, Y.M.; Kim, J.A.; Park, J.Y.; Ha, T.K.; Park, D.; Chun, P.; Park, N.H.; Moon, H.R.; Chung, H.Y. A novel synthesized tyrosinase inhibitor: (E)-2-((2,4-dihydrophenyl)diazinyl)phenyl-4-methylbenzenesulfonate as an azo-resveratrol analog. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.J.; Pan, Y. Imine resveratrol analogues: Molecular design, Nrf2 activation and SAR analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayhoub, A.S.; Marler, L.; Kondratyuk, T.P.; Park, E.J.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Cushman, M. Optimization of the aromatase inhibitory activities of pyridylthiazole analogues of resveratrol. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 2427–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellina, F.; Guazzelli, N.; Lessi, M.; Manzini, C. Imidazole analogues of resveratrol: Synthesis and cancer cell growth evaluation. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 2298–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.C.; Pereira, I.; Pereira-Silva, M.; Ferreira, L.; Caldas, M.; Magalhaes, M.; Figueiras, A.; Ribeiro, A.J.; Veiga, F. Nanocariers for resveratrol delivery: Impact on stability and solubility concerns. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshawih, S.; Mydin, R.B.S.M.N.; Kalakotla, S.; Jarrar, Q.B. Potential applications of resveratrol in nanocarriers against cancer: Overview and future trends. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intagliata, S.; Modica, M.N.; Santagati, L.M.; Montenegro, L. Strategies to improve resveratrol systemic and topical bioavailability: An update. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lian, B.; Wu, M.; Feng, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhong, C.; Zhao, X. Folate-conjugated human serum albumin-encapsulated resveratrol nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization, bioavailability and targeting of liver tumors. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Chen, H.; Song, C.; Zeng, X.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, X.; Zheng, X. Pharmacological activities and structure-modification of resveratrol analogues. Pharmazie 2015, 70, 765–771. [Google Scholar]
- Biasutto, L.; Mattarei, A.; Azzolini, M.; La Spina, M.; Sassi, N.; Romio, M.; Paradisi, C.; Zoratti, M. Resveratrol derivatives as a pharmacological tool. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1403, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomini, E.; Rupiani, S.; Guidotti, L.; Recanatini, M.; Roberti, M. The use of stilbene scaffold in medicinal chemistry and Multi Target Drug design. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 2439–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solladié, G.; Pasturel-Jacopé, Y.; Maignan, J. A re-investigation of resveratrol synthesis by Perkin reaction. Application to the synthesis of aryl cinnamic acids. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Pany, S.; Majhi, A. Chemical modifications of resveratrol for improved protein kinase C alpha activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 5321–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudose, A.; Maj, A.; Sauvage, X.; Delaude, L.; Demonceau, A.; Noels, A.F. Synthesis of stilbenoids via the Suzuki-Miyaura reaction catalyzed by palladium N-heterocyclic carbene complexes. J. Mol. Cat. A Chem. 2006, 257, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.; Dandawate, P.; Rub, R.; Padhye, S.; Aphale, S.; Moghe, A.; Jagyasi, A.; Swamy, K.V.; Singh, B.; Chatterjee, A.; et al. Novel aza-resveratrol analogs: Synthesis, characterization and anti-cancer activity against breast cancer cell lines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ko, H.; Park, J.E.; Jung, S.; Lee, S.K.; Chun, Y.J. Design, synthesis and discovery of novel trans-stilbene analogues as potent and selective human cytochrome P450 1B1 inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotora, P.; Sersen, F.; Filo, J.; Loos, D.; Gregan, J.; Gregan, F. The scavenging of DPPH, galvinoxyl and ABTS radicals by imine analogs of resveratrol. Molecules 2016, 21, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.M.; Ha, Y.M.; Kim, J.A.; Chung, K.W.; Uehara, Y.; Lee, K.J.; Chun, P.; Byun, Y.; Chung, H.Y.; Moon, H.R. Synthesis of novel azo-resveratrol, azo-oxyresveratrol and their derivatives as potent tyrosinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 7451–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.Z.; Liu, Z.Q. Free-radical scavenging effect of carbazole derivatives on DPPH and ABTS radicals. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2007, 2, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, C.; Chai, Y.F.; Yang, D.Y.; Sun, C.R. The anti-oxidant effect of imine resveratrol analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 5744–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.S.; Johnson, E.J.; DiLabio, G.A. Predicting the activity of phenolic antioxidants: Theoretical method, analysis of substituents effects, and application to major families of antioxidants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zou, B.; Pan, Y.; Liang, H.; Yi, X.; Wang, H. Antioxidant activities and transition metal ion chelating studies of some hydroxyl Schiff base derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anekonda, T.S. Resveratrol–A boon for treating Alzheimer’s disease? Brain Res. Rev. 2006, 52, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.H.; Surh, Y.J. Protective effect of resveratrol on β-amyloid-induced oxidative PC12 cell death. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancino, A.M.; Hindo, S.S.; Kochi, A.; Lim, M.H. Effects of clioquinol on metal-triggered amyloid-β aggregation revisited. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 9596–9598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.; Alcendor, R.; Rahman, T.; Podgorny, M.; Sanogo, I.; McCurdy, R. Ionophoric polyphenols selectively bind Cu2+, display potent antioxidant and anti-amyloidogenic properties, and are non-toxic toward Tetrahymena thermophila. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 3657–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Qiang, X.; Li, Y.; Luo, L.; Xu, R.; Zheng, Y.; Cao, Z.; Tan, Z.; Deng, Y. Pyridoxine-resveratrol hybrids Mannich base derivatives as novel dual inhibitors of AChE and MAO-B with anti-oxidant and metal-chelating properties for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 71, 305–314. [Google Scholar]
- Battaini, G.; Monzani, E.; Casella, L.; Santagostini, L.; Pagliarin, R. Inhibition of the catecholase activity of biomimetic dinuclear copper complexes by kojic acid. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 5, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.L.; Lima, R.M.; da Silva, A.F.; do Carmo, A.M.R.; da Silva, A.D.; Raposo, N.R.B. Azastilbene analogs as tyrosinase inhibitors: New molecules with depigmenting potential. ScientificWorldJournal 2013, 2013, 274643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann-Franco, D.C.; Esteves, B.; Lacerda, L.M.; de Oliveira Souza, I.; dos Santos, J.A.; de Castro Campos Pinto, N.; Scio, E.; da Silva, A.D.; Macedo, G.C. In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory properties of imine resveratrol analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4898–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coimbra, E.S.; Santos, J.A.; Lima, L.L.; Machado, P.A.; Campos, D.L.; Pavan, F.R.; Silva, A.D. Synthesis, antitubercular and leishmanicidal evaluation of resveratrol analogues. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2016, 27, 2161–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucinska, M.; Piotrowska, H.; Luczak, M.W.; Mikula-Pietrasik, J.; Ksiazek, K.; Wozniak, M.; Wierzchowski, M.; Dudka, J.; Jäger, W.; Murias, M. Effects of hydroxylated resveratrol analogs on oxidative stress and cancer cells death in human acute T cell leukemia cell line: Prooxidative potential of hydroxylated resveratrol analogs. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 209, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.X.; Tang, J.J.; Luo, H.; Jin, X.L.; Dai, F.; Yang, J.; Qian, Y.P.; Li, X.Z.; Zhou, B. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of hydroxyl-substituted Schiff bases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2417–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronghe, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Singh, B.; Dandawate, P.; Murphy, L.; Bhat, N.K.; Padhye, S.; Bhat, H.K. Differential regulation of estrogen receptors α and β by 4-(E)-{(4-hydroxyphenylimino)-methylbenzene-1,2-diol}, a novel resveratrol analog. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 144, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronghe, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Singh, B.; Dandawate, P.; Abdalla, F.; Bhat, N.K.; Padhye, S.; Bhat, H.K. 4-(E)-{(p-tolylimino)-methylbenzene-1,2-diol}, a novel resveratrol differentially regulates estrogen receptors α and β in breast cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 301, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Zeng, X. Synthesis of diaryl-azo derivatives as potential antifungal agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4193–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deri, B.; Kanteev, M.; Goldfeder, M.; Lecina, D.; Guallar, V.; Adir, N.; Fishman, A. The unravelling of the complex pattern of tyrosinase inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Algarni, A.S.; Hargreaves, A.J.; Dickenson, J.M. Activation of transglutaminase 2 by nerve growth factor in differentiating neuroblastoma cells: A role in cell survival and neurite outgrowth. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 820, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

















© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lizard, G.; Latruffe, N.; Vervandier-Fasseur, D. Aza- and Azo-Stilbenes: Bio-Isosteric Analogs of Resveratrol. Molecules 2020, 25, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030605
Lizard G, Latruffe N, Vervandier-Fasseur D. Aza- and Azo-Stilbenes: Bio-Isosteric Analogs of Resveratrol. Molecules. 2020; 25(3):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030605
Chicago/Turabian StyleLizard, Gérard, Norbert Latruffe, and Dominique Vervandier-Fasseur. 2020. "Aza- and Azo-Stilbenes: Bio-Isosteric Analogs of Resveratrol" Molecules 25, no. 3: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030605